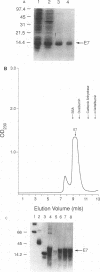
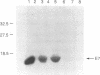
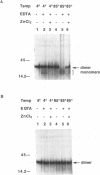
Abstract
Human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV-18) E7 proteins bind zinc through Cys-X-X-Cys repeats located at the C terminus of the protein. In order to examine the role of these cysteine motifs in E7 function, we expressed the HPV-18 E7 protein in bacteria and found that purified E7 forms a dimer through interactions with zinc. Mutants with single mutations within the Cys-X-X-Cys motifs bound a reduced level of zinc in a zinc blot assay, while a double mutant lost all zinc-binding activity. When expressed in vivo, none of the mutants cooperated with an activated ras oncogene to transform primary rat embryo fibroblasts, but all mutants retained nearly wild-type Rb-binding activity. The results indicate that the cysteine motifs play an important role in transformation by HPV-18 E7 but do not contribute to Rb binding.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Phelps W. C., Lindgren V., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Howley P. M. Structural and transcriptional analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 sequences in cervical carcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):962–971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.962-971.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa M. S., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Papillomavirus polypeptides E6 and E7 are zinc-binding proteins. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1404–1407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1404-1407.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A. Identification of human papillomavirus type 18 transforming genes in immortalized and primary cells. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1247–1255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1247-1255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Laimins L. A. The E6-E7 region of human papillomavirus type 18 is sufficient for transformation of NIH 3T3 and rat-1 cells. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3635–3640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3635-3640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Proposed structure for the zinc-binding domains from transcription factor IIIA and related proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):99–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters P. M., McCance D. J. Human papillomavirus types 6 and 16 in cooperation with Ha-ras transform secondary rat embryo fibroblasts. J Gen Virol. 1989 Feb;70(Pt 2):353–365. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-2-353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters P. M., Vousden K. H., Edmonds C., McCance D. J. Analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 open reading frame E7 immortalizing function in rat embryo fibroblast cells. J Gen Virol. 1990 Feb;71(Pt 2):449–453. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-2-449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culp J. S., Webster L. C., Friedman D. J., Smith C. L., Huang W. J., Wu F. Y., Rosenberg M., Ricciardi R. P. The 289-amino acid E1A protein of adenovirus binds zinc in a region that is important for trans-activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Mulkerrin M. G., Wells J. A. Dimerization of human growth hormone by zinc. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.1907025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Howley P. M., Münger K., Harlow E. The human papilloma virus-16 E7 oncoprotein is able to bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Science. 1989 Feb 17;243(4893):934–937. doi: 10.1126/science.2537532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Dzarlieva-Petrusevska R. T., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Gissmann L. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of immortalized human primary keratinocytes obtained after transfection with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds C., Vousden K. H. A point mutational analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2650–2656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2650-2656.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Bredt D. S., Pabo C. O. Tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus forms a metal-linked dimer. Science. 1988 Apr 1;240(4848):70–73. doi: 10.1126/science.2832944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. D., Chen L., Cotter R. J., Pabo C. O. Dimerization of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus: a cysteine-rich peptide mimics the normal metal-linked dimer interface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6297–6300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage J. R., Meyers C., Wettstein F. O. The E7 proteins of the nononcogenic human papillomavirus type 6b (HPV-6b) and of the oncogenic HPV-16 differ in retinoblastoma protein binding and other properties. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):723–730. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.723-730.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck D. V., Yee C. L., Howley P. M., Münger K. Efficiency of binding the retinoblastoma protein correlates with the transforming capacity of the E7 oncoproteins of the human papillomaviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4442–4446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P. S., Patrick D. R., Edwards G., Goodhart P. J., Huber H. E., Miles L., Garsky V. M., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Protein domains governing interactions between E2F, the retinoblastoma gene product, and human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):953–960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson J. B., Bedell M. A., McCance D. J., Laiminis L. A. Immortalization and altered differentiation of human keratinocytes in vitro by the E6 and E7 open reading frames of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):519–526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.519-526.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jewers R. J., Hildebrandt P., Ludlow J. W., Kell B., McCance D. J. Regions of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein required for immortalization of human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1329–1335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1329-1335.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Human papillomavirus type 16 open reading frame E7 encodes a transforming gene for rat 3Y1 cells. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):610–613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.610-613.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda T., Watanabe S., Yoshiike K. Immortalization of primary rat cells by human papillomavirus type 16 subgenomic DNA fragments controlled by the SV40 promoter. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):321–325. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90694-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., McDougall J. K. Characterization of primary human keratinocytes transformed by human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1917–1924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1917-1924.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laue T. M., Rhodes D. G. Determination of size, molecular weight, and presence of subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1990;182:566–587. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)82045-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner M. S., Mack D. H., Finicle A. B., Crook T., Vousden K. H., Laimins L. A. Human papillomavirus E6 proteins bind p53 in vivo and abrogate p53-mediated repression of transcription. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3045–3052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05375.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorincz A. T., Lancaster W. D., Temple G. F. Cloning and characterization of the DNA of a new human papillomavirus from a woman with dysplasia of the uterine cervix. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):225–229. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.225-229.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab J. C., Walkinshaw S. A., Cordiner J. W., Clements J. B. Human papillomavirus in clinically and histologically normal tissue of patients with genital cancer. N Engl J Med. 1986 Oct 23;315(17):1052–1058. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198610233151703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Schneider J., Banks L., Jones N., Murray A., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA cooperates with activated ras in transforming primary cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1741–1746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCance D. J., Kopan R., Fuchs E., Laimins L. A. Human papillomavirus type 16 alters human epithelial cell differentiation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7169–7173. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean I. W., Nakane P. K. Periodate-lysine-paraformaldehyde fixative. A new fixation for immunoelectron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1974 Dec;22(12):1077–1083. doi: 10.1177/22.12.1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Werness B. A., Dyson N., Phelps W. C., Harlow E., Howley P. M. Complex formation of human papillomavirus E7 proteins with the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor gene product. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4099–4105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08594.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick D. R., Zhang K., Defeo-Jones D., Vuocolo G. R., Maigetter R. Z., Sardana M. K., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Characterization of functional HPV-16 E7 protein produced in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6910–6915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Yee C. L., Münger K., Howley P. M. The human papillomavirus type 16 E7 gene encodes transactivation and transformation functions similar to those of adenovirus E1A. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):539–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90570-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirisi L., Yasumoto S., Feller M., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Transformation of human fibroblasts and keratinocytes with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1061-1066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls J. A., Pusztai R., Green M. Chemical synthesis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein: autonomous protein domains for induction of cellular DNA synthesis and for trans activation. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6121–6129. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6121-6129.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff L. A., Nibert M. L., Fields B. N. Characterization of a zinc blotting technique: evidence that a retroviral gag protein binds zinc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Phelps W. C., Zhang Y. L., Barbosa M. Quantitative keratinocyte assay detects two biological activities of human papillomavirus DNA and identifies viral types associated with cervical carcinoma. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3181–3187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. The major human papillomavirus protein in cervical cancers is a cytoplasmic phosphoprotein. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1686–1689. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1686-1689.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smotkin D., Wettstein F. O. Transcription of human papillomavirus type 16 early genes in a cervical cancer and a cancer-derived cell line and identification of the E7 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. H., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A., Lowy D. R. The E7 open reading frame of human papillomavirus type 16 encodes a transforming gene. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):167–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Kanda T., Sato H., Furuno A., Yoshiike K. Mutational analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 E7 functions. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):207–214. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.207-214.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth C. D., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Immortalization of human foreskin keratinocytes by various human papillomavirus DNAs corresponds to their association with cervical carcinoma. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):159–164. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.159-164.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzopulos J., Kozloff L. M. Identification of T4D bacteriophage gene product 12 as the baseplate zinc metalloprotein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5543–5547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]