Abstract
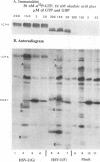
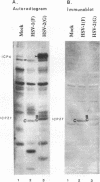
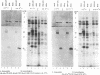
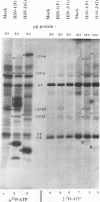
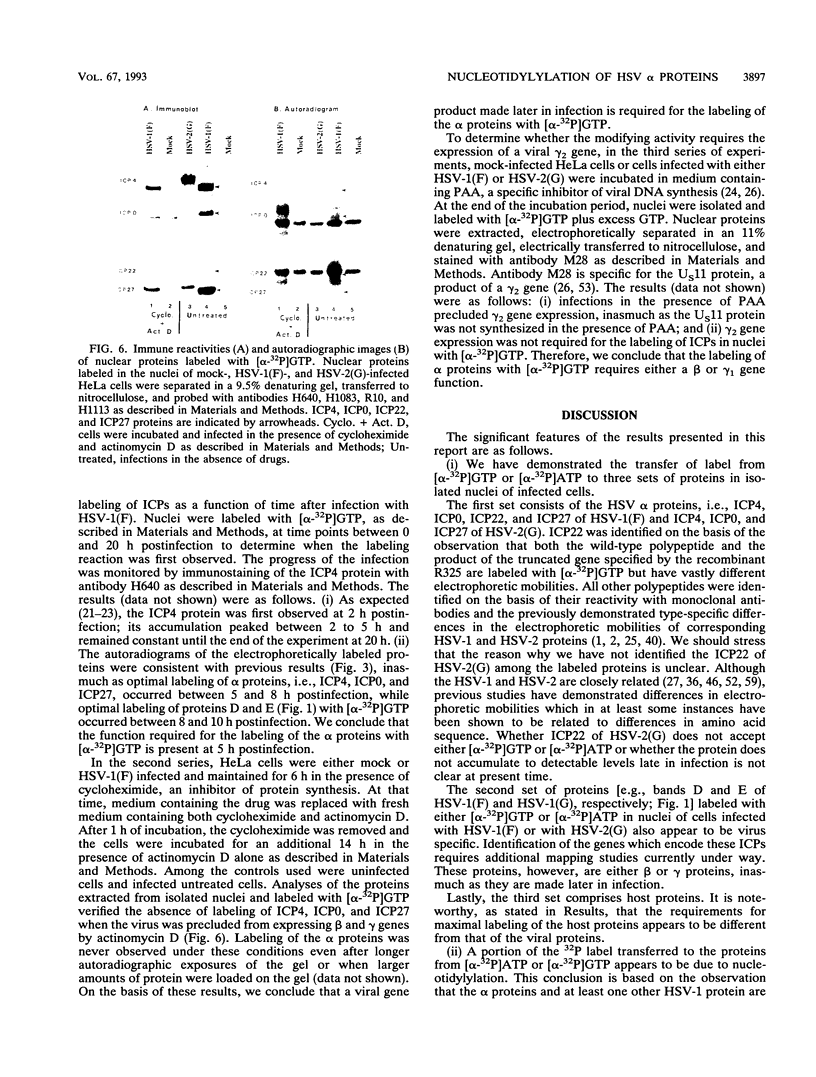
Herpes simplex virus genes form several groups whose expression is coordinately regulated and sequentially ordered in a cascade fashion. Most of the products of the first group, the alpha genes, appear to have regulatory functions. We report that the alpha proteins, infected cell proteins 4, 0, 22, and 27 of herpes simplex virus 1 and 4, 0, and 27 of herpes simplex virus 2, were labeled in the isolated nuclei of infected HeLa cells with [alpha-32P]GTP or [alpha-32P]ATP late in infection and that these proteins represent the largest group of virus-specific proteins labeled in this fashion. Studies with [2-3H]ATP, in which the label is in the purine ring, showed that a portion of the label in alpha proteins and in at least one other infected cell protein is due to nucleotidylylation. Analyses of the labeling reactions in nuclei of (i) cells infected with temperature-sensitive mutants at nonpermissive temperatures, (ii) cells infected with wild-type virus and harvested at different times postinfection, and (iii) cells treated with inhibitors of protein synthesis or of synthesis of viral DNA led to the conclusion that viral gene functions expressed after the synthesis of alpha proteins are required for the labeling of the alpha proteins with [alpha-32P]GTP. We conclude that several of the alpha proteins are extensively posttranslationally modified and that these modifications include nucleotidylylation.
Full text
PDF

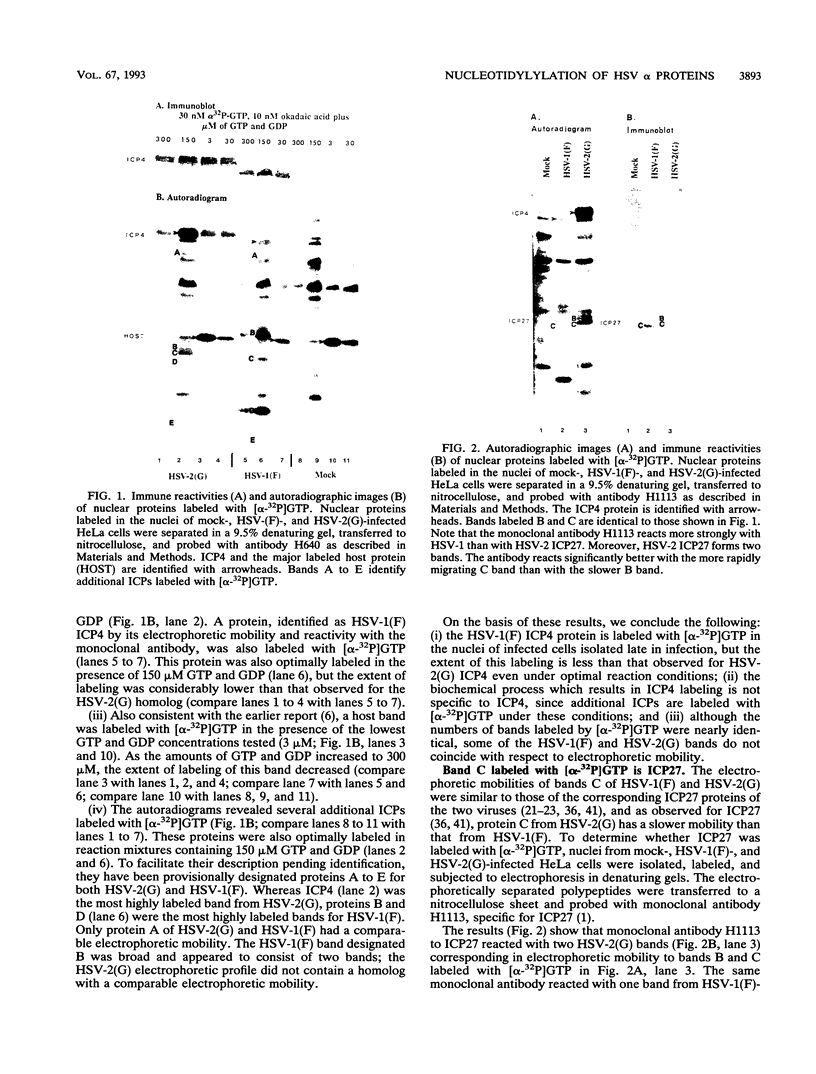

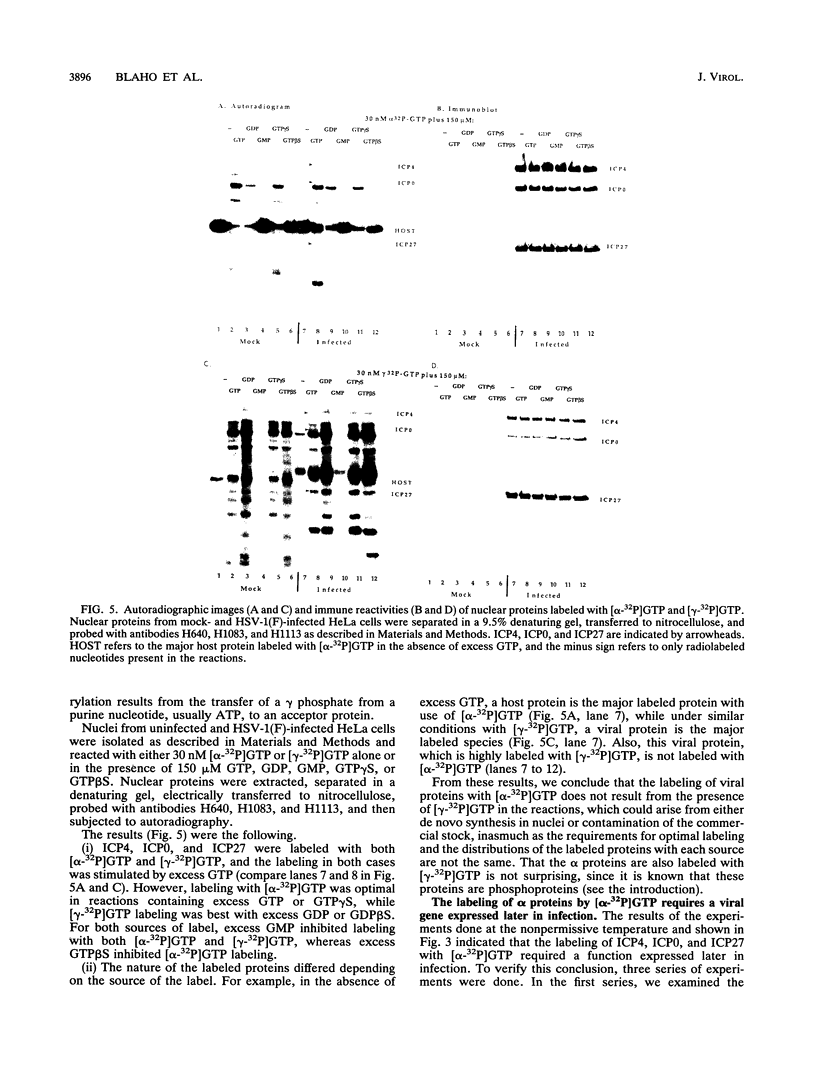



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Braun D. K., Pereira L., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha proteins 0, 4, and 27 with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):108–118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.108-118.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann M., Sarmiento M., Roizman B. Application of antibody to synthetic peptides for characterization of the intact and truncated alpha 22 protein specified by herpes simplex virus 1 and the R325 alpha 22- deletion mutant. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):207–215. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.207-215.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Faber S., Wilcox K. W., Pizer L. I. Herpes simplex virus immediate early infected-cell polypeptide 4 binds to DNA and promotes transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4016–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaho J. A., Michael N., Kang V., Aboul-Ela N., Smulson M. E., Jacobson M. K., Roizman B. Differences in the poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation patterns of ICP4, the herpes simplex virus major regulatory protein, in infected cells and in isolated nuclei. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6398–6407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6398-6407.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaho J. A., Roizman B. ICP4, the major regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus, shares features common to GTP-binding proteins and is adenylated and guanylated. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3759–3769. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3759-3769.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll D., Santoro N., Marshak D. R. Regulating cell growth: casein-kinase-II-dependent phosphorylation of nuclear oncoproteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):91–95. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo F., Campadelli-Fiume G., Foa-Tomasi L., Cassai E. Evidence that herpes simplex virus DNA is transcribed by cellular RNA polymerase B. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):996–1001. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.996-1001.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activation of immediate-early, early, and late promoters by temperature-sensitive and wild-type forms of herpes simplex virus type 1 protein ICP4. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1997–2008. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber S. W., Wilcox K. W. Association of herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 with sequences spanning the ICP4 gene transcription initiation site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):555–570. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber S. W., Wilcox K. W. Association of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 with specific nucleotide sequences in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6067–6083. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber S. W., Wilcox K. W. Characterization of a herpes simplex virus regulatory protein: aggregation and phosphorylation of a temperature-sensitive variant of ICP 4. Arch Virol. 1986;91(3-4):297–312. doi: 10.1007/BF01314289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firzlaff J. M., Galloway D. A., Eisenman R. N., Lüscher B. The E7 protein of human papillomavirus type 16 is phosphorylated by casein kinase II. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):44–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Co-ordinate regulation of herpes simplex virus gene expression is mediated by the functional interaction of two immediate early gene products. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):395–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90135-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelman I. H., Silverstein S. Identification of immediate early genes from herpes simplex virus that transactivate the virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5265–5269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilz H., Fanick W., Klapproth K. 2'-Phosphoadenylylation of eukaryotic proteins: a type of covalent modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6267–6271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. XI. Identification and relative molar rates of synthesis of structural and nonstructural herpes virus polypeptides in the infected cell. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1347–1365. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1347-1365.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Herpes simplex virus resistance and sensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):584–600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.584-600.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
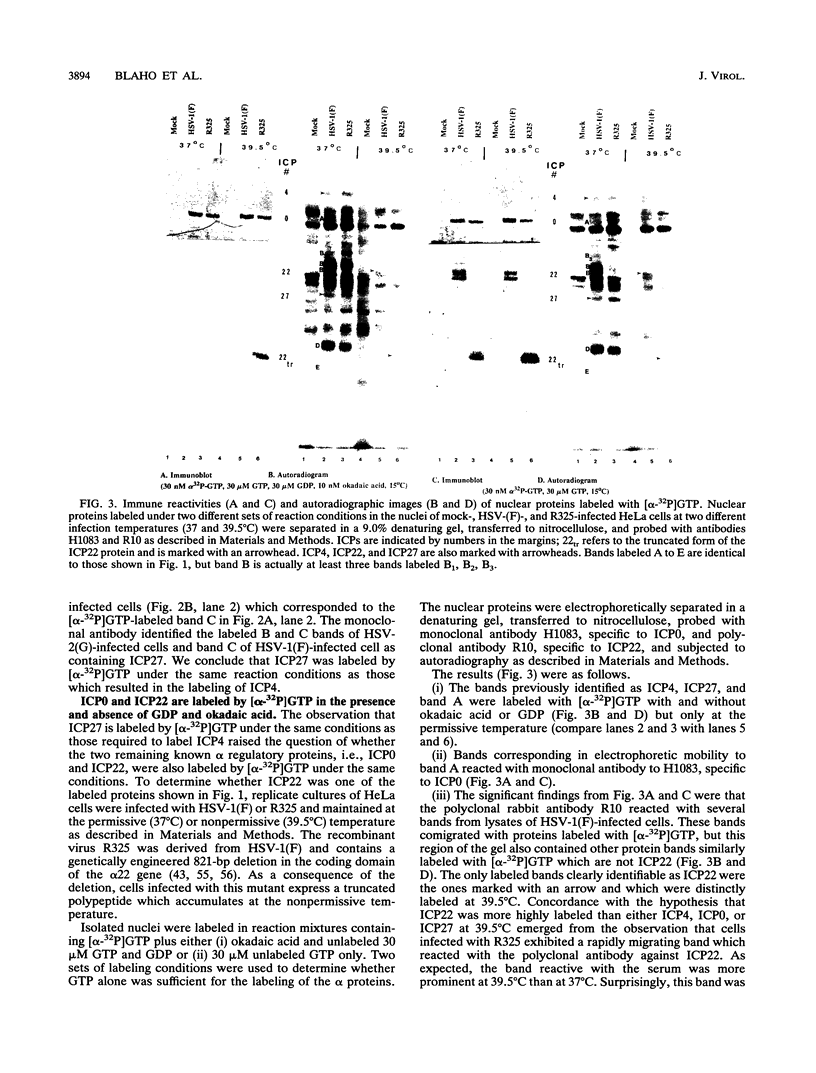
- Hubenthal-Voss J., Houghten R. A., Pereira L., Roizman B. Mapping of functional and antigenic domains of the alpha 4 protein of herpes simplex virus 1. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):454–462. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.454-462.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., MacLean C., Marsden H. S., Dalziel R. G., Everett R. D. The product of gene US11 of herpes simplex virus type 1 is expressed as a true late gene. J Gen Virol. 1986 May;67(Pt 5):871–883. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-5-871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieff E. D., Bachenheimer S. L., Roizman B. Size, composition, and structure of the deoxyribonucleic acid of herpes simplex virus subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):125–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.125-132.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Ruyechan W. T., Roizman B., Halliburton I. W. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus: demonstration of regions of obligatory and nonobligatory identity within diploid regions of the genome by sequence replacement and insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Maridor G., Nigg E. A. Casein kinase II is a predominantly nuclear enzyme. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):43–55. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. DNA-binding site of major regulatory protein alpha 4 specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Frost J., Deng T., Smeal T., al-Alawi N., Kikkawa U., Hunter T., Brenner D., Karin M. Casein kinase II is a negative regulator of c-Jun DNA binding and AP-1 activity. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90311-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: temporal order of transcription of alpha genes is not dependent on the stringency of inhibition of protein synthesis. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):319–322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.319-322.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy A. M., McMahan L., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 deletion mutants exhibit altered patterns of transcription and are DNA deficient. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):18–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.18-27.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahan L., Schaffer P. A. The repressing and enhancing functions of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP27 map to C-terminal regions and are required to modulate viral gene expression very early in infection. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3471–3485. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3471-3485.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael N., Spector D., Mavromara-Nazos P., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. The DNA-binding properties of the major regulatory protein alpha 4 of herpes simplex viruses. Science. 1988 Mar 25;239(4847):1531–1534. doi: 10.1126/science.2832940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Comparison of upstream sequence requirements for positive and negative regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene by three virus-encoded trans-acting factors. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.190-199.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfreyman J. W., Maclean J. B., Messeder E., Sheppard R. C. Successful use of oligopeptides as immunogens in the preparation of antisera to immediate-early gene products of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1984 May;65(Pt 5):865–874. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-5-865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Wolff M. H., Fenwick M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. V. Properties of alpha polypeptides made in HSV-1 and HSV-2 infected cells. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):733–749. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90495-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Roizman B. A generalized technique for deletion of specific genes in large genomes: alpha gene 22 of herpes simplex virus 1 is not essential for growth. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Abnormal properties of an immediate early polypeptide in cells infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):357–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.357-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Notarianni E. L. Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early polypeptide. Virology. 1983 Dec;131(2):492–501. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90515-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Davison A. J., Marsden H. S., Timbury M. C., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Recombinants between herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2: analyses of genome structures and expression of immediate early polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):499–517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.499-517.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purves F. C., Roizman B. The UL13 gene of herpes simplex virus 1 encodes the functions for posttranslational processing associated with phosphorylation of the regulatory protein alpha 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7310–7314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Knipe D. M. Stimulation of expression of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein by two viral functions. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):957–963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Knipe D. M. Gene-specific transactivation by herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3814–3823. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3814-3823.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice S. A., Su L. S., Knipe D. M. Herpes simplex virus alpha protein ICP27 possesses separable positive and negative regulatory activities. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3399–3407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3399-3407.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roller R. J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 RNA binding protein US11 is a virion component and associates with ribosomal 60S subunits. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3624–3632. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3624-3632.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Schaffer P. A. Deletion mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate-early protein ICP0 exhibit impaired growth in cell culture. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):829–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.829-839.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salas M. Protein-priming of DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:39–71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears A. E., Halliburton I. W., Meignier B., Silver S., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus 1 mutant deleted in the alpha 22 gene: growth and gene expression in permissive and restrictive cells and establishment of latency in mice. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):338–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.338-346.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekulovich R. E., Leary K., Sandri-Goldin R. M. The herpes simplex virus type 1 alpha protein ICP27 can act as a trans-repressor or a trans-activator in combination with ICP4 and ICP0. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4510–4522. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4510-4522.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shatkin A. J. mRNA cap binding proteins: essential factors for initiating translation. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):223–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Schaffer P. A. Intertypic recombinants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 infected-cell polypeptide 4. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):176–182. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90058-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. L., Hardwicke M. A., Sandri-Goldin R. M. Evidence that the herpes simplex virus immediate early protein ICP27 acts post-transcriptionally during infection to regulate gene expression. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):74–86. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90062-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R. Discovery of glutamine synthetase cascade. Methods Enzymol. 1990;182:793–809. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)82062-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L., Knipe D. M. Herpes simplex virus alpha protein ICP27 can inhibit or augment viral gene transactivation. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):496–504. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90441-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. H., Seeger C. The reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B virus acts as a protein primer for viral DNA synthesis. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):663–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90599-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox K. W., Kohn A., Sklyanskaya E., Roizman B. Herpes simplex virus phosphoproteins. I. Phosphate cycles on and off some viral polypeptides and can alter their affinity for DNA. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):167–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.167-182.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E. Genome-linked proteins of viruses. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):199–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90335-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]