Abstract
Increasing evidence suggests that emotion regulation (ER) strategies modulate encoding of information presented during regulation; however, no studies have assessed the impact of cognitive reappraisal ER strategies on the processing of stimuli presented after the ER period. Participants in the present study regulated emotions to unpleasant pictures and then judged whether a word was negative or neutral. Electromyographic measures (corrugator supercilli) confirmed that individuals increased and decreased negative affect according to ER condition. Event-related potential analyses revealed smallest N400 amplitudes to negative and neutral words presented after decreasing unpleasant emotions and smallest P300 amplitudes to words presented after increasing unpleasant emotions whereas reaction time data failed to show ER modulations. Results are discussed in the context of the developing ER literature, as well as theories of emotional incongruity (N400) and resource allocation (P300).
A growing interest in emotion regulation (ER) has led to a number of inquiries on the behavioral, emotional, cognitive, and physiological correlates of different ER strategies (Demaree, Schmeichel, Robinson, & Everhart, 2004; Gross, 1998, 2002; Jackson, Malmstadt, Larson, & Davidson, 2000; Moser, Hajcak, Bukay, & Simons, 2006; Richards & Gross, 2000). This work has been extended recently by neuroimaging studies, which have begun to identify the brain regions recruited during the cognitive control of emotion and have emphasized the role of anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and lateral prefrontal cortex (PFC) regions, including their modulatory effects on limbic (e.g., amygdalar) regions, when individuals regulate their emotions (Kim & Hamann, 2007; Ochsner, Bunge, Gross, & Gabrieli, 2002; Ochsner et al., 2004; Schaefer et al., 2002; Urry et al., 2006; for a review see Ochsner & Gross, 2005). However, emotionally charged events and our reactions to these events often exert considerable influence over subsequent experiences. For example, increasing one's unpleasant emotion following criticism from a colleague may affect the way we process subsequent cues in the environment. To date, whether or not the effects of ER strategies extend temporally has not been examined. We investigated this issue by examining behavioral and electrophysiological responses to negative and neutral words presented after participants increased, maintained, or decreased their emotions via cognitive reappraisal strategies.
Emotional Expectancies and Resource Allocation
Numerous studies suggest that the emotional valence of the context or the preceding stimulus impacts cognitive functions, including expectancies and attention (Ellis & Ashbrook, 1988; Fazio, Sanbonmatsu, Powell, & Kardes, 1986). For example, when target words are inconsistent with the preceding emotional prosody or violate affective expectations of the sentence, larger N400 amplitudes and slower reaction times occur (Besson, Magne, & Schon, 2002; Chung et al., 1996; Schirmer, Kotz, & Friederici, 2002, 2005; Zhang, Lawson, Guo, & Jiang, 2006). In the present study, unpleasant images followed by negative words should share a more similar affective state than unpleasant images followed by neutral words, resulting in larger N400 amplitudes and slower reaction times (RT) in the latter condition. Moreover, if the regulation of unpleasant emotions affects the congruence between affect in the regulation period and affect elicited by a verbal stimulus, N400 amplitudes and RTs should be modulated accordingly. Thus, increasing an unpleasant emotion evoked by an arousing picture should further increase the discrepancy between the affective state elicited by the picture and that elicited by the words, resulting in larger N400 amplitudes and slower RTs. Decreasing unpleasant emotions should decrease this discrepancy and modulate N400 amplitudes accordingly.1
Changes of emotional state may also influence the cognitive resources available to process other stimuli and be reflected in modulation of the P300, a measure sensitive to resource allocation in dual-task paradigms (Israel, Chesney, Wickens, & Donchin, 1980). Ellis and Ashbrook (1988) hypothesized that negative affective states reduce available attentional resources for performing other tasks, an assumption that has been supported by studies noting reduced P300 amplitude in different emotional contexts, including (1) increased fear among healthy controls (e.g., Moser, Hajcak, & Simons, 2005), (2) sustained depressed mood (Blackburn, Roxborough, Muir, Glabus, & Blackwood, 1990; cf. Deldin, Keller, Gergen, & Miller, 2000; Dietrich et al., 2000), and (3) presentation of cues simultaneously or in close temporal proximity to affectively charged stimuli (Ellis & Ashbrook, 1988; Keil et al., 2007; Kliegel, Horn, & Zimmer, 2003). In the present study, the degree to which increasing unpleasant emotions further depletes available cognitive resources should be reflected in smaller P300 amplitudes to words presented after this ER condition relative to ER strategies that reduce unpleasant emotions and presumably cognitive load. The largest P300 amplitudes should exist in the least resource-consuming condition occurring after successful down-regulation of unpleasant emotions.2
The Current Study and Specific Hypotheses
The first aim of the study was to evaluate whether participants could successfully regulate their emotions according to task instructions. Although numerous ER studies note different physiological consequences of up- and down-regulation of unpleasant affect, non-self-report measures of changes in affect are infrequent (for exceptions, see Eippert et al., 2007; Jackson et al., 2000). In the present study, electromyographic (EMG) activity from the corrugator supercilli was used to evaluate the level of negative affect participants experienced during the pre- and post- ER instruction phases of the picture viewing (Bradley, Cuthbert, & Lang, 1990; Lang, Greenwald, Bradley, & Hamm, 1993). We hypothesized the following:
Participants should exhibit greater levels of EMG when viewing unpleasant images relative to neutral images, confirming that the pictures elicited the expected emotions.
Successful increasing of unpleasant emotions should result in greater EMG in the post-ER instruction phase relative to the pre-ER instruction phase of picture viewing, and successful decreasing of unpleasant emotions should result in smaller EMG during the post-ER instruction phase relative to the pre-ER instruction phase. No change between the pre- and post-ER instruction period is expected when participants maintain unpleasant emotions.
Relative to maintaining unpleasant emotions, EMG during the post-ER instruction phase should be larger following instructions to increase unpleasant emotions and smaller in response to instructions to decrease unpleasant emotions.
The second aim was to capitalize on the temporal specificity of event-related brain potentials (ERPs) to elucidate the stages at which ER strategies may influence the processing of negative and neutral stimuli. Reaction time data as well as two ERP components - the N400 and P300 - were examined in order to explore whether cognitive processes are influenced by ER strategies. Based on the literature reviewed above, we hypothesized that following the regulation of unpleasant emotions, the following should occur:
Negative words should elicit smaller N400 amplitudes and larger P300 amplitudes than neutral words, as well as faster RT regardless of ER condition.
Manipulations of unpleasant emotions should modulate the discrepancy between the unpleasant affective state experienced during the regulation period and that elicited by the negative or neutral word relative to the other two ER conditions. Thus, compared to maintaining unpleasant emotions, N400 amplitudes and RTs should be largest to words following the increase ER condition and smallest following the decrease ER condition (see also footnote 1).
Increasing levels of unpleasant affect should decrease the amount of cognitive resources available to process the verbal stimuli. Thus, compared to maintaining unpleasant emotions, P300 amplitudes are hypothesized to be smallest after increasing unpleasant emotions and largest after decreasing unpleasant emotions.3
Method
Participants
Newspaper advertisements and flyers posted in the Boston area as well as postings on the Harvard University Department of Psychology Study Pool website were used to recruit healthy volunteers for a study of “the physiological consequences of emotion regulation.” A structured phone screen using the overview and initial module A and B questions from the Structured Clinical Interview for the DSM-IV (First, Spitzer, Gibbon, & Williams, 1995) was used to determine eligibility. Participants who endorsed probable lifetime history of MDD, bipolar disorder, psychosis, anxiety disorders, substance dependence, eating disorders, or seizure disorders based on these screening questions were excluded. Participants were also excluded if they self-reported cognitive impairments (i.e., learning disabilities), head injuries resulting in loss of consciousness for more than 5 min, or left-handedness, were non-native-English speaking, or had prior treatment for any psychiatric disorder.
Thirty-two individuals (25 women), ages 19 to 30 (M=23.97, SD=2.95) with a mean education level of 16.14 years (SD=1.71) participated in the study. Twenty-six participants identified as Caucasian (81.3%), two as African-American (6.3%), two identified as Asian (6.3%), and two participants identified as “other” (mixed ethnicity; 6.3%). Data from 2 study participants were excluded due to task noncompliance. Data from additional study participants were lost due to excessive artifact in the physiological recording leading to insufficient amounts of data available for reliable analyses. The following numbers of participants were available for each set of analyses: RT (n=30), EMG (n=26), and ERP (n=24).
Consistent with Harvard Institutional Review Board (Committee on the Use of Human Subjects) approval, the details of the study were explained to all participants and written consent was obtained prior to participation in the physiology session. Study participation lasted approximately 3 h and participants were compensated $10/h. Data from the present study were collected during the first 2 h of the testing session.
Stimuli
Participants viewed two types of stimuli: pictures and words. Pictures consisted of 72 unpleasant and 24 neutral images drawn from the International Affective Picture Set (IAPS; Lang, Bradley, & Cuthbert, 1997; see Appendix A). Each image was presented three times (once in each ER condition). Word stimuli consisted of 144 neutral and 144 negative words drawn from the Affective Norms for English Words collection (ANEW: Bradley & Lang, 1999; see Appendix B). Each word was presented once.
ER Instructions
Three different ER strategies were examined: “enhance,” “maintain,” and “suppress.” Specific instructions for each regulation condition were given to participants based on prior work by Jackson and colleagues (2000).4 To “enhance” emotions, participants were told to imagine that the situation depicted in the picture was happening to themselves or someone that they are close to. To “maintain,” participants were asked to attend to and be aware of the emotions they were experiencing as well as to maintain them without trying to change them. To “suppress,” participants were instructed to imagine that the situation depicted in the picture was not real, but rather that it was part of a dream or movie. Consequently, both the “enhance” and “suppress” conditions are cognitive reappraisal strategies, similar to those used in prior neuroimaging work on ER (Ochsner et al., 2004). Participants were instructed not to regulate their emotions by looking away from the picture or by generating another emotion in order to alter their emotional response to the picture (e.g., thinking of positive things in order to decrease negative emotion to a picture).
Procedure
During the task, individuals viewed the picture for 10 s (Figure 1). During the first 5 s individuals were instructed to passively view the image; no specific regulation was required. After the initial 5 s, an automated voice presented over a set of speakers above the monitor instructed participants to regulate their emotional experience using one of the three ER conditions detailed above. All three ER conditions were used following unpleasant pictures. Based on pilot work by Jackson et al. (2000) indicating that participants found instructions to increase or decrease neutral emotions too confusing, neutral pictures were always followed by instructions to maintain the emotion. The ER phase lasted for 5 s, at which point the picture disappeared from the screen. Following a variable (600−900 ms) delay the word appeared in the center of the screen. To ensure that participants attended to the word, they were asked to identify whether the word was negative or neutral and to press response buttons accordingly. Following their response to the word, an intertrial interval of 4 s commenced prior to presentation of the next trial.
Figure 1.
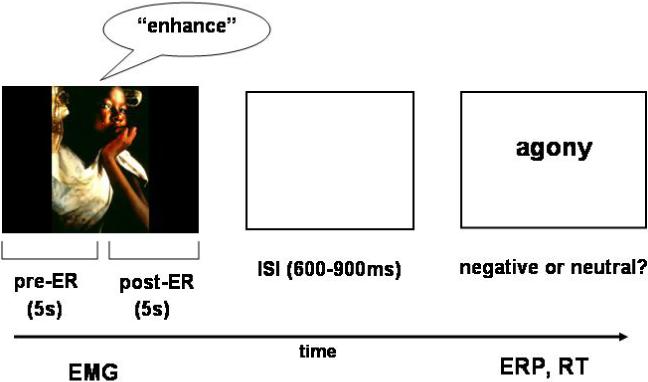
Schematic of the ER paradigm. Unpleasant and neutral images were viewed for 5 seconds before an instruction to enhance, maintain, or suppress their emotional state was given. After a 5 second regulation period and a short delay, participants saw a negative and neutral word. They were asked to press response buttons indicating whether the word was negative and neutral. EMG during picture viewing and regulation period was calculated as an assessment of emotional state. RT and ERPs were measured in response to the negative and neutral words based on the ER condition that preceded the word.
There were a total of 288 trials. Seventy-two unpleasant pictures were presented three times, once in each ER condition for a total of 216 unpleasant image trials. Twenty-four neutral images were presented three times in the maintain ER condition for a total of 72 neutral image trials. Half of the 288 trials were presented with negative words and half with neutral words. This led to a total of 36 trials within each of the four ER instruction/ picture valence and word valence combinations that were available for the ERP analyses. To minimize fatigue, trials were broken down into eight blocks of 36 trials each (approximately 8.5 min/block), and participants were permitted to take a brief break between each block.
Careful counterbalancing and randomization efforts were made to ensure that there were no systematic differences or relationships between pictures presented in certain ER conditions and the words presented in each trial. First, trials were pseudo randomized such that no more than three of the same regulation strategy instructions or valenced stimuli were presented sequentially. The order in which the three ER instructions were presented for each unpleasant image was randomized using an in-house matlab-based code, and valence and arousal ratings did not differ between unpleasant images presented in different ER instruction orders. Negative words were divided into four separate lists, equated for valence and arousal ratings based on ANEW norms (Bradley &Lang, 1999). Each list was assigned to one of the four picture valence and ER condition combinations. For example, for a given participant, words in the enhanceunpleasant, maintainunpleasant, suppressunpleasant, and the maintainneutral conditions were drawn from Lists A, B, C, and D, respectively. To avoid any systematic relationship between the different stimuli and ER instructions, 24 different word–picture–ER condition combinations were generated and used across participants. Accordingly, pairing between a specific word and a specific picture occurred only once across these 24 lists. To control for laterality effects from motor movements, participants used both left and right hands to make each word judgment; response button allocation was counterbalanced across participants.
Physiological Recording, Data Reduction, and Statistical Analysis
In the interest of brevity, and because our hypotheses were specific to the modulation of unpleasant emotion according to the three different ER strategies, our analyses focus on ERPs following the regulation of unpleasant emotions only. However, because participants were asked to down-regulate their emotional response to unpleasant stimuli by reinterpreting the stimuli in a more neutral fashion, we wanted to explore whether the resulting affective state led to similar processing as when participants maintained a neutral emotion, or whether the regulation of unpleasant emotional states led to distinct processing of subsequently presented words. Consequently, targeted analyses were conducted between the suppressunpleasant and maintainneutral conditions. In addition, to ensure that behavioral and ERP findings were related to successful ER processes, the analyses were limited to individuals who increased or decreased EMG in the enhance and suppress conditions, respectively (additional details are presented below). Due to excessive artifact in the EMG measures, only 26 participants' data were considered in these analyses. As described below, 24 participants successfully increased and/or decreased their EMG in line with task instructions and were included in the behavioral analyses. Data from two additional participants were unavailable for the ERP analyses due to excessive artifact in this measure; thus, final ERP analyses included 22 subjects.
Reaction time
Trials in which participants failed to respond, made an error, or responded slower than 2500 ms or faster than 150 ms were excluded from analyses (8.5% of total trials). RT data were log transformed (ln), and trials with responses greater than 3 SD from the mean of that subject and condition were removed as outliers (0.4% of total number of trials). Remaining RT data (91.1% of total trials) and accuracy rates were averaged across conditions for each participant and submitted to separate 2 × 3 ANOVAs with Word Valence (negative, neutral) and ER Instruction (enhanceunpleasant, maintainunpleasant, suppressunpleasant) as within-subjects factors.
ERP and EMG recording
A Geodesic Sensor Net System (Electrical Geodesic, Inc., Eugene, OR; Tucker, 1993) was used to record 128-channel EEG. Data were sampled at 500 Hz (bandwidth: 0.01−100 Hz), referenced to Cz during recording, and impedances were kept below 45 kΩ. EMG analysis. Based on recent work by Shackman, Maxwell, and Davidson (2004), four sensors from the EGI net were re-referenced to a bipolar montage (#2 vs. #8; #5 vs. #26) and submitted to a Fast Fourier transform. Mean spectral power density was computed for data in the 45−200 Hz range and log10 transformed to provide a measure of EMG activity. EMG activity was calculated during two phases of picture viewing (5 s of picture viewing and 5 s of ER) separately for each sensor pair and then averaged across the two pairs for a more robust estimate. EMG data from the pre-ER instruction period for neutral and negative pictures (regardless of ER condition and regardless of word valence) were compared using a t test to confirm that the two picture types elicited different levels of negative affect. Next, EMG data were submitted to a 3 × 2 ANOVA with ER Instruction (enhanceunpleasant, maintainunpleasant, suppressunpleasant) and Time (pre-ER instruction, post-ER instruction) as within-subjects factors in order to evaluate whether participants were able to regulate their emotions according to the task instructions. Comparisons between ER conditions during the post-ER instruction period are analogous to those conducted in a related prior ER study (Jackson et al., 2000). To provide more fine-grained information about the temporal course of EMG modulations, EMG values were calculated for each second of the post-ER instruction time periods and entered into a repeated measures ANOVA with ER Instruction (enhance, maintain, suppress) and Time (seconds 5−6, 6−7, 7−8, 8−9, and 9−10) as within-subjects factors.
ERP analysis
ERP data were analyzed using Netstation (Electrical Geodesic, Inc.), Brain Vision Analyzer (Brain Products GmbH, Gilching, Germany), and custom-made software. Off-line, EEG data were resampled to 250 Hz and low-pass filtered at 50 Hz (24 db/octave). An independent component analysis algorithm was used to correct for eyeblinks, EKG, horizontal eye movements, and 60-Hz noise (Makeig, Jung, Bell, Ghahremani, & Sejnowski, 1997). A linear interpolation was used to correct corrupted channels (Hjorth, 1975). ERPs were time-locked to the word onset in order to evaluate how ER instructions impact ERPs elicited by subsequently presented words. ERP data were extracted for a 924–ms interval beginning with word stimulus onset, compared to a preword baseline of 100 ms, and segments were manually inspected to ensure exclusion of trials with artifact. Data were then averaged for each condition and low-pass filtered at 30 Hz (12 db/octave) and rereferenced to an average reference.
A space-oriented field analysis was used to empirically define the N400 and P300 windows (Lehmann, 1987; Pizzagalli, Lehmann, Koenig, Regard, & Pascual-Marqui, 2000; Pizzagalli, Regard, & Lehmann, 1999). This process involves the data-driven identification of “microstates” - periods of quasi-stable electric brain field configurations – using custom-made software (Koenig & Lehmann, 1996). Microstates were defined based on the grand mean ERP averaged across all conditions and subjects. Two microstates were evaluated to represent the two ERP components of interest: N400 (a left lateralized fronto/frontcentral negativity 236−480 ms), and P300 (a centroparietal positivity 548−792 ms).
N400 and P300 amplitudes were calculated by averaging the amplitude within their respective latency windows separately for each word and ER instruction combination. Next, separate repeated measures ANOVAs were performed on ERPs elicited by negative and neutral words following the three different ER instructions to unpleasant pictures. Electrode sites were chosen based on the literature and after visual inspection of the ERP grand average waveforms (N400: C3, Cz, C4, FC3, FCz, FC4; P300: CP3, CPz, CP4, P3, Pz, P4). For the N400, the following within-subjects factors were used: Region (central, frontocentral) × Laterality (left, midline, right) × Word Valence (negative, neutral) × ER Instruction (enhanceunpleasant, maintainunpleasant, suppressunpleasant). For the P300, an identical ANOVA was run (the factor Region involved centroparietal and parietal sites). Analogous repeated measures ANOVAs were also performed to compare activity between the suppressunpleasant and maintainneutral conditions.
Overall, the Greenhouse–Geisser correction was employed to correct for sphericity violations, and partial η2 values were calculated as an estimate of effect size. Simple univariate ANOVAs and post hoc Neuman–Keuls analyses were performed in order to interpret higher-order interactions in the analyses described above. In the interest of brevity, only findings that included Word Valence and ER Instruction are presented.
Results
EMG Data
As expected, unpleasant images elicited greater EMG during the pre-ER instruction period than neutral images, t(25)=2.59, p<.02. A 3 × 2 repeated measures ANOVA was conducted to evaluate whether participants successfully regulated their emotions (Table 1). A main effect of ER instruction, F(2,50)=10.32, p<.001, partial η2=.29, was qualified by a significant interaction between ER Instruction (enhanceunpleasant,maintainunpleasant, suppressunpleasant) and Time (pre- vs. post-ER instruction), F(2,50)=8.28, p<.01, partial η2=.25. There was no significant main effect of Time. To clarify the significant interaction, within instruction and between-instructions simple effects ANOVAs were performed.
Table 1.
EMG
| pre-ER instruction |
post-ER instruction |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| enhanceunpleasant | −0.89 | 0.31 | −0.84 | 0.34 |
| maintainunpleasant | −0.90 | 0.32 | −0.89 | 0.33 |
| suppressunpleasant | −0.90 | 0.31 | −0.92 | 0.32 |
| maintainneutral | −0.93 | 0.33 | −0.94 | 0.33 |
EMG values were calculated from the 26 participants with usable EMG data. Values represent the log-transformation of mean spectral activity in the 40−200 Hz range during the first 5 seconds of picture presentation (pre-ER instruction) and the 5 seconds of ER (post-ER instruction).
Within-instruction modulations
Analyses revealed significant increases and decreases in EMG between the pre- and post-ER instruction periods for the enhanceunpleasant and suppressunpleasant ER conditions, respectively: Time, F(1,25)=5.88, p<.03, partial η2=.19; Time, F(1,25)=5.63, p<.03, partial η2=.18 (see Figure 2). EMG did not differ between the pre- and post-ER instruction time periods for the maintainunpleasant condition, consistent with the instruction of maintaining level of negative affect in this condition. To assess whether these findings reflected the ER abilities of a subset of participants, we further analyzed how many participants exhibited the expected EMG changes between the pre- and post-ER instruction periods. Twenty-two participants (84.6%) exhibited greater EMG values during the post-ER instruction period relative to the pre-ER instruction period in the enhanceunpleasant condition, and 20 (76.9%) exhibited a decrease between the time periods in the suppressunpleasant condition, binomial P(20,26)<.001.
Figure 2.
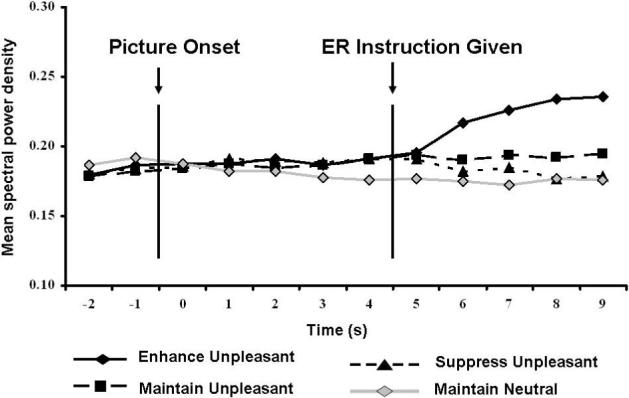
EMG for each ER Condition over time. Each value represents an average mean spectral power density over a 1 second period beginning two seconds prior to image onset and continuing through the last second of image presentation. Note: power values are presented here for ease of viewing. Statistics were calculated on log-transformed data.
Between-instruction modulations
As expected, no significant differences among the ER conditions emerged for the pre-ER instruction period (ps>.50); however, EMG levels differed significantly during the post-ER instruction time period: ER Instruction, F(2,50)=11.42, p<.001, partial η2=.31. Post hoc Neuman–Keuls comparisons indicated that EMG during the post-ER instruction period was significantly greater in the enhanceunpleasant condition relative to both the maintainunpleasant and suppressunpleasant conditions (ps<.001). No differences emerged between the maintainunpleasant and suppressunpleasant conditions when considering the entire 5-s ER period (p>.30). Fine-grained analyses regarding the temporal course of EMG modulations revealed significant differences among the ER conditions: ER Instruction, F(2,50)=11.70, p<.001, partial η2=.32). Post hoc comparisons clarified that, compared to the maintainunpleasant condition, EMG was significantly greater in the enhanceunpleasant condition but significantly lower in the suppressunpleasant condition (all ps<.01), suggesting that participants regulated their unpleasant emotions according to task instructions and replicating prior findings (Jackson et al., 2000). Neither a significant effect of Time nor an interaction between ER Instruction and Time emerged.
Reaction Time
Participants responded more quickly, F(1,23)=7.10, p<.02, partial η2= .24, and more accurately F(1,23)=3.09, p<.03, partial η2= .21, to negative words versus neutral words (Table 2). Contrary to our hypotheses, no significant effects involving ER Instruction emerged.
Table 2.
Reaction Time Results
| Reaction Time |
Accuracy |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | Word Type | Mean | SD | Mean | SD |
| enhanceunpleasant | negative word | 954.98 | 173.29 | 94.56 | 4.97 |
| neutral word | 1003.44 | 180.23 | 90.83 | 6.02 | |
| maintainunpleasant | negative word | 965.46 | 161.81 | 96.23 | 4.05 |
| neutral word | 1002.51 | 182.00 | 92.39 | 6.00 | |
| suppressunpleasant | negative word | 969.03 | 157.76 | 94.74 | 4.67 |
| neutral word | 1008.31 | 170.87 | 92.37 | 4.49 | |
| maintainneutral | negative word | 973.39 | 146.18 | 95.59 | 3.67 |
| neutral word | 1035.19 | 199.35 | 90.59 | 4.98 | |
Analyses were based on 24 participants who successfully regulated their emotions. Reaction Time data represent the average time (in ms) participants required in order to make the valence judgment. Note: RT analyses were conducted on the logarithmic transformation of the original RT data.
N400
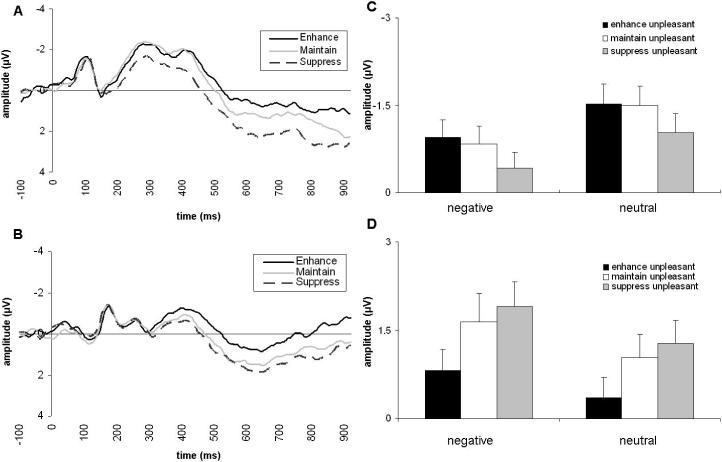
For the N400, the main effects of Word Valence and ER Instruction, but not their interaction, were expected to be significant. These hypotheses were confirmed. The ANOVA revealed a Word Valence effect, due to larger amplitudes to neutral relative to negative words, F(1,21)=35.04, p<.001, partial η2= .63 (Table 3). A main effect of ER Instruction also emerged, F(2,42)=6.34, p<.005, partial η2= .23. As expected, the ER Instruction × Word Valence interaction was not significant, F(2,42)=0.08, p>.90, partial η2= .004. Subsequent post hoc Neuman–Keuls analyses indicated that N400 amplitudes in the enhanceunpleasant and maintainunpleasant conditions were significantly larger (i.e., more negative) than those in the suppressunpleasant condition (ps<.01; Figure 3). Contrary to our hypotheses, no difference between the enhanceunpleasant and maintainunpleasant conditions emerged (p>.60). Interestingly, targeted comparisons indicated that the suppressunpleasant condition (M= −0.73; SD=1.33) led to similar N400 amplitude as the maintainneutral condition (M= −0.85; SD=1.42): ER Instruction, F(1,21)=0.87, p>.30, partial η2= .04.
Table 3.
Significant Main Effects and Interactions for Various ERP Analyses Comparing three ER Conditions for Unpleasant Images Only
| ERP | Factor | df | F | p < | eta2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N400 | ER Instruction | 2,42 | 6.34 | .01 | .23 |
| N400 | Word Valence | 1,21 | 35.04 | .001 | .63 |
| N400 | Laterality | 2,42 | 19.84 | .001 | .49 |
| N400 | Word Valence × Laterality | 2,42 | 3.25 | .05 | .13 |
| P300 | ER Instruction | 2,42 | 13.06 | .001 | .38 |
| P300 | Word Valence | 1,21 | 17.22 | .001 | .45 |
| P300 | Laterality | 2,42 | 4.94 | .02 | .19 |
| P300 | Word Valence × Region | 1,21 | 5.18 | .04 | .20 |
| P300 | ER Instruction × Laterality | 4,84 | 2.63 | .04 | .11 |
Figure 3.
N400 and P300 ERP results. Panel A depicts the grand average ERP for both negative and neutral words in the three different ER categories at a representative sensor site (Cz). Panel B depicts the grand average ERP for both negative and neutral words in the three different ER categories at Pz. Panel C represents the N400 mean amplitudes in each different ER condition for negative and neutral words. Panel D represents P300 mean amplitudes in each different ER condition for negative and neutral words. Error bars indicate standard errors.
P300
Similar to the N400 findings, we hypothesized significant main effects of Word Valence and ER Instruction, but no interaction. As expected, P300 amplitudes were larger to negative compared with neutral words: Word Valence, F(1,21)=17.22, p<.001, partial η2= .45 (Table 3). A main effect of ER Instruction, F(2,42)=13.06, p<.001, partial η2= .38, and subsequent Neuman– Keuls analyses indicated that P300 amplitudes were, as expected, smallest to words in the enhanceunpleasant condition relative to the other ER conditions (ps<.001), but did not differ between the maintainunpleasant and suppressunpleasant conditions (p>.20; see Figure 3). The ER Instruction × Word Valence interaction was not significant. Of note, targeted comparisons indicated that the suppressunpleasant condition (M=1.59; SD=1.87) led to similar P300 amplitude as the maintainneutral condition (M=1.82; SD=2.06): ER Instruction, F(1,21) =1.73, p>.20, partial η2= .08.
Discussion
Emotion regulation strategies are hypothesized to influence emotional, physiological, and cognitive processes while regulatory processes are engaged; however, it is possible that different ER strategies and the resulting affective states may impact the same processes elicited by stimuli presented after the regulation phase has concluded. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the impact of ER strategies and the corresponding affective states on behavioral and physiological responses to stimuli presented after different cognitive reappraisal strategies, and it provides initial electrophysiological evidence that manipulations of unpleasant emotional state continue to impact cognitive processes after the ER period, in line with prior work documenting the influence of emotional states on stimuli presented during affective contexts (Erk et al., 2003; Kensinger, Brierley, Medford, Growdon, & Corkin, 2002; Moser et al., 2005). Before discussing the implications and limitations of the present findings, it is important to emphasize that analyses of corrugator EMG activity confirmed that (a) the emotional pictures elicited the intended affective states, and (b) participants regulated their emotions according to the study instructions. These findings indicate that the present paradigm was successful in modulating participants' unpleasant emotional states and highlight a promising avenue for investigating ER deficits among individuals with psychiatric disorders.
ERP Findings
Both N400 and P300 amplitudes to words presented after up and down-regulation of unpleasant affective states were modulated by different cognitive reappraisal strategies. Specifically, N400 amplitudes were smallest in response to word stimuli after participants decreased unpleasant emotions and were comparable to those after the maintenance of neutral emotions. In light of prior findings indicating that the N400 component indexes the emotional congruity between two stimuli (Schirmer et al., 2002, 2005) and participants' expectations about the emotional valence of an upcoming stimulus (Chung et al., 1996), decreased N400 amplitudes likely reflect a greater emotional congruity between post-down-regulation affect and that elicited by the words, relative to the other ER conditions.
Modulation of emotional state also influenced P300 amplitudes, which were smallest in response to words presented after increasing an unpleasant emotion relative to maintaining or decreasing that emotion. Given prior literature noting that P300 amplitude is sensitive to attentional resources and is decreased during dual tasks (e.g., Israel et al., 1980) and emotional states (Keil et al., 2007; Kliegel et al., 2003), it is likely that increasing unpleasant affect in the present study limited cognitive resources above and beyond that of maintaining a negative affective state. This is consistent both with Ellis and Ashbrook's (1988) theory as well as informal comments made by study participants at the end of the experiment. During debriefing, several participants noted that “switching gears” after increasing unpleasant emotions in order to respond to the word stimulus was difficult.
Contrary to expectations, N400 and P300 amplitudes did not differ between each of the three ER conditions. Rather, N400 amplitudes in the increase and maintain conditions and P300 amplitudes in the decrease and maintain conditions were statistically equivalent. The reasons for this lack of a full modulation of the N400 and P300 effects are not immediately clear. One possibility is that N400 amplitudes are less sensitive to slight differences in emotional congruency. Previous studies have noted that N400 amplitudes are smaller when individuals view two negative stimuli in a row, relative to when they view a negative stimulus preceded by a positive context (e.g., Schirmer et al., 2002, 2005). No studies exist comparing negative stimuli presented after intense levels of unpleasant affect relative to moderate levels of unpleasant affect, and it is possible that N400 amplitudes are only sensitive to more dramatic differences in emotional congruity (as when stimuli of different valences are presented together).
Similarly, P300 amplitudes did not differ between the maintain and suppress ER conditions. One possible explanation stems from recent neuroimaging research documenting the neural demands of both up- and down-regulating unpleasant emotions. These studies suggest that effortful up- and down-regulation of unpleasant emotions activate PFC and ACC regions and modulate amygdalar activation (for a review, see Ochsner & Gross, 2005), and are therefore likely to demand cognitive resources, potentially limiting their availability to process a subsequently presented word. Although we originally predicted that the relative neutral affective state participants experienced after downregulating emotions should have increased resources relative to the other ER conditions, we may have underestimated the lingering effects of the cognitively taxing down-regulation ER strategy. Indeed, work by Ochsner and colleagues (2004) suggests that participants found down-regulation to be more difficult than up-regulation. If down-regulation taxes cognitive resources, it should result in reduced P300 amplitudes relative to a nonregulation condition or equivalent P300 amplitudes to individuals experiencing a moderate level of unpleasant affect (as in the “maintain” ER condition). However, this idea warrants further investigation, perhaps by using more effortful down-regulation strategies and evaluating whether such effortful downregulation would decrease P300 amplitudes relative to the maintenance of unpleasant emotions.
Consistent with prior literature (Schirmer et al., 2002, 2005) and our predictions, N400 amplitudes were larger to neutral as compared with negative words following the presentation of unpleasant images and P300 amplitudes were larger to negative versus neutral words, likely reflecting attention allocation to emotionally salient and arousing stimuli (Cuthbert, Schupp, Bradley, McManis, & Lang, 1998; Herbert, Kissler, Junghöfer, Peyk, & Rockstroh, 2006; Schupp et al., 2000). However, although the cognitive reappraisal strategies modulated N400 and P300 amplitudes, they did not impact ERP responses to negative and neutral words differentially. We speculate that this finding might be explained by differences in the amount of affect elicited by the words and pictures used in the present study. Specifically, we hypothesize that the discrepancy in affective tone between negative and neutral words occurring immediately after arousing unpleasant pictures was very modest in comparison to the discrepancy between words and pictures. Future studies that parametrically vary the arousal of both pictures and words will be required for testing this hypothesis.
Behavioral Findings
Surprisingly, and inconsistent with our hypotheses, RTs in the valence-identification task were not impacted by ER strategy. Although it is possible that ER strategies do not impact reaction times, several methodological issues might explain these null findings. First, prior studies investigating emotional priming have compared RTs in response to similarly valenced stimuli (a sentence spoken with negative prosody completed by a negative word) with dissimilar valenced stimuli (a sentence spoken with negative prosody completed by a positive word; e.g., Schirmer et al., 2002). Priming effects may be more difficult to detect behaviorally when stimuli are of the same valence, but different intensities, as in the present study. Second, most priming studies use stimuli from the same category as the prime and the target (e.g., two words) and we are unaware of any studies documenting semantic priming effects between visually presented images and visually presented words. It is thus possible that this latter type of cross-modal priming may be less sensitive to RT effects. Third, many priming studies present the prime and target stimuli in rapid succession (Fazio, 2001), and our longer delay between stimuli (600−900 ms) may have “washed out” any priming effects (however, see Holcomb & Anderson, 1993). Finally, it is possible that the valence judgment task was not cognitively taxing enough to manifest the processing differences that the ERP findings suggest existed to words presented following different ER strategies.
Limitations and Conclusions
Several limitations of the present study should be acknowledged. First, due to efforts to use highly arousing unpleasant stimuli and the limited number of stimuli available, each picture was presented three times in each of the three ER conditions. Careful attention was paid to ensure that there were no systematic differences (e.g., valence, arousal, length, part of speech, frequency of use, and percentage of images with people vs. animals) or sequencing confounds among conditions. However, informal debriefing of study participants suggested that some habituation to the stimuli might have occurred during the study, which may have diluted some of the study findings. If this is the case, our findings are conservative estimates of the impact of ER strategies on subsequently presented stimuli. Second, as mentioned above, RT data failed to show any ER-related modulation, highlighting a dissociation between behavioral and ERP measures of cognitive reappraisal. It is currently unclear whether the lack of behavioral modulation was a limitation of the current task design, or whether these findings indicate that ERPs might be more sensitive for detecting the effects of ER strategies on other processes.
These limitations notwithstanding, the present findings suggest that the regulation of brief affective states using cognitive reappraisal strategies influences processing of word stimuli presented after ER and thus extend prior research in this area. Compared to up-regulating or maintaining an unpleasant affect, down-regulating an unpleasant affect led to reduced N400 to negative and neutral words, indicating reduced emotional discrepancy between the experienced affect and incoming information. Moreover, compared to down-regulating or maintaining an unpleasant affect, up-regulating an unpleasant affect led to smaller P300 to the word stimuli, raising the possibility that enhancement of unpleasant emotions might usurp cognitive resources available to process upcoming information (Ellis & Ashbrook, 1988). If replicated, the present findings might provide a valuable framework for testing emotional dysregulation processes in clinical populations.
Author Notes
This research was supported by the a Sackler Scholar in Psychobiology Research Grant, a McMasters Fund Harvard University Research Grant and NIH pre-doctoral NRSA (F31 MH7424601) to CMD. DAP was supported by grants from NIMH (R01 MH68376) and NCCAM (R21 AT002974). We gratefully acknowledge the suggestions, contributions, and assistance of the members of the Affective Neuroscience Lab, especially Pearl Chiu, Dan Dillon, Decklin Foster, Avram Holmes, Tiffany Meites, James O'Shea, and Kyle Ratner. We are also grateful to Alexander Shackman, Heather Urry, and Carien Van Reekum for their assistance in implementing the EMG data collection and analyses as well as for the comments made by the anonymous reviewers. Finally, we are extremely appreciative of the individuals who volunteered their time to participate in the study.
Appendix A: List of IAPS pictures used in the experiment
Unpleasant images (Mvalence= 2.38, SDvalence= 0.36; Marousal= 5.69, SDarousal= 0.81)
2141, 2205, 2276, 2700, 2710, 2750, 2751, 2753, 2800, 2900, 3160, 3180, 3181, 3220, 3230, 3300, 3301, 3350, 3500, 3530, 3550, 6212, 6213, 6230, 6242, 6243, 6260, 6312, 6313, 6350, 6360, 6510, 6550, 6560, 6570, 6821, 6831, 6834, 6838, 7380, 9000, 9007, 9040, 9041, 9050, 9120, 9140, 9181, 9220, 9250, 9265, 9300, 9400, 9410, 9415, 9421, 9430, 9432, 9433, 9520, 9530, 9560, 9571, 9600, 9611, 9800, 9810, 9830, 9910, 9911, 9920, 9921
Neutral images (Mvalence= 5.05, SDvalence= 0.32; Marousal= 3.35, SDarousal= 0.53)
1121, 1670, 2190, 2200, 2210, 2214, 2215, 2383, 2385, 2410, 2480, 2487, 2495, 2514, 2516, 2570, 2749, 2850, 2870, 2880, 6150, 7233, 7550, 9700
Appendix B: List of ANEW words used in the experiment
Negative words (Mvalence= 2.20, SDvalence= 0.37; Marousal= 5.79, SDarousal= 0.96)
abuse, accident, ache, afraid, agony, alone, ambulance, anger, anguished, assault, bomb, burdened, burial, cancer, cemetery, coffin, corpse, coward, crash, crisis, cruel, crushed, danger, dead, death, debt, defeated, demon, depressed, depression, deserter, despairing, devil, disaster, discomfort, disgusted, disloyal, distressed, divorce, dreadful, enraged, execution, failure, fat, fear, fearful, fever, filth, fire, fraud, frustrated, funeral, gangrene, gloom, grief, guillotine, hardship, hatred, headache, hell, helpless, horror, hostage, illness, infection, injury, insecure, jail, jealousy, killer, leprosy, lice, lonely, lost, mad, maggot, malaria, malice, massacre, measles, misery, mistake, morgue, murderer, neglect, nightmare, obesity, pain, paralysis, penalty, poison, poverty, prison, punishment, rabies, rage, rape, regretful, rejected, roach, robber, rotten, rude, sad, scum, selfish, sick, sickness, sin, slaughter, slave, slum, starving, stench, stress, stupid, suicide, syphilis, terrible, terrified, terrorist, thief, toothache, torture, toxic, tragedy, traitor, trash, trauma, trouble, troubled, tumor, ugly, ulcer, unhappy, upset, useless, venom, victim, violent, vomit, war, whore, wounds
Neutral words (Mvalence= 5.21, SDvalence= 0.47; Marousal= 4.11, SDarousal= 0.80)
aloof, ankle, appliance, astonished, avenue, bandage, banner, barrel, basket, bathroom, bland, blasé, blond, bowl, building, butter, cabinet, cannon, chair, chin, clock, clumsy, coarse, column, consoled, context, cord, cork, corridor, crash, curious, curtains, danger, doctor, elbow, elevator, engine, fabric, finger, foot, fork, glacier, golfer, green, hairdryer, hairpin, hammer, haphazard, hay, headlight, hospital, humble, hydrant, icebox, indifferent, industry, inhabitant ,innocent, iron, item, journal, jug, kerchief, ketchup, kettle, knot, lamp, lantern, lavish, lawn, lightbulb, lightning, limber, locker, machine, mantel, material, medicine, metal, moral, muddy, museum, naked, news, noisy, nonchalant, nonsense, nun, odd, pamphlet, paper, passage, patent, patient, pencil, phase, pig, plain, poster, quart, quiet, radiator, rain, rattle, repentant, reserved, reverent, rough, scissors, seat, serious, sheltered, skeptical, smooth, solemn, sphere, spray, startled, statue, stiff, stomach, storm, stove, subdued, swamp, swift, table, tank, taxi, tease, theory, tidy, tool, truck, trunk, umbrella, utensil, vest, violin, volcano, wagon, windmill, wounds, yellow
Footnotes
These hypotheses rest on the assumptions that (1) the unpleasant images used in the present study elicited stronger negative affect than the negatively valenced words, and (2) the arousing/valenced nature of the words is so mild relative to the images that even suppressed negative affect elicited by a picture is still stronger than negative affect elicited by a word.
Note that we are not assuming that the process of down-regulating a negative emotion is less cognitive taxing than up-regulating such an emotion, and indeed there is empirical evidence suggesting that similar cognitive efforts is required (Ochsner et al., 2004; Dillon, Ritchey, Johnson & LaBar, 2007). Rather we are assuming that the “enhance” condition used in the present study would lead to increased negative affect after the emotion regulation, which in turn will usurp cognitive resources required for further processing.
Previous research suggests that the N400 component is not as sensitive as the P300 to the amount of cognitive resources available after increasing negative affect. Findings derived from linguistic studies combining N400 paradigms with a second task suggest that the second task did not affect N400 amplitude (but lengthened its latency), especially when the tasks are in close temporal proximity (Hohlfeld, Sangals, & Sommer, 2004; Hohlfeld & Sommer, 2005). Along similar lines, D'Arcy, Service, Connolly, & Hawco (2005) reported that increased working memory load did not modulate N400 amplitudes elicited by words that were semantically incongruent with a prior sentence.
The terms “enhance”, “maintain”, and “suppress” were used based on prior instructions by Jackson et al. (2000). The “enhance” and “suppress” instructions in this study are up- and down-regulation cognitive reappraisal strategies and should not be confused with the “suppress” instructions used by James Gross (1998, 2002), which refer to emotional expression suppression, or the “suppress” instructions of Daniel Wegner (Wegner, Schneider, Carter & White, 1987) which refer to not thinking about a target stimulus.
References
- Besson M, Magne C, Schon D. Emotional prosody: sex differences in sensitivity to speech melody. Trends in Cognitive Science. 2002;6:405–407. doi: 10.1016/s1364-6613(02)01975-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn IM, Roxborough HM, Muir WJ, Glabus M, Blackwood DH. Perception and physiological dysfunction in depression. Psychological Medicine. 1990;20:95–103. doi: 10.1017/s003329170001326x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN, Lang PJ. Startle reflex modification: emotion or attention? Psychophysiology. 1990;27:513–522. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1990.tb01966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley MM, Lang PJ. Technical Report C-1. The Center for Research in Psychophysiology, University of Florida; Gainesville, Florida: 1999. Affective norms for English words (ANEW): Instruction manual and affective ratings. [Google Scholar]
- Chung G, Tucker DM, West P, Potts GF, Liotti M, Luu P, Hartry AL. Emotional expectancy: brain electrical activity associated with an emotional bias in interpreting life events. Psychophysiology. 1996;33:218–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1996.tb00419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbert BN, Schupp HT, Bradley M, McManis M, Lang PJ. Probing affective pictures: Attended startle and tone probes. Psychophysiology. 1998;35:344–347. doi: 10.1017/s0048577298970536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Arcy RC, Service E, Connolly JF, Hawco CS. The influence of increased working memory load on semantic neural systems: A high-resolution event-related brain potential study. Cognitive Brain Research. 2005;22:177–191. doi: 10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2004.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deldin PJ, Keller J, Gergen JA, Miller GA. Right-posterior face processing anomaly in depression. Journal of Abnormal Psychology. 2000;109:116–121. doi: 10.1037//0021-843x.109.1.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demaree HA, Schmeichel BJ, Robinson JL, Everhart DE. Behavioural, affective, and physiological effects of negative and positive emotional exaggeration. Cognition & Emotion. 2004;18:1079–1097. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich DE, Emrich HM, Waller C, Wieringa BM, Johannes S, Muente TF. Emotion/cognition-coupling in word recognition memory of depressive patients: An event-related potential study. Psychiatry Research. 2000;96:15–29. doi: 10.1016/s0165-1781(00)00187-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon DG, Ritchey M, Johnson BD, LaBar KS. Dissociable effects of conscious emotion regulation strategies on explicit and implicit memory. Emotion. 2007;7:354–365. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.7.2.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eippert F, Veit R, Weiskopf N, Erb M, Birbaumer N, Anders S. Regulation of emotional responses elicited by threat-related stimuli. Human Brain Mapping. 2007;28:409–23. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis HC, Ashbrook PW. Resource allocation model of the effects of depressed mood states on memory. In: Fiedler K, Forgas J, editors. Affect, cognition and social behaviour. Hogrefe; Toronto: 1988. pp. 25–43. [Google Scholar]
- Erk S, Kiefer M, Grothe J, Wunderlich AP, Spitzer M, Walter H. Emotional context modulates subsequent memory effect. Neuroimage. 2003;18:439–447. doi: 10.1016/s1053-8119(02)00015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio RH. On the automatic activation of associated evaluations: An overview. Cognition and Emotion. 2001;15:115–141. [Google Scholar]
- Fazio RH, Sanbonmatsu DM, Powell MC, Kardes FR. On the automatic activation of attitudes. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1986;50:229–238. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.50.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW. Structured Clinical Interview for the DSM-IV Axis I Disorders – Patient Edition (SCID I-P, Version 2.0) American Psychiatric Press; Washington, DC: 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Gross JJ. Antecedent- and response-focused emotion regulation: Divergent consequences for experience, expression, and physiology. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1998;74:224–237. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.74.1.224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross JJ. Emotion regulation: Affective, cognitive, and social consequences. Psychophysiology. 2002;39:281–291. doi: 10.1017/s0048577201393198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert C, Kissler J, Junghöfer M, Peyk P, Rockstroh B. Processing of emotional adjectives: Evidence from startle EMG and ERPs. Psychophysiology. 2006;43:197–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2006.00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth B. An on-line transformation of EEG scalp potentials into orthogonal source derivations. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology. 1975;39:526–530. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(75)90056-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holcomb PJ, Anderson JE. Cross-modal semantic priming: A time-course analysis using event-related brain potentials. Language and Cognitive Processes. 1993;8:379–411. [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld A, Sangals J, Sommer W. Effects of additional tasks on language perception: An event-related brain potential investigation. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition. 2004;30:1012–1025. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.30.5.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohlfeld A, Sommer W. Semantic processing of unattended meaning is modulated by additional task load: Evidence from electrophysiology. Cognitive Brain Research. 2005;24:500–512. doi: 10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2005.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel JB, Chesney GL, Wickens CD, Donchin E. P300 and tracking difficulty: evidence for multiple resources in dual-task performance. Psychophysiology. 1980;17:259–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1980.tb00146.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson DC, Malmstadt JR, Larson CL, Davidson RJ. Suppression and enhancement of emotional responses to unpleasant pictures. Psychophysiology. 2000;37:515–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil A, Bradley MM, Junghofer M, Russmann T, Lowenthal W, Lang PJ. Cross-modal attention capture by affective stimuli: Evidence from event-related potentials. Cognitive, Affective, & Behavioral Neuroscience. 2007;7:18–24. doi: 10.3758/cabn.7.1.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kensinger EA, Brierley B, Medford N, Growdon JH, Corkin S. Effects of normal aging and Alzheimer's disease on emotional memory. Emotion. 2002;2:118–134. doi: 10.1037/1528-3542.2.2.118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim SH, Hamann S. Neural correlates of positive and negative emotion regulation. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2007;19:776–798. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2007.19.5.776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliegel M, Horn AB, Zimmer H. Emotional after-effects on the P3 component of the event-related brain potential. International Journal of Psychophysiology. 2003;38:129–137. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig T, Lehmann D. Microstates in language-related brain potential maps show noun-verb differences. Brain and Language. 1996;53:169–182. doi: 10.1006/brln.1996.0043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert B. International Affective Picture System. NIMH Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention; Gainesville, Florida: 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lang PJ, Greenwald MK, Bradley MM, Hamm AO. Looking at pictures: Affective, facial, visceral, and behavioral reactions. Psychophysiology. 1993;30:261–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1993.tb03352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann D. Principles of spatial analysis. In: Gevins AS, Remond A, editors. Handbook of electroencephalography and clinical neurophysiology: Methods of analysis of brain electrical and magnetic signals. Vol. 1. Elsevier; Amsterdam: 1987. pp. 309–354. (Revised series). [Google Scholar]
- Makeig S, Jun TP, Bell AJ, Ghahremani D, Sejnowski TJ. Blind separation of auditory event-related brain responses into independent components. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1997;94:10979–10984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.20.10979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser JS, Hajcak G, Bukay E, Simons RF. Intentional regulation of emotional responding to unpleasant pictures: an ERP study. Psychophysiology. 2006;43:292–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2006.00402.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser JS, Hajcak G, Simons RF. The effects of fear on performance monitoring and attentional allocation. Psychophysiology. 2005;42:261–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2005.00290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochsner KN, Bunge SA, Gross JJ, Gabrieli JD. Rethinking feelings: An FMRI study of the cognitive regulation of emotion. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2002;14:1215–1229. doi: 10.1162/089892902760807212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochsner KN, Gross JJ. The cognitive control of emotion. Trends in Cognitive Science. 2005;9:242–249. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2005.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochsner KN, Ray RD, Cooper JC, Robertson ER, Chopra S, Gabrieli JD, Gross JJ. For better or for worse: Neural systems supporting the cognitive down- and up-regulation of negative emotion. Neuroimage. 2004;23:483–499. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.06.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzagalli D, Lehmann D, Koenig T, Regard M, Pascual-Marqui RD. Face-elicited ERPs and affective attitude: Brain electric microstate and tomography analyses. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2000;111:521–531. doi: 10.1016/s1388-2457(99)00252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizzagalli D, Regard M, Lehmann D. Rapid emotional face processing in the human right and left brain hemispheres: An ERP study. NeuroReport. 1999;10:2691–2698. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199909090-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards JM, Gross JJ. Emotion regulation and memory: The cognitive costs of keeping one's cool. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 2000;79:410–424. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.79.3.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer SM, Jackson DC, Davidson RJ, Aguirre GK, Kimberg DY, Thompson-Schill SL. Modulation of amygdalar activity by the conscious regulation of negative emotion. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2002;14:913–921. doi: 10.1162/089892902760191135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer A, Kotz SA, Friederici AD. Sex differentiates the role of emotional prosody during word processing. Cognitive Brain Research. 2002;14:228–233. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6410(02)00108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer A, Kotz SA, Friederici AD. On the role of attention for the processing of emotions in speech: Sex differences revisited. Cognitive Brain Research. 2005;24:442–52. doi: 10.1016/j.cogbrainres.2005.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schupp HT, Cuthbert BN, Bradley MM, Cacioppo JT, Ito T, Lang PJ. Affective picture processing: the late positive potential is modulated by motivational relevance. Psychophysiology. 2000;37:257–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackman AJ, Maxwell JS, Davidson RJ. Prefrontal EEG asymmetry, corrugator EMG and self-report measures of threat-evoked anxiety. Psychophysiology. 2004;41:S59. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker DM. Spatial sampling of head electrical fields: the geodesic sensor net. Electroencephalography & Clinical Neurophysiology. 1993;87:154–163. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(93)90121-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry HL, van Reekum CM, Johnstone T, Kalin NH, Thurow ME, Schaefer HS, Jackson CA, Frye CJ, Greischar LL, Alexander AL, Davidson RJ. Amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex are inversely coupled during regulation of negative affect and predict the diurnal pattern of cortisol secretion among older adults. Journal of Neuroscience. 2006;26:4415–4425. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3215-05.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner DM, Schneider DJ, Carter SR, White TL. Paradoxical effects of thought suppression. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology. 1987;53:5–13. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.53.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Q, Lawson A, Guo C, Jiang Y. Electrophysiological correlates of visual affective priming. Brain Research Bulletin. 2006;71:312–323. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2006.09.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]