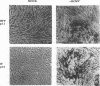
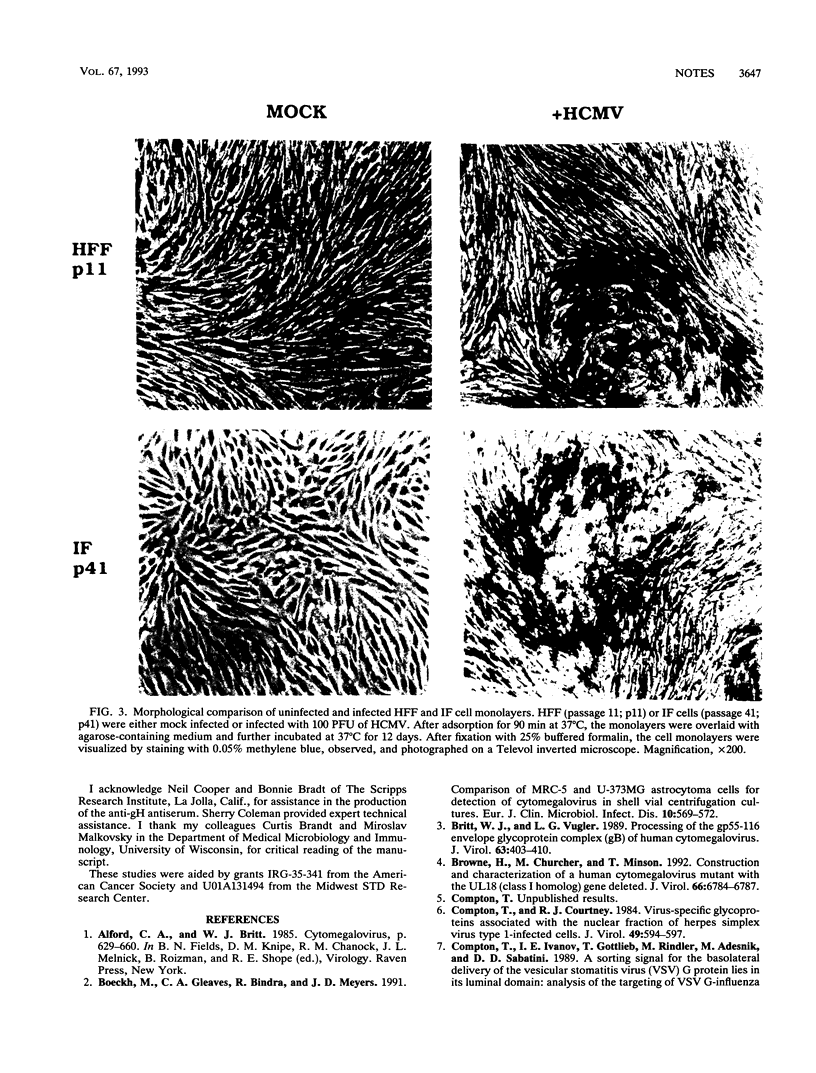
Abstract
Human foreskin fibroblasts (HFF) were immortalized via retrovirus-mediated gene transfer of the E6 and E7 genes of human papillomavirus type 16. An immortalized fibroblast (IF) cell line which was morphologically akin to the parental cell line was isolated. The IF cell line was evaluated for permissiveness to human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection after the IF cell line surpassed the normal passage limitation of diploid fibroblasts. Western immunoblot analysis of representative HCMV-encoded immediate-early (72-kDa), early (gB), and late (gH) gene products demonstrated that the IF cell line produced these proteins analogous to those produced by the parental HFF cells. Similar quantities of infectious virus were produced in the IF and HFF cell lines as determined in one-step growth curve experiments. Compared with the HFF cells, morphologically identical plaques were produced in the IF cell line in approximately 10 to 12 days postinfection. These findings indicate that fibroblast cell lines immortalized with transforming genes of human papillomavirus retain complete permissiveness to HCMV infection and support plaque formation. The IF cell line will be useful for future genetic analysis of HCMV.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeckh M., Gleaves C. A., Bindra R., Meyers J. D. Comparison of MRC-5 and U-373MG astrocytoma cells for detection of cytomegalovirus in shell vial centrifugation cultures. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;10(7):569–572. doi: 10.1007/BF01967276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britt W. J., Vugler L. G. Processing of the gp55-116 envelope glycoprotein complex (gB) of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):403–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.403-410.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browne H., Churcher M., Minson T. Construction and characterization of a human cytomegalovirus mutant with the UL18 (class I homolog) gene deleted. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6784–6787. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6784-6787.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton T., Courtney R. J. Virus-specific glycoproteins associated with the nuclear fraction of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):594–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.594-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton T., Nepomuceno R. R., Nowlin D. M. Human cytomegalovirus penetrates host cells by pH-independent fusion at the cell surface. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):387–395. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranage M. P., Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S., Weston K., Tomlinson P., Barrell B., Hart H., Bell S. E., Minson A. C. Identification of the human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein B gene and induction of neutralizing antibodies via its expression in recombinant vaccinia virus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3057–3063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cranage M. P., Smith G. L., Bell S. E., Hart H., Brown C., Bankier A. T., Tomlinson P., Barrell B. G., Minson T. C. Identification and expression of a human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein with homology to the Epstein-Barr virus BXLF2 product, varicella-zoster virus gpIII, and herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein H. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1416–1422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1416-1422.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gretch D. R., Gehrz R. C., Stinski M. F. Characterization of a human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein complex (gcI). J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gretch D. R., Kari B., Rasmussen L., Gehrz R. C., Stinski M. F. Identification and characterization of three distinct families of glycoprotein complexes in the envelopes of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):875–881. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.875-881.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert C. L., Demers G. W., Galloway D. A. The E7 gene of human papillomavirus type 16 is sufficient for immortalization of human epithelial cells. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):473–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.473-478.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho D. D., Rota T. R., Andrews C. A., Hirsch M. S. Replication of human cytomegalovirus in endothelial cells. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):956–957. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutter J. A., Scott J., Wreghitt T., Higenbottam T., Wallwork J. The importance of cytomegalovirus in heart-lung transplant recipients. Chest. 1989 Mar;95(3):627–631. doi: 10.1378/chest.95.3.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibanez C. E., Schrier R., Ghazal P., Wiley C., Nelson J. A. Human cytomegalovirus productively infects primary differentiated macrophages. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6581–6588. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6581-6588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. A., Mills J. Serious cytomegalovirus disease in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Clinical findings, diagnosis, and treatment. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Apr;108(4):585–594. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-108-4-585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Muzithras V. P. A cluster of dispensable genes within the human cytomegalovirus genome short component: IRS1, US1 through US5, and the US6 family. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2541–2546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2541-2546.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Muzithras V. P., Gluzman Y. Replacement mutagenesis of the human cytomegalovirus genome: US10 and US11 gene products are nonessential. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5860–5872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5860-5872.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kari B., Liu Y. N., Goertz R., Lussenhop N., Stinski M. F., Gehrz R. Structure and composition of a family of human cytomegalovirus glycoprotein complexes designated gC-I (gB). J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2673–2680. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kari B., Radeke R., Gehrz R. Processing of human cytomegalovirus envelope glycoproteins in and egress of cytomegalovirus from human astrocytoma cells. J Gen Virol. 1992 Feb;73(Pt 2):253–260. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Browne H., Stoffel M., Minson T. The UL16 gene of human cytomegalovirus encodes a glycoprotein that is dispensable for growth in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6609–6615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6609-6615.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R., Hayward G. S. Constitutive and retinoic acid-inducible expression of cytomegalovirus immediate-early genes in human teratocarcinoma cells. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):434–440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.434-440.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathey J. L., Wiley C. A., Verity M. A., Nelson J. A. Cultured human brain capillary endothelial cells are permissive for infection by human cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):266–273. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90252-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers J. D., Flournoy N., Thomas E. D. Risk factors for cytomegalovirus infection after human marrow transplantation. J Infect Dis. 1986 Mar;153(3):478–488. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowlin D. M., Cooper N. R., Compton T. Expression of a human cytomegalovirus receptor correlates with infectibility of cells. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3114–3121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3114-3121.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland S. D., Costello P., Dekaban G. A., Rice G. P. Cytomegalovirus in the brain: in vitro infection of human brain-derived cells. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1252–1262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N., Dummer J. S., Kusne S., Breinig M. K., Armstrong J. A., Makowka L., Starzl T. E., Ho M. Infections with cytomegalovirus and other herpesviruses in 121 liver transplant recipients: transmission by donated organ and the effect of OKT3 antibodies. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;158(1):124–131. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smiley M. L., Mar E. C., Huang E. S. Cytomegalovirus infection and viral-induced transformation of human endothelial cells. J Med Virol. 1988 Jun;25(2):213–226. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890250212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Insertion and deletion mutagenesis of the human cytomegalovirus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7213–7217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Span A. H., Mullers W., Miltenburg A. M., Bruggeman C. A. Cytomegalovirus induced PMN adherence in relation to an ELAM-1 antigen present on infected endothelial cell monolayers. Immunology. 1991 Mar;72(3):355–360. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
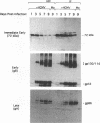
- Spector D. H., Klucher K. M., Rabert D. K., Wright D. A. Human cytomegalovirus early gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:21–45. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Depto A. S., Fortney J., Nelson J. A. Regulated expression of early and late RNAs and proteins from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2699–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2699-2708.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takekoshi M., Maeda-Takekoshi F., Ihara S., Sakuma S., Watanabe Y. Site-specific stable insertion into the human cytomegalovirus genome of a foreign gene under control of the SV40 promoter. Gene. 1991 May 30;101(2):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman W. J., Roberts W. H., Davis D. H., Williams M. V., Sedmak D. D., Stephens R. E. Preservation of natural endothelial cytopathogenicity of cytomegalovirus by propagation in endothelial cells. Arch Virol. 1991;117(3-4):143–164. doi: 10.1007/BF01310761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshenker B. G., Wilton S., Rice G. P. Phorbol ester-induced differentiation permits productive human cytomegalovirus infection in a monocytic cell line. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1625–1631. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]