Abstract
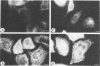
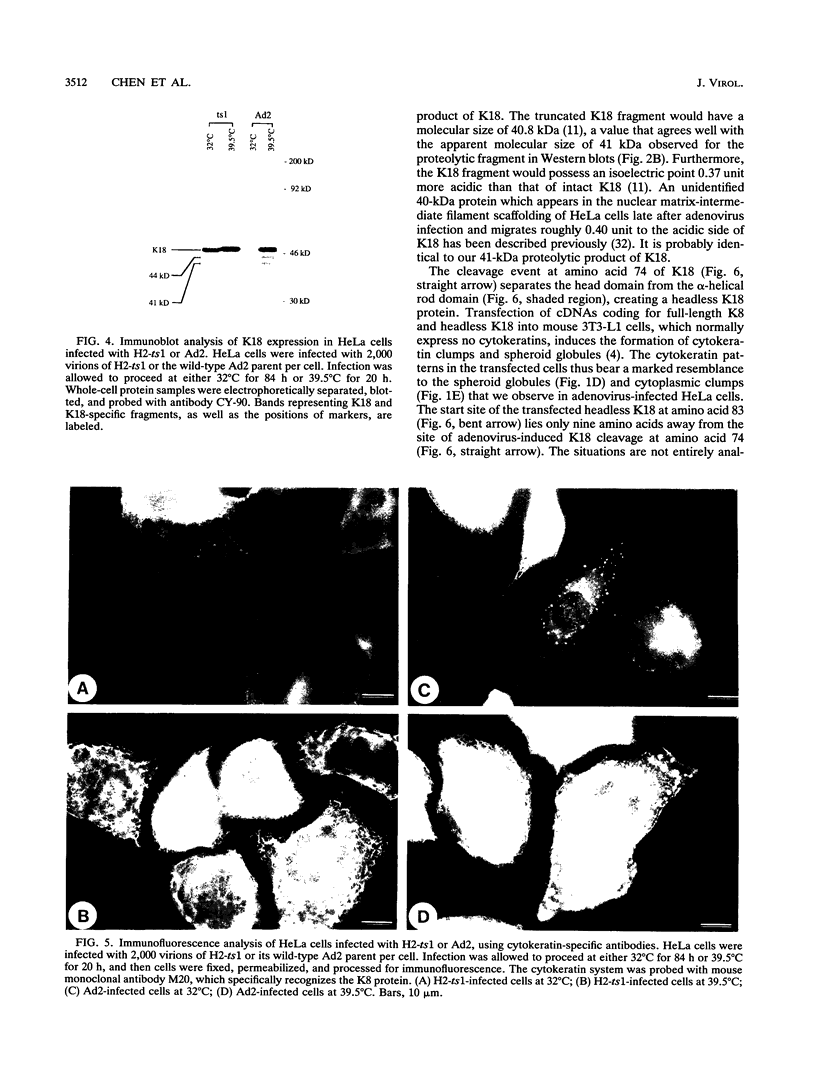
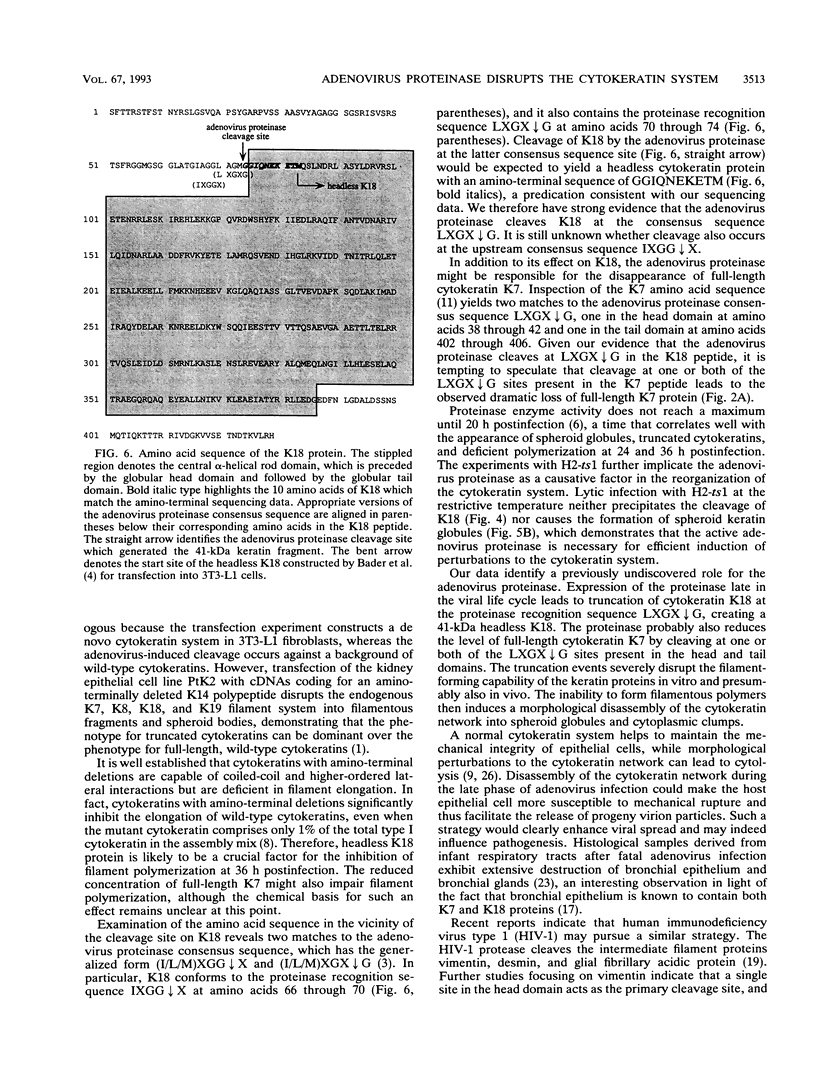
Immunofluorescence studies revealed that adenovirus induces a reorganization of the cytokeratin system in lytically infected HeLa cells. At 24 h postinfection, the cytokeratin network began to disassemble into prominent spheroid globules. By 36 h postinfection, host cell lysis occurred, accompanied by the formation of perinuclear cytokeratin clumps and additional spheroid globules. Immunoblots detected 41- and 44-kDa fragments of cytokeratin 18 and reduced levels of cytokeratin 7 at 24 and 36 h postinfection. Cytokeratin proteins isolated from HeLa cells at 36 h postinfection were deficient in filament polymerization. The 41-kDa proteolytic cytokeratin 18-specific fragment was purified, and its amino-terminal sequence was determined to be GGIQNEKETM. These residues correspond to amino acids 74 through 83 of cytokeratin 18, identifying a cleavage site at the junction of the globular head domain and the alpha-helical rod domain. Moreover, this truncation event occurs at a consensus cleavage site for the adenovirus L3 23-kDa proteinase. The temperature-sensitive mutant H2-ts1, which contains a mutation in the proteinase, neither induced cleavage of cytokeratin 18 nor precipitated the formation of spheroid globules during lytic infection at the nonpermissive temperature. The active proteinase is therefore required for cleavage of cytokeratin 18 and morphological rearrangement of the cytokeratins. We suggest that disruptions in the cytokeratin system weaken the mechanical integrity of the cell, thus promoting host cell lysis and release of progeny virions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albers K., Fuchs E. Expression of mutant keratin cDNAs in epithelial cells reveals possible mechanisms for initiation and assembly of intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W. The proteinase polypeptide of adenovirus serotype 2 virions. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):259–272. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90479-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader B. L., Magin T. M., Freudenmann M., Stumpp S., Franke W. W. Intermediate filaments formed de novo from tail-less cytokeratins in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(5):1293–1307. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.5.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin M. T., Boulanger P. Processing of vimentin occurs during the early stages of adenovirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2559–2566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2559-2566.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhatti A. R., Weber J. Protease of adenovirus type 2: partial characterization. Virology. 1979 Jul 30;96(2):478–485. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capco D. G., Wan K. M., Penman S. The nuclear matrix: three-dimensional architecture and protein composition. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):847–858. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90446-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe P. A., Chan Y. M., Albers K., Fuchs E. Deletions in epidermal keratins leading to alterations in filament organization in vivo and in intermediate filament assembly in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 2):3049–3064. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.3049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombe P. A., Hutton M. E., Vassar R., Fuchs E. A function for keratins and a common thread among different types of epidermolysis bullosa simplex diseases. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1661–1674. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defer C., Belin M. T., Caillet-Boudin M. L., Boulanger P. Human adenovirus-host cell interactions: comparative study with members of subgroups B and C. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3661–3673. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3661-3673.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey E. G., Wan K. M., Penman S. Epithelial cytoskeletal framework and nuclear matrix-intermediate filament scaffold: three-dimensional organization and protein composition. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):1973–1984. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigi O., Geiger B., Eshhar Z., Moll R., Schmid E., Winter S., Schiller D. L., Franke W. W. Detection of a cytokeratin determinant common to diverse epithelial cells by a broadly cross-reacting monoclonal antibody. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1429–1437. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01334.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Benveniste R. E., Sowder R., Copeland T. D., Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. Molecular characterization of gag proteins from simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVMne). J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2587–2595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2587-2595.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. Isolation of adenovirus type 5 host range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):683–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90275-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Sarnow P., Duprey E., Levine A. J. Monoclonal antibodies which recognize native and denatured forms of the adenovirus DNA-binding protein. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):480–484. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90274-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoeman R. L., Höner B., Stoller T. J., Kesselmeier C., Miedel M. C., Traub P., Graves M. C. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease cleaves the intermediate filament proteins vimentin, desmin, and glial fibrillary acidic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6336–6340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoeman R. L., Mothes E., Höner B., Kesselmeier C., Traub P. Effect of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease on the intermediate filament subunit protein vimentin: cleavage, in vitro assembly and altered distribution of filaments in vivo following microinjection of protease. Acta Histochem Suppl. 1991;41:129–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoeman R. L., Mothes E., Kesselmeier C., Traub P. Intermediate filament assembly and stability in vitro: effect and implications of the removal of head and tail domains of vimentin by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1990 Jul;14(7):583–594. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(90)90038-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staufenbiel M., Epple P., Deppert W. Progressive reorganization of the host cell cytoskeleton during adenovirus infection. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1186–1191. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1186-1191.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tölle H. G., Weber K., Osborn M. Keratin filament disruption in interphase and mitotic cells--how is it induced? Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;43(1):35–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassar R., Coulombe P. A., Degenstein L., Albers K., Fuchs E. Mutant keratin expression in transgenic mice causes marked abnormalities resembling a human genetic skin disease. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):365–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90645-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R. Role of adenovirus E1B proteins in transformation: altered organization of intermediate filaments in transformed cells that express the 19-kilodalton protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):120–130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E., Cipriani R. Specific disruption of intermediate filaments and the nuclear lamina by the 19-kDa product of the adenovirus E1B oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9886–9890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh-Kai L., Akusjärvi G., Aleström P., Pettersson U., Tremblay M., Weber J. Genetic identification of an endoproteinase encoded by the adenovirus genome. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 15;167(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zantema A., Fransen J. A., Davis-Olivier A., Ramaekers F. C., Vooijs G. P., DeLeys B., Van der Eb A. J. Localization of the E1B proteins of adenovirus 5 in transformed cells, as revealed by interaction with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1985 Apr 15;142(1):44–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90421-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhai Z. H., Wang X., Qian X. Y. Nuclear matrix-intermediate filament system and its alteration in adenovirus infected HeLa cell. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1988 Feb;12(2):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(88)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]