Abstract
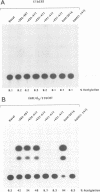
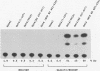
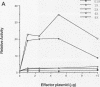
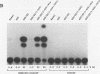
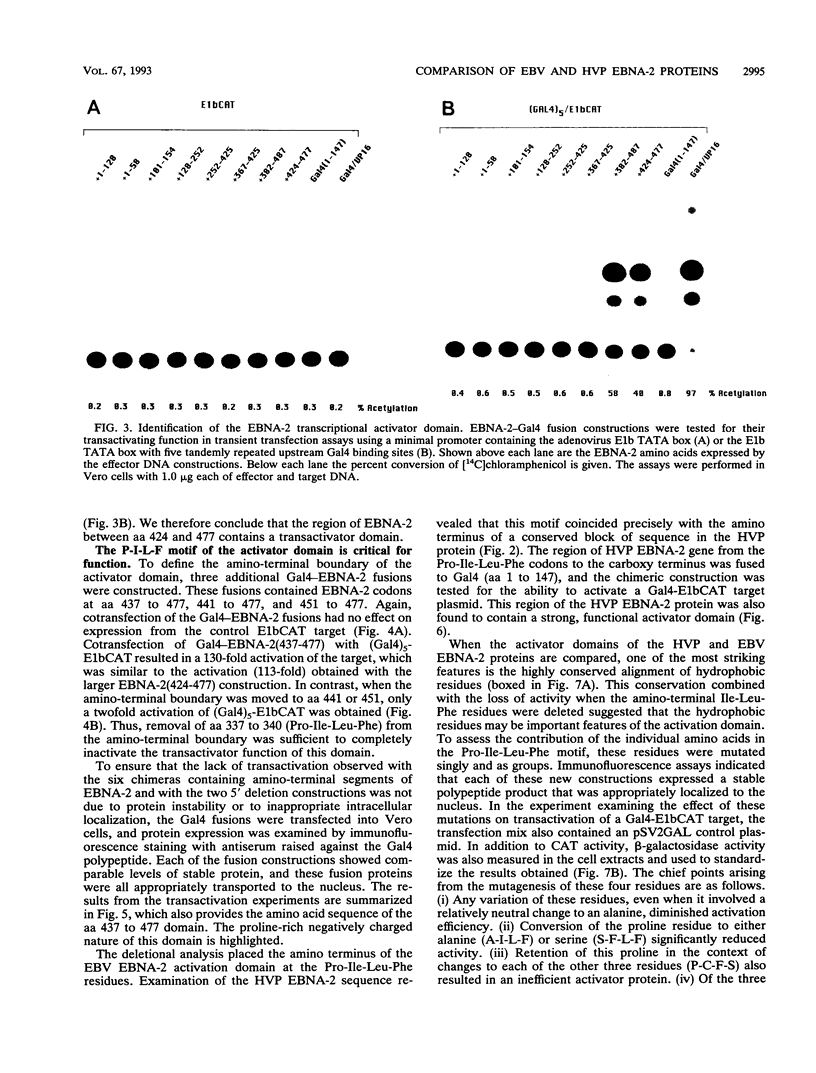
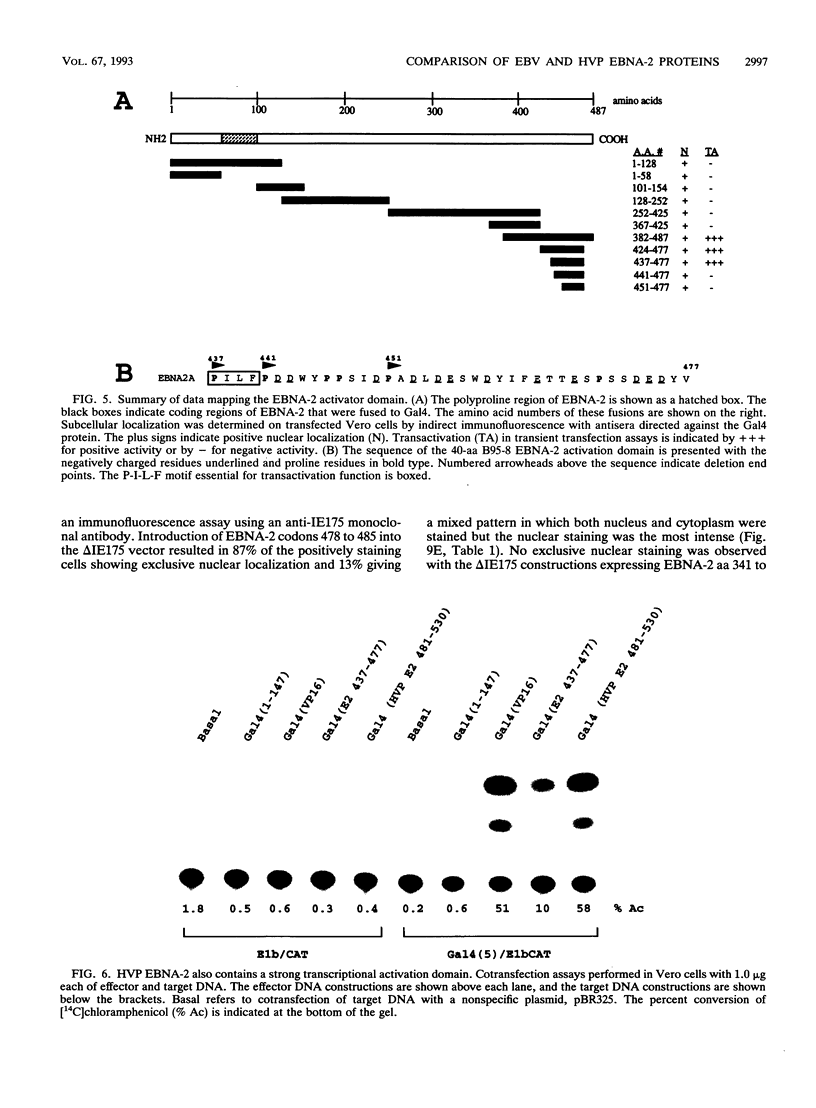
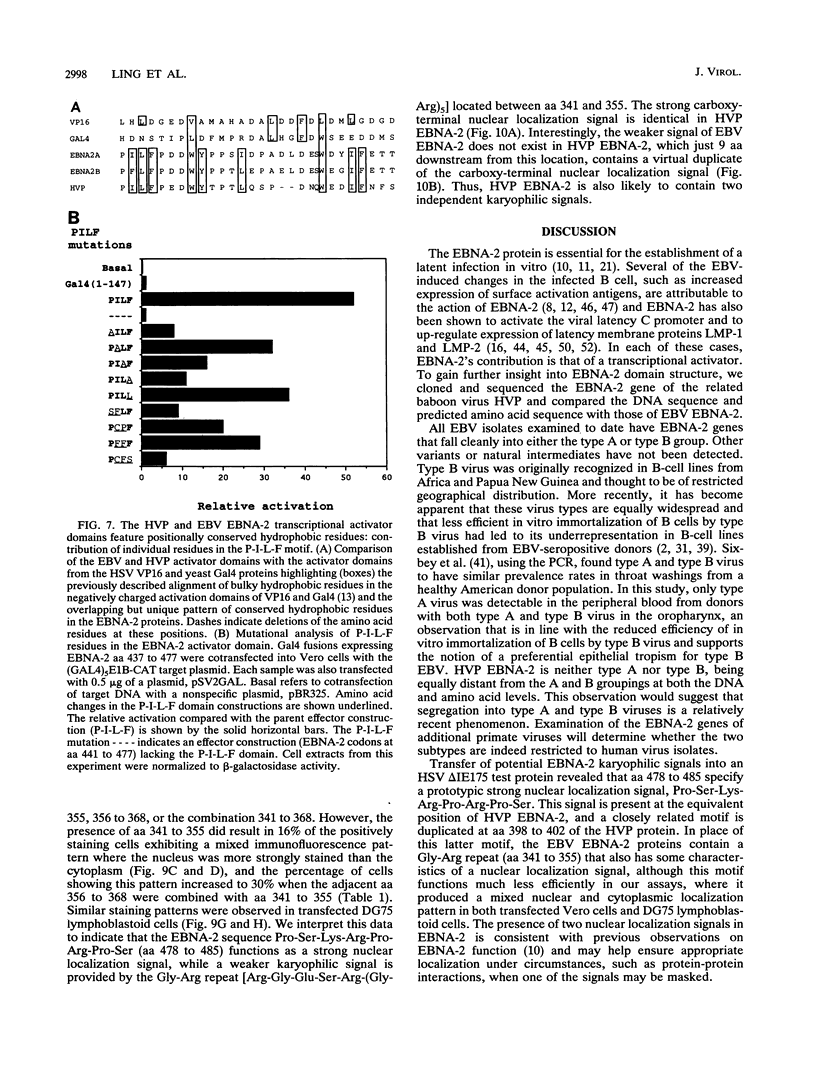
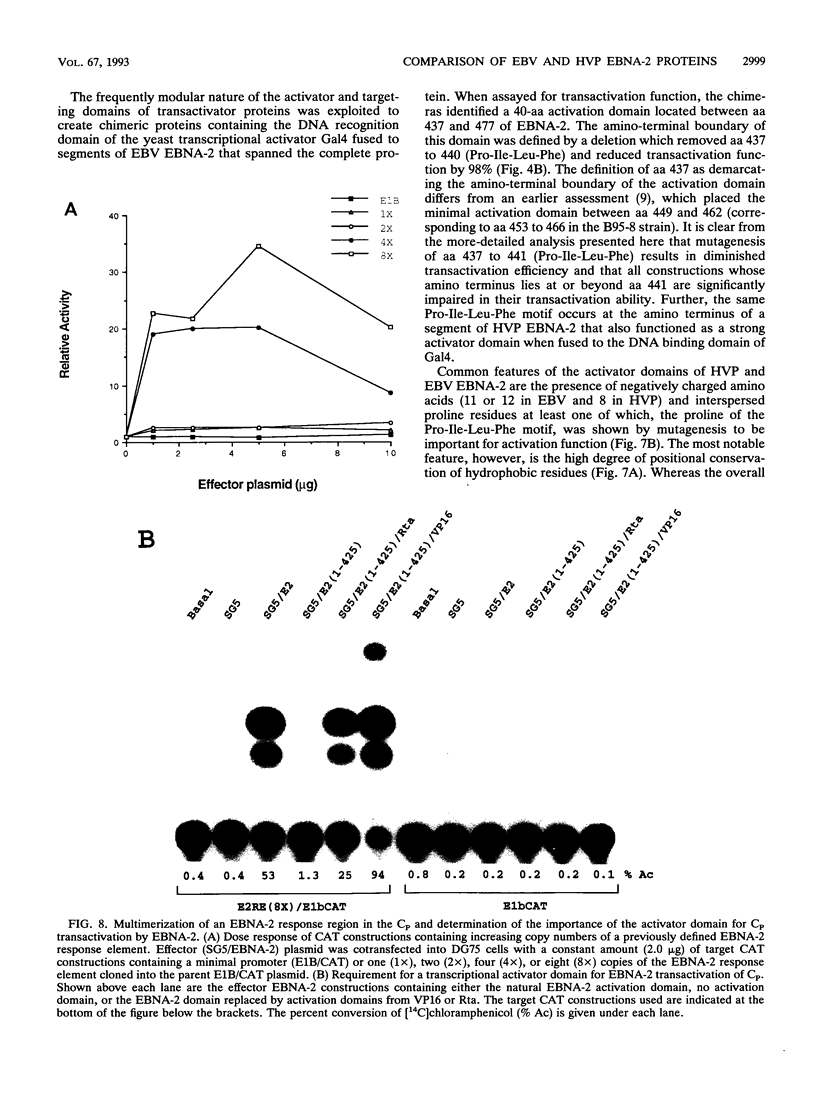
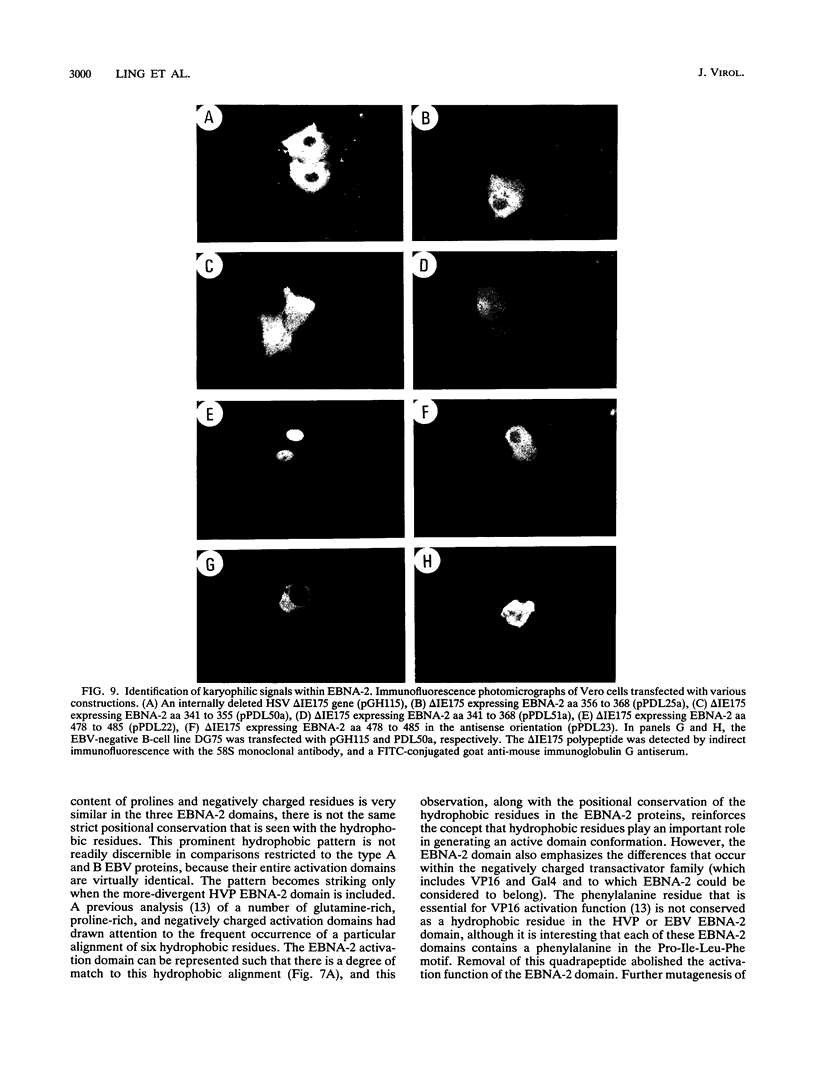
EBNA-2 contributes to the establishment of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latency in B cells and to the resultant alterations in B-cell growth pattern by up-regulating expression from specific viral and cellular promoters. We have taken a comparative approach toward characterizing functional domains within EBNA-2. To this end, we have cloned and sequenced the EBNA-2 gene from the closely related baboon virus herpesvirus papio (HVP). All human EBV isolates have either a type A or type B EBNA-2 gene. However, the HVP EBNA-2 gene falls into neither the type A category nor the type B category, suggesting that the separation into these two subtypes may have been a recent evolutionary event. Comparison of the predicted amino acid sequences indicates 37% amino acid identity with EBV type A EBNA-2 and 35% amino acid identity with type B EBNA-2. To define the domains of EBNA-2 required for transcriptional activation, the DNA binding domain of the GAL4 protein was fused to overlapping segments of EBV EBNA-2. This approach identified a 40-amino-acid (40-aa) EBNA-2 activation domain located between aa 437 and 477. Transactivation ability was completely lost when the amino-terminal boundary of this domain was moved to aa 441, indicating that the motif at aa 437 to 440, Pro-Ile-Leu-Phe, contains residues critical for function. The aa 437 boundary identified in these experiments coincides precisely with a block of conserved sequences in HVP EBNA-2, and the comparable carboxy-terminal region of HVP EBNA-2 also functioned as a strong transcriptional activation domain when fused to the Gal4(1-147) protein. The EBV and HVP EBNA-2 activation domains share a mixed proline-rich, negatively charged character with a striking conservation of positionally equivalent hydrophobic residues. The importance of the individual amino acids making up the Pro-Ile-Leu-Phe motif was examined by mutagenesis. Any alteration of these residues was found to reduce transactivation efficiency, with changes at the Pro-437 and Phe-440 positions producing the most deleterious effects. Activation of the EBV latency C promoter by EBNA-2 was shown to be dependent on the presence of the carboxy-terminal activation domain. However, this requirement was generic, rather than specific, since the EBNA-2 activation domain could be replaced with those from the herpes simplex virus (HSV) VP16 protein or the EBV Rta protein. Potential karyophilic signals within EBNA-2 were examined by introducing oligonucleotides encoding positively charged amino acid groupings that might serve in this capacity into a cytoplasmic test protein, HSV delta IE175, and by examining the intracellular localization of the resulting proteins. This assay identified a strong nuclear localization signal between EBV amino acids (aa) 478 to 485, which was conserved in HVP, and a weaker noncanonical signal between EBV aa 341 to 355, which was not conserved in HVP.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbot S. D., Rowe M., Cadwallader K., Ricksten A., Gordon J., Wang F., Rymo L., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 induces expression of the virus-encoded latent membrane protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2126–2134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2126-2134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adldinger H. K., Delius H., Freese U. K., Clarke J., Bornkamm G. W. A putative transforming gene of Jijoye virus differs from that of Epstein-Barr virus prototypes. Virology. 1985 Mar;141(2):221–234. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90253-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alfieri C., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus infection of human B lymphocytes. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):595–608. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90893-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allday M. J., Crawford D. H., Griffin B. E. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression during the initiation of B cell immortalization. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jul;70(Pt 7):1755–1764. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-7-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambinder R. F., Mullen M. A., Chang Y. N., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. Functional domains of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA-1. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1466–1478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1466-1478.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodescot M., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A promoter for the highly spliced EBNA family of RNAs of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3424–3430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3424-3430.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 domain essential for transformation is a direct transcriptional activator. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5880–5885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5880-5885.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 mutations define essential domains for transformation and transactivation. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2545–2554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2545-2554.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Mannick J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 is a key determinant of lymphocyte transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9558–9562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Zimber U., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Banchereau J., Tursz T., Bornkamm G., Lenoir G. M. Stable transfection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2 in lymphoma cells containing the EBV P3HR1 genome induces expression of B-cell activation molecules CD21 and CD23. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1002–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1002-1013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1846049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Hennessy K., Chamnankit L., Kieff E. U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA may encode Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Bernards R., Friend S. H., Gooding L. R., Hassell J. A., Major E. O., Pipas J. M., Vandyke T., Harlow E. Large T antigens of many polyomaviruses are able to form complexes with the retinoblastoma protein. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1353–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1353-1356.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk L., Deinhardt F., Nonoyama M., Wolfe L. G., Bergholz C. Properties of a baboon lymphotropic herpesvirus related to Epstein-Barr virus. Int J Cancer. 1976 Dec 15;18(6):798–807. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910180611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Jansson A., Ricksten A., Sjöblom A., Rymo L. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen 2 activates the viral latent membrane protein promoter by modulating the activity of a negative regulatory element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7390–7394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bustos J., Heitman J., Hall M. N. Nuclear protein localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):83–101. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90013-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber P., Kalter S. S., Schidlovsky G., Peterson W. D., Jr, Daniel M. D. Biologic and antigenic characteristics of Epstein-Barr virus-related Herpesviruses of chimpanzees and baboons. Int J Cancer. 1977 Sep 15;20(3):448–459. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):393–397. doi: 10.1038/340393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Yanagi K. Amino acid sequence homology of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen-2 to adenovirus E1A, human papilloma virus-16 E7 and SV40 large T antigen in the functional domains for growth transformation. Oncogene. 1991 Mar;6(3):461–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick J. M., Tse L., Applegren N., Nicholas J., Veliuona M. A. The Epstein-Barr virus R transactivator (Rta) contains a complex, potent activation domain with properties different from those of VP16. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5500–5508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5500-5508.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller M., Kieff E. Colinearity between the DNAs of Epstein-Barr virus and herpesvirus papio. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):821–826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.821-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin X. W., Speck S. H. Identification of critical cis elements involved in mediating Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2-dependent activity of an enhancer located upstream of the viral BamHI C promoter. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2846–2852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2846-2852.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C. The level of c-fgr RNA is increased by EBNA-2, an Epstein-Barr virus gene required for B-cell immortalization. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2530–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2530-2536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Hardwick J. M., Hayward S. D. Responsiveness of the Epstein-Barr virus NotI repeat promoter to the Z transactivator is mediated in a cell-type-specific manner by two independent signal regions. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3040–3050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3040-3050.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacMahon E. M., Glass J. D., Hayward S. D., Mann R. B., Becker P. S., Charache P., McArthur J. C., Ambinder R. F. Epstein-Barr virus in AIDS-related primary central nervous system lymphoma. Lancet. 1991 Oct 19;338(8773):969–973. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)91837-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzorno M. C., Mullen M. A., Chang Y. N., Hayward G. S. The functionally active IE2 immediate-early regulatory protein of human cytomegalovirus is an 80-kilodalton polypeptide that contains two distinct activator domains and a duplicated nuclear localization signal. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3839–3852. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3839-3852.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Young L. S., Rowe M. Influence of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA 2 on the growth phenotype of virus-transformed B cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1310-1317.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C. M., Brimmell M., Buschle M., Allan G., Farrell P. J., Kolman J. L. Host cell and EBNA-2 regulation of Epstein-Barr virus latent-cycle promoter activity in B lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):496–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.496-504.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney C., Howe J. G., Speck S. H., Miller G. Influence of Burkitt's lymphoma and primary B cells on latent gene expression by the nonimmortalizing P3J-HR-1 strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1531–1539. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1531-1539.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Hummel M., Braun D., Birkenbach M., Kieff E. Nucleotide sequences of mRNAs encoding Epstein-Barr virus nuclear proteins: a probable transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Young L., Martin B., Chatman T., Kieff E., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus types 1 and 2 differ in their EBNA-3A, EBNA-3B, and EBNA-3C genes. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4084–4092. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4084-4092.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W. H., Horvath G., Spoth B., Hearing J. C. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 in insect cells from a baculovirus vector. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):428–431. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90792-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sculley T. B., Apolloni A., Hurren L., Moss D. J., Cooper D. A. Coinfection with A- and B-type Epstein-Barr virus in human immunodeficiency virus-positive subjects. J Infect Dis. 1990 Sep;162(3):643–648. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.3.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixbey J. W., Shirley P., Chesney P. J., Buntin D. M., Resnick L. Detection of a second widespread strain of Epstein-Barr virus. Lancet. 1989 Sep 30;2(8666):761–765. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90829-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck S. H., Strominger J. L. Analysis of the transcript encoding the latent Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen I: a potentially polycistronic message generated by long-range splicing of several exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8305–8309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal S. P., Ambinder R., Beschorner W. E., Hayward G. S., Mann R. A survey of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in lymphoid tissue. Frequent detection in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1989 Jan;91(1):1–5. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/91.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung N. S., Kenney S., Gutsch D., Pagano J. S. EBNA-2 transactivates a lymphoid-specific enhancer in the BamHI C promoter of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2164–2169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2164-2169.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang S. F., Wang F., Izumi K. M., Kieff E. Delineation of the cis-acting element mediating EBNA-2 transactivation of latent infection membrane protein expression. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6765–6771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6765-6771.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C., Sample C., Rowe M., Liebowitz D., Murray R., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2309–2318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2309-2318.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Kikutani H., Tsang S. F., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 transactivates a cis-acting CD23 DNA element. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4101–4106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4101-4106.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Tsang S. F., Kurilla M. G., Cohen J. I., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates latent membrane protein LMP1. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3407–3416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3407-3416.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Jin X. W., Yandava C. N., Furmanski L. A., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Role for the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 in viral promoter switching during initial stages of infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3942–3946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Yandava C. N., Furmanski L. A., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Promoter switching in Epstein-Barr virus during the initial stages of infection of B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. C., Mann R. B., Charache P., Hayward S. D., Staal S., Lambe B. C., Ambinder R. F. Detection of EBV gene expression in Reed-Sternberg cells of Hodgkin's disease. Int J Cancer. 1990 Nov 15;46(5):801–804. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910460509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Laux G., Eick D., Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 activates transcription of the terminal protein gene. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):415–423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.415-423.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]