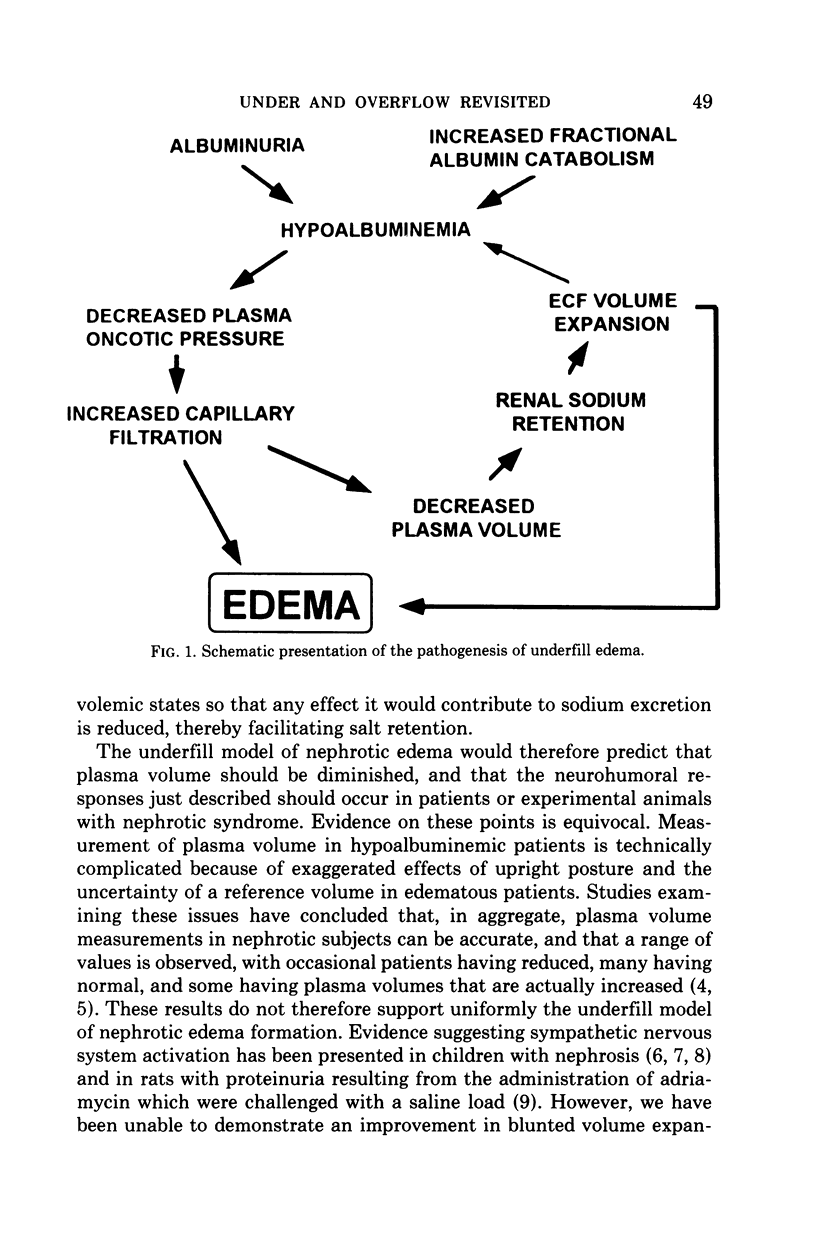
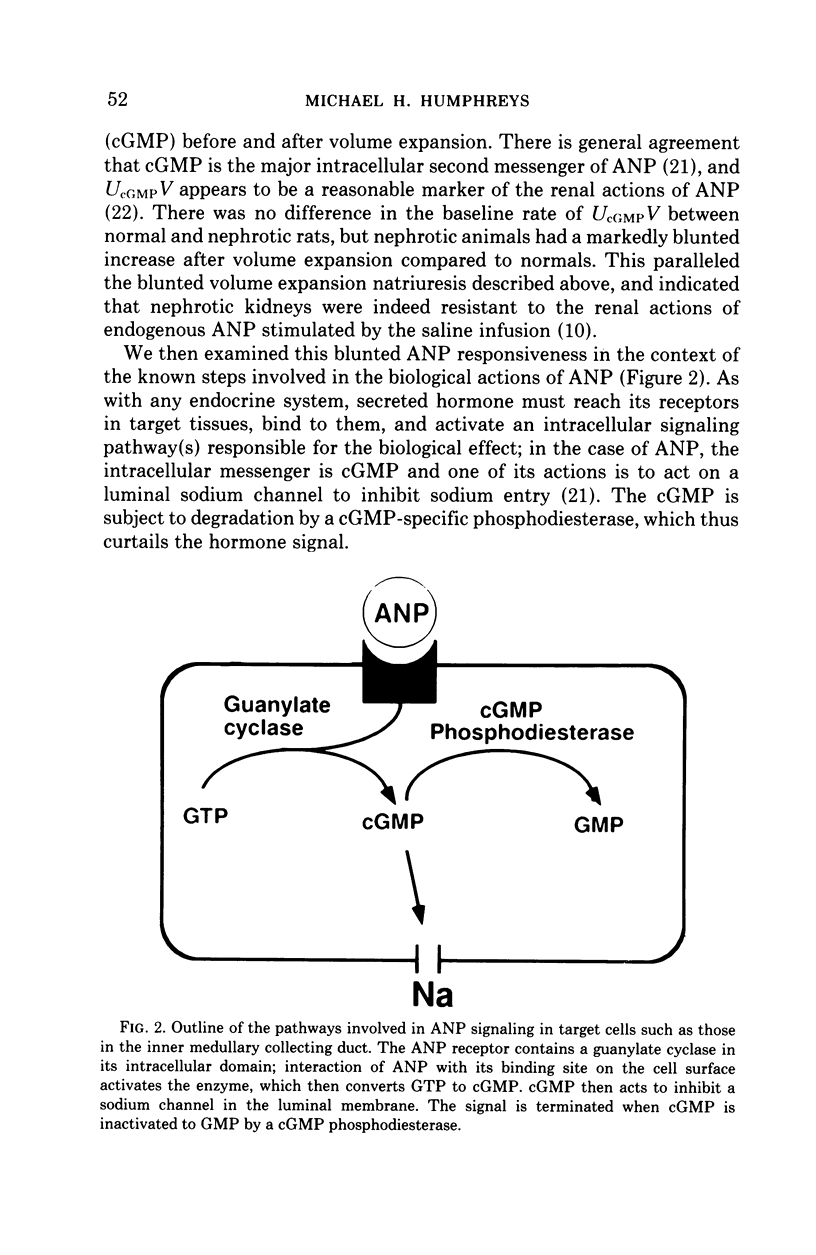
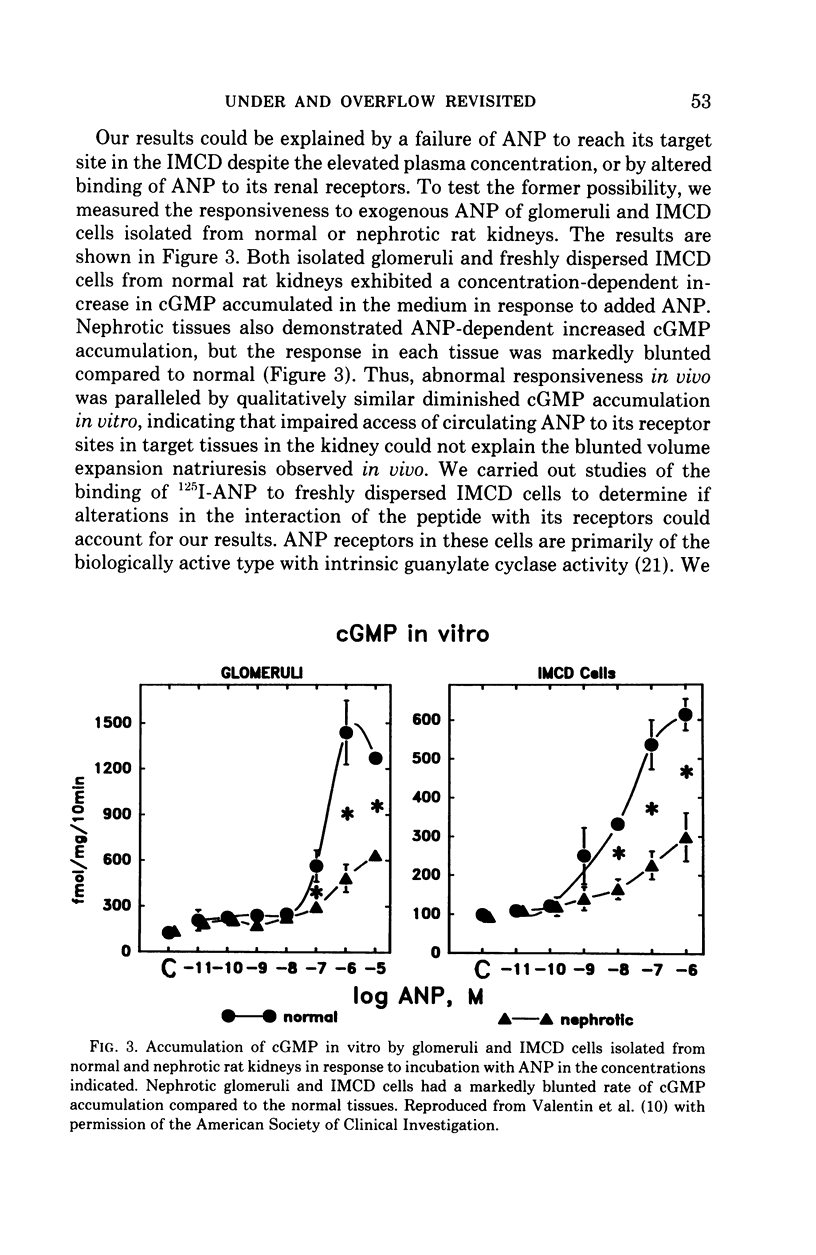
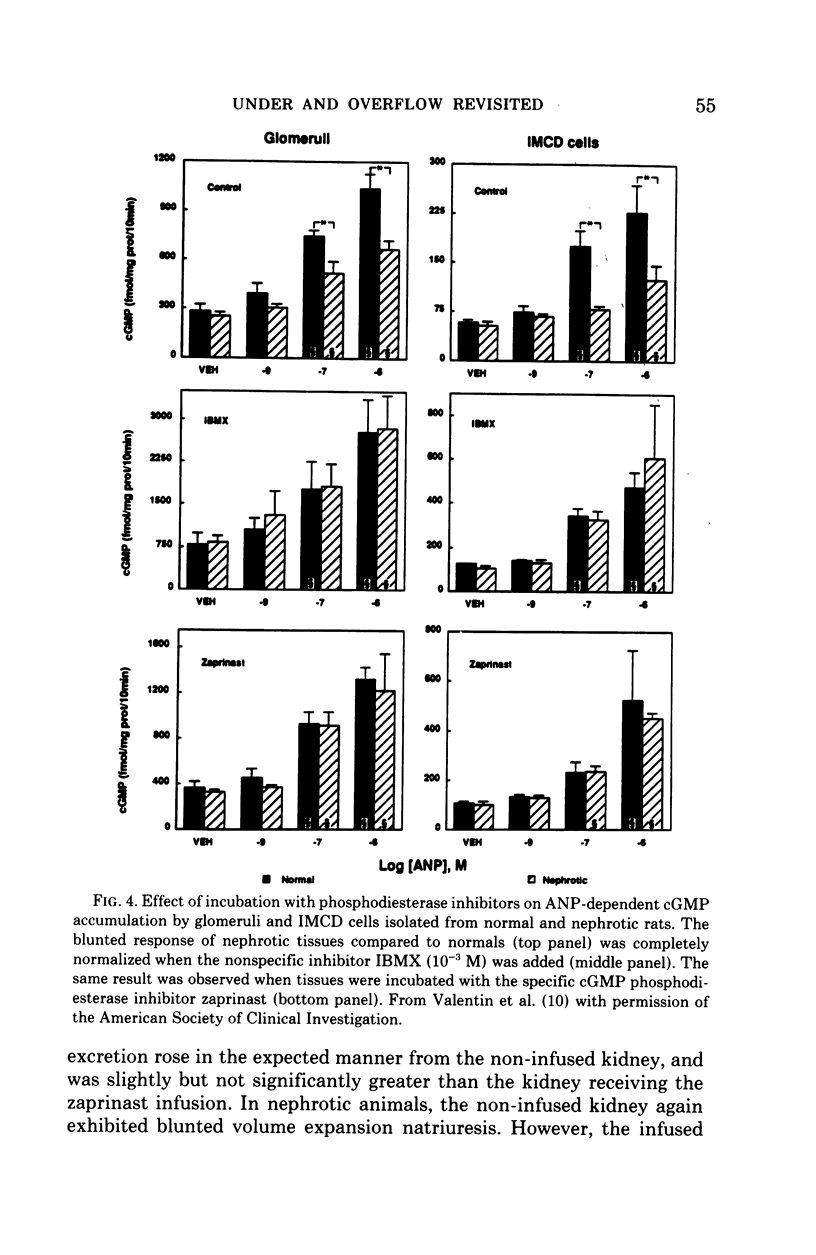
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner B. M., Ballermann B. J., Gunning M. E., Zeidel M. L. Diverse biological actions of atrial natriuretic peptide. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):665–699. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. A., Markandu N. D., Sagnella G. A., Squires M., Jones B. E., MacGregor G. A. Evidence that some mechanism other than the renin system causes sodium retention in nephrotic syndrome. Lancet. 1982 Dec 4;2(8310):1237–1240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chonko A. M., Bay W. H., Stein J. H., Ferris T. F. The role of renin and aldosterone in the salt retention of edema. Am J Med. 1977 Dec;63(6):881–889. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90541-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti M., Jin S. L., Monaco L., Repaske D. R., Swinnen J. V. Hormonal regulation of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Endocr Rev. 1991 Aug;12(3):218–234. doi: 10.1210/edrv-12-3-218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiBona G. F., Herman P. J., Sawin L. L. Neural control of renal function in edema-forming states. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jun;254(6 Pt 2):R1017–R1024. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1988.254.6.R1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorhout Mees E. J., Geers A. B., Koomans H. A. Blood volume and sodium retention in the nephrotic syndrome: a controversial pathophysiological concept. Nephron. 1984;36(4):201–211. doi: 10.1159/000183155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geers A. B., Koomans H. A., Roos J. C., Boer P., Dorhout Mees E. J. Functional relationships in the nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 1984 Sep;26(3):324–330. doi: 10.1038/ki.1984.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz K. L. Evidence that atriopeptin is not a physiological regulator of sodium excretion. Hypertension. 1990 Jan;15(1):9–19. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisanaga S., Yamamoto Y., Kida O., Kato J., Fujimoto S., Tanaka K. Plasma concentration and renal effect of human atrial natriuretic peptide in nephrotic syndrome. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 1989 Jun;31(6):661–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichikawa I., Rennke H. G., Hoyer J. R., Badr K. F., Schor N., Troy J. L., Lechene C. P., Brenner B. M. Role for intrarenal mechanisms in the impaired salt excretion of experimental nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jan;71(1):91–103. doi: 10.1172/JCI110756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaysen G. A., Gambertoglio J., Felts J., Hutchison F. N. Albumin synthesis, albuminuria and hyperlipemia in nephrotic patients. Kidney Int. 1987 Jun;31(6):1368–1376. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaysen G. A., Paukert T. T., Menke D. J., Couser W. G., Humphreys M. H. Plasma volume expansion is necessary for edema formation in the rate with Heymann nephritis. Am J Physiol. 1985 Feb;248(2 Pt 2):F247–F253. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.2.F247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelsch R. C., Light G. S., Oliver W. J. The effect of albumin infusion upon plasma norepinephrine concentration in nephrotic children. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Apr;79(4):516–525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer J. I., Keim H. J., Laragh J. H., Sealey J. E., Jan K. M., Chien S. Nephrotic syndrome: vasoconstriction and hypervolemic types indicated by renin-sodium profiling. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):688–696. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver W. J., Kelsch R. C., Chandler J. P. Demonstration of increased catecholamine excretion in the nephrotic syndrome. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Aug-Sep;125(4):1176–1180. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perico N., Delaini F., Lupini C., Benigni A., Galbusera M., Boccardo P., Remuzzi G. Blunted excretory response to atrial natriuretic peptide in experimental nephrosis. Kidney Int. 1989 Jul;36(1):57–64. doi: 10.1038/ki.1989.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C., Madsen B., Perlman A., Chan A. Y., Myers B. D. Atrial natriuretic peptide and the renal response to hypervolemia in nephrotic humans. Kidney Int. 1988 Dec;34(6):825–831. doi: 10.1038/ki.1988.256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. D., Hasbargen J., Hensen J., Schrier R. W. Role of aldosterone in the sodium retention of patients with nephrotic syndrome. Am J Nephrol. 1990;10(1):44–48. doi: 10.1159/000168052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulassay T., Rascher W., Lang R. E., Seyberth H. W., Schärer K. Atrial natriuretic peptide and other vasoactive hormones in nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Int. 1987 Jun;31(6):1391–1395. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentin J. P., Qiu C., Muldowney W. P., Ying W. Z., Gardner D. G., Humphreys M. H. Cellular basis for blunted volume expansion natriuresis in experimental nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1302–1312. doi: 10.1172/JCI115995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. R., Xie M. H., Shi L. B., Liu F. Y., Huang C. L., Gardner D. G., Cogan M. G. Urinary cGMP as biological marker of the renal activity of atrial natriuretic factor. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 2):F1220–F1224. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1988.255.6.F1220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


