Abstract
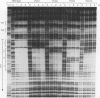
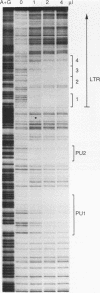
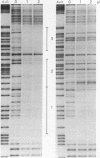
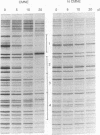
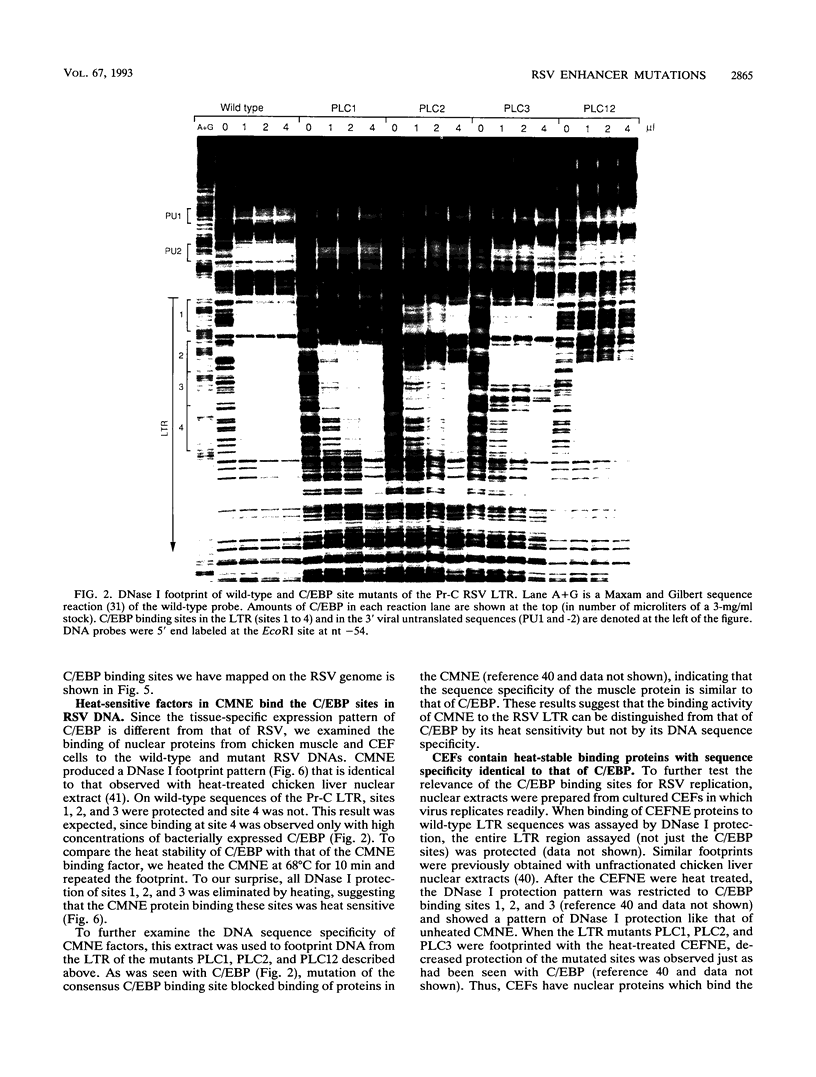
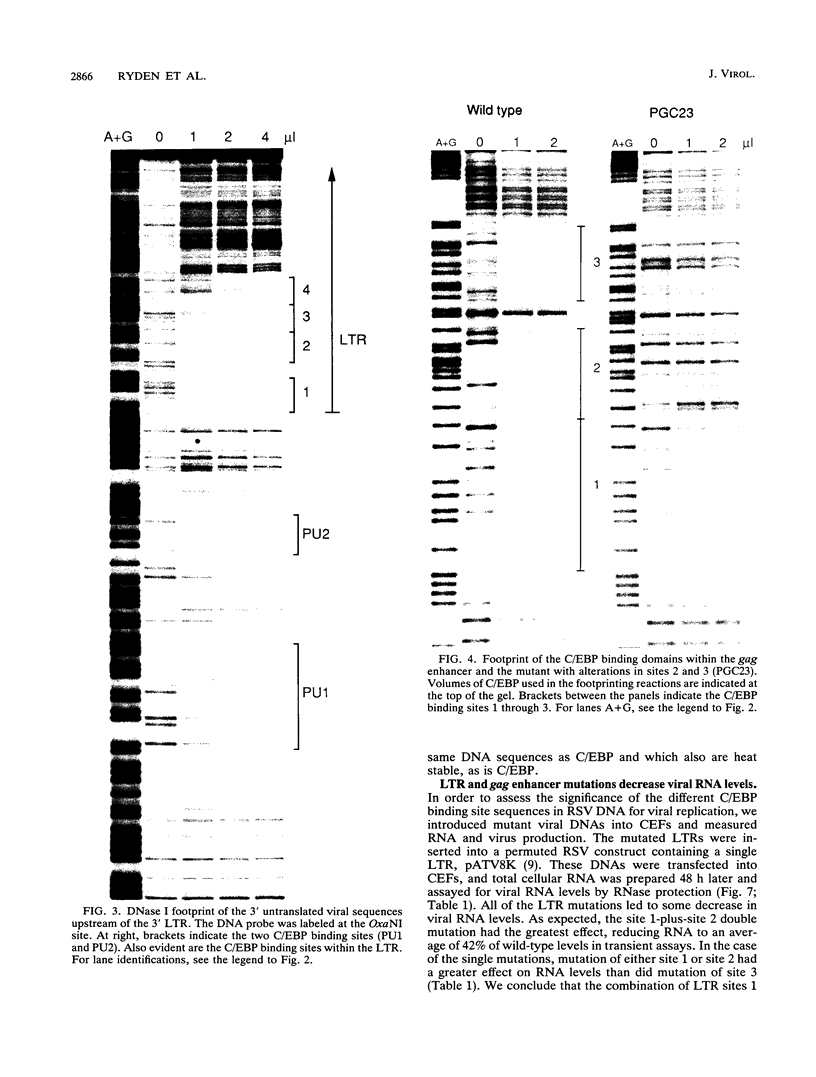
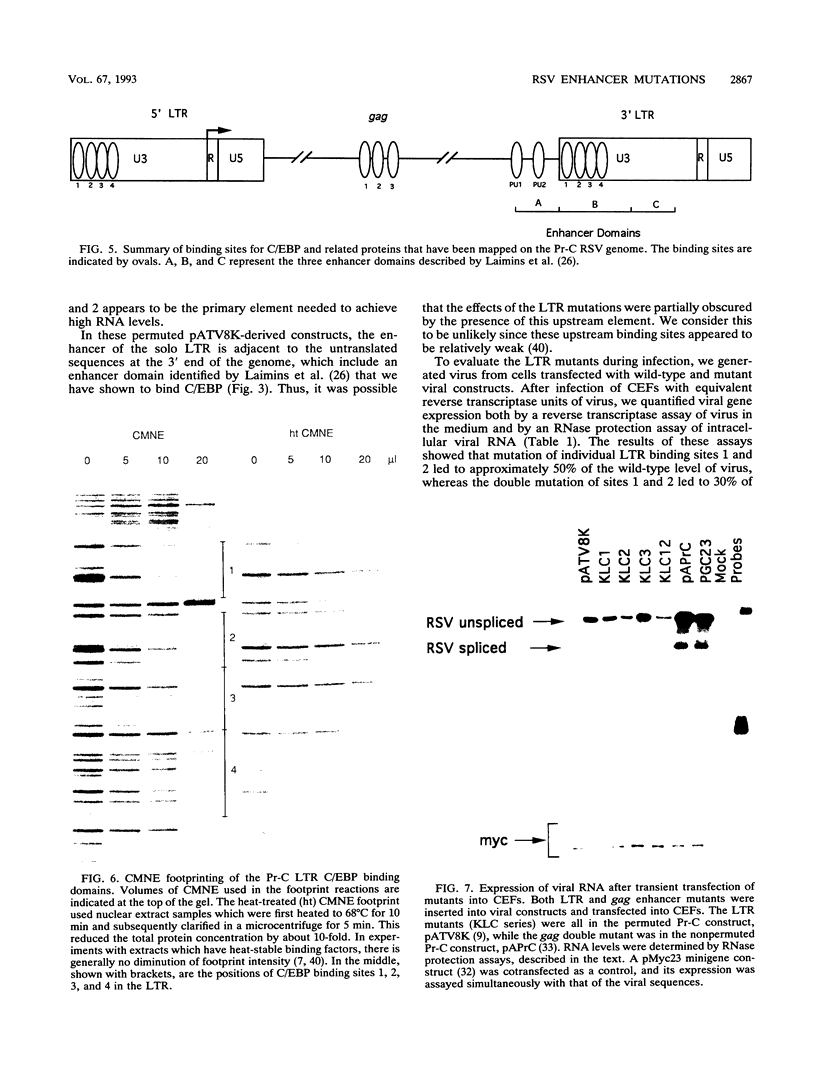
Several C/EBP binding sites within the Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) long terminal repeat (LTR) and gag enhancers were mutated, and the effect of these mutations on viral gene expression was assessed. Minimal site-specific mutations in each of three adjacent C/EBP binding sites in the LTR reduced steady-state viral RNA levels. Double mutation of the two 5' proximal LTR binding sites resulted in production of 30% of wild-type levels of virus. DNase I footprinting analysis of mutant DNAs indicated that the mutations blocked C/EBP binding at the affected sites. Additional C/EBP binding sites were identified upstream of the 3' LTR and within the 5' end of the LTRs. Point mutations in the RSV gag intragenic enhancer region, which blocked binding of C/EBP at two of three adjacent C/EBP sites, also reduced virus production significantly. Nuclear extracts prepared from both chicken embryo fibroblasts (CEFs) and chicken muscle contained proteins binding to the same RSV DNA sites as did C/EBP, and mutations that prevented C/EBP binding also blocked binding of these chicken proteins. It appears that CEFs and chicken muscle contain distinct proteins binding to these RSV DNA sites; the CEF binding protein was heat stable, as is C/EBP, while the chicken muscle protein was heat sensitive.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akira S., Isshiki H., Sugita T., Tanabe O., Kinoshita S., Nishio Y., Nakajima T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. A nuclear factor for IL-6 expression (NF-IL6) is a member of a C/EBP family. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1897–1906. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S., Beemon K. Regulation of Rous sarcoma virus RNA splicing and stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4858–4867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S., Yun M., Beemon K. cis-acting regulatory elements within gag genes of avian retroviruses. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):388–397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Gwynn B., Howard S., Jerry J., Gordon J. I., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. Tissue-specific expression, developmental regulation, and genetic mapping of the gene encoding CCAAT/enhancer binding protein. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1146–1156. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowers W. J., Ruddell A. a1/EBP: a leucine zipper protein that binds CCAAT/enhancer elements in the avian leukosis virus long terminal repeat enhancer. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6578–6586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6578-6586.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z., Umek R. M., McKnight S. L. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1538–1552. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlberg K., Ryden T. A., Beemon K. Localization and footprinting of an enhancer within the avian sarcoma virus gag gene. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1617–1624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1617-1624.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobrinik D., Katz R., Terry R., Skalka A. M., Leis J. Avian sarcoma and leukosis virus pol-endonuclease recognition of the tandem long terminal repeat junction: minimum site required for cleavage is also required for viral growth. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1999–2008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1999-2008.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Raymond K., Ju G. Functional analysis of the transcription control region located within the avian retroviral long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):438–447. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., DeLorbe W., Swanstrom R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Tischer E., Goodman H. M. The nucleotide sequence of an untranslated but conserved domain at the 3' end of the avian sarcoma virus genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2967–2984. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolberg D. S., Hollingsworth R., Hertle M., Bissell M. J. Wounding and its role in RSV-mediated tumor formation. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):676–678. doi: 10.1126/science.2996144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamant F., Le Guellec D., Verdier G., Nigon V. M. Tissue specificity of retrovirus expression in inoculated avian embryos revealed by in situ hybridization to whole-body section. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):301–304. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H. Identification of three sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins which interact with the Rous sarcoma virus enhancer and upstream promoter elements. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2186–2190. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2186-2190.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gowda S., Rao A. S., Kim Y. W., Guntaka R. V. Identification of sequences in the long terminal repeat of avian sarcoma virus required for efficient transcription. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):243–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90415-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves B. J., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Homologous recognition of a promoter domain common to the MSV LTR and the HSV tk gene. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):565–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90266-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herget T., Burba M., Schmoll M., Zimmermann K., Starzinski-Powitz A. Regulated expression of nuclear protein(s) in myogenic cells that binds to a conserved 3' untranslated region in pro alpha 1 (I) collagen cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;9(7):2828–2836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.7.2828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., Landschulz W. H., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Identification of a rat liver nuclear protein that binds to the enhancer core element of three animal viruses. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):133–146. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane S. E., Beemon K. Inhibition of methylation at two internal N6-methyladenosine sites caused by GAC to GAU mutations. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3422–3427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnitz L., Faber S., Chalkley R. Specific nuclear proteins interact with the Rous sarcoma virus internal enhancer and share a common element with the enhancer located in the long terminal repeat of the virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9841–9859. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnitz L., Poon D., Weil P. A., Chalkley R. Purification and properties of the Rous sarcoma virus internal enhancer binding factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1929–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny S., Guntaka R. V. Localization by mutational analysis of transcription factor binding sequences in the U3 region of Rous sarcoma virus LTR. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):483–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90018-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Tsichlis P., Khoury G. Multiple enhancer domains in the 3' terminus of the Prague strain of Rous sarcoma virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6427–6442. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luciw P. A., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E., Capecchi M. R. Location and function of retroviral and SV40 sequences that enhance biochemical transformation after microinjection of DNA. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J. The structure and function of retroviral long terminal repeats. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:49–92. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally M. T., Gontarek R. R., Beemon K. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus intronic sequences that negatively regulate splicing. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90758-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Coffin J. M. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus sequences essential for viral gene expression. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1171–1179. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1171-1179.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. A., Graves B. J. Alkylation interference identifies essential DNA contacts for sequence-specific binding of the eukaryotic transcription factor C/EBP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3992–3996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeek P. A., Lai S. P., Van Quill K. R., Westphal H. Tissue-specific expression in transgenic mice of a fused gene containing RSV terminal sequences. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1574–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.3006249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray A., Tatter S. B., Santhanam U., Helfgott D. C., May L. T., Sehgal P. B. Regulation of expression of interleukin-6. Molecular and clinical studies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman C., Platero J. S., Shuman J., Calame K. Ig/EBP-1: a ubiquitously expressed immunoglobulin enhancer binding protein that is similar to C/EBP and heterodimerizes with C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1404–1415. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddell A., Linial M. L., Groudine M. Tissue-specific lability and expression of avian leukosis virus long terminal repeat enhancer-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5660–5668. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryden T. A., Beemon K. Avian retroviral long terminal repeats bind CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):1155–1164. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey L., Chalkley R. At least two nuclear proteins bind specifically to the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):787–798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears R. C., Sealy L. Characterization of nuclear proteins that bind the EFII enhancer sequence in the Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6338–6352. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6338-6352.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Chang L. J., Cripe T. P., Turek L. P. Efficient transformation by Prague A Rous sarcoma virus plasmid DNA requires the presence of cis-acting regions within the gag gene. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3401–3409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3401-3409.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams S. C., Cantwell C. A., Johnson P. F. A family of C/EBP-related proteins capable of forming covalently linked leucine zipper dimers in vitro. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1553–1567. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]