Abstract
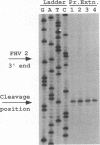
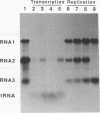
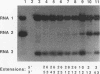
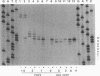
To examine the cis-acting requirements for RNA replication, a cDNA clone of flock house virus (FHV) RNA 2 was transfected into baby hamster kidney cells and transcribed to yield RNAs that had terminal extensions of different lengths or that lacked internal regions of the molecule. These RNAs were tested for their ability to be replicated by FHV replicase that was provided by cotransfection of purified FHV RNA 1. The results showed that RNA replication was inhibited by terminal extensions, particularly those at the 5' end of the RNA, despite the fact that these extensions were corrected during RNA replication. A negative-sense transcript with a 12-nucleotide 3' extension was replicated to produce a positive-sense RNA that had the correct 5' end, showing that the replicase could select its correct initiation site from within a longer template. A uridine residue at the second position of the positive strand was an important determinant of template activity. RNA molecules with large internal deletions that amounted to almost 50% of the 1,400 nucleotides of RNA 2 replicated as efficiently as full-length molecules, but only if they contained an internal region that lay between nucleotides 538 and 616. Thirty-six spontaneous deletions of RNA 2 that arose during sequential replicative passages all conserved the same internal region of the molecule. These results establish that both terminal and internal regions of FHV RNA 2 play essential roles in making the molecule a competent template for replication.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ball L. A., Amann J. M., Garrett B. K. Replication of nodamura virus after transfection of viral RNA into mammalian cells in culture. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2326–2334. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2326-2334.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball L. A. Cellular expression of a functional nodavirus RNA replicon from vaccinia virus vectors. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2335–2345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2335-2345.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruening G. Compilation of self-cleaving sequences from plant virus satellite RNAs and other sources. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:546–558. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buzayan J. M., Gerlach W. L., Bruening G. Satellite tobacco ringspot virus RNA: A subset of the RNA sequence is sufficient for autolytic processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8859–8862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta R., Sgro J. Y. Nucleotide sequences of three Nodavirus RNA2's: the messengers for their coat protein precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7525–7526. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasmahapatra B., Dasgupta R., Ghosh A., Kaesberg P. Structure of the black beetle virus genome and its functional implications. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90337-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasmahapatra B., Dasgupta R., Saunders K., Selling B., Gallagher T., Kaesberg P. Infectious RNA derived by transcription from cloned cDNA copies of the genomic RNA of an insect virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):63–66. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Moss B. Structure of vaccinia virus early promoters. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 20;210(4):749–769. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Earl P. L., Moss B. Use of a hybrid vaccinia virus-T7 RNA polymerase system for expression of target genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2538–2544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. M., Friesen P. D., Rueckert R. R. Autonomous replication and expression of RNA 1 from black beetle virus. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):481–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.481-489.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. M., Rueckert R. R. Assembly-dependent maturation cleavage in provirions of a small icosahedral insect ribovirus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3399–3406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3399-3406.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haltiner M., Kempe T., Tjian R. A novel strategy for constructing clustered point mutations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):1015–1025. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaesberg P., Dasgupta R., Sgro J. Y., Wery J. P., Selling B. H., Hosur M. V., Johnson J. E. Structural homology among four nodaviruses as deduced by sequencing and X-ray crystallography. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 20;214(2):423–435. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90191-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr S. M., Johnston L. H., Odell M., Duncan S. A., Law K. M., Smith G. L. Vaccinia DNA ligase complements Saccharomyces cerevisiae cdc9, localizes in cytoplasmic factories and affects virulence and virus sensitivity to DNA damaging agents. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4343–4350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling M. L., Risman S. S., Klement J. F., McGraw N., McAllister W. T. Abortive initiation by bacteriophage T3 and T7 RNA polymerases under conditions of limiting substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1605–1618. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattnaik A. K., Ball L. A., LeGrone A. W., Wertz G. W. Infectious defective interfering particles of VSV from transcripts of a cDNA clone. Cell. 1992 Jun 12;69(6):1011–1020. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90619-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrotta A. T., Been M. D. A pseudoknot-like structure required for efficient self-cleavage of hepatitis delta virus RNA. Nature. 1991 Apr 4;350(6317):434–436. doi: 10.1038/350434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scotti P. D., Dearing S., Mossop D. W. Flock House virus: a nodavirus isolated from Costelytra zealandica (White) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Arch Virol. 1983;75(3):181–189. doi: 10.1007/BF01315272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selling B. H., Allison R. F., Kaesberg P. Genomic RNA of an insect virus directs synthesis of infectious virions in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):434–438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selling B. H., Rueckert R. R. Plaque assay for black beetle virus. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):251–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.251-253.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong W., Dasgupta R., Rueckert R. Evidence that the packaging signal for nodaviral RNA2 is a bulged stem-loop. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11146–11150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]