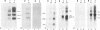Abstract
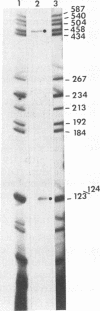
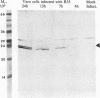
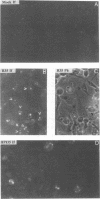
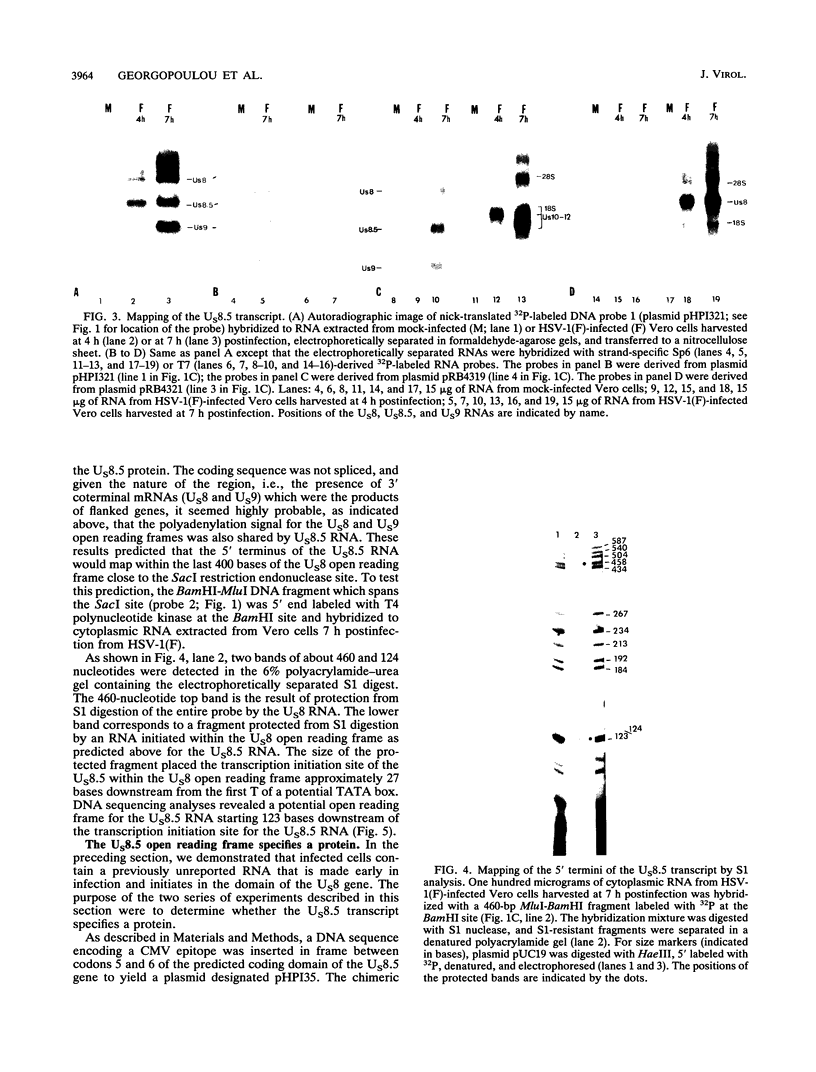
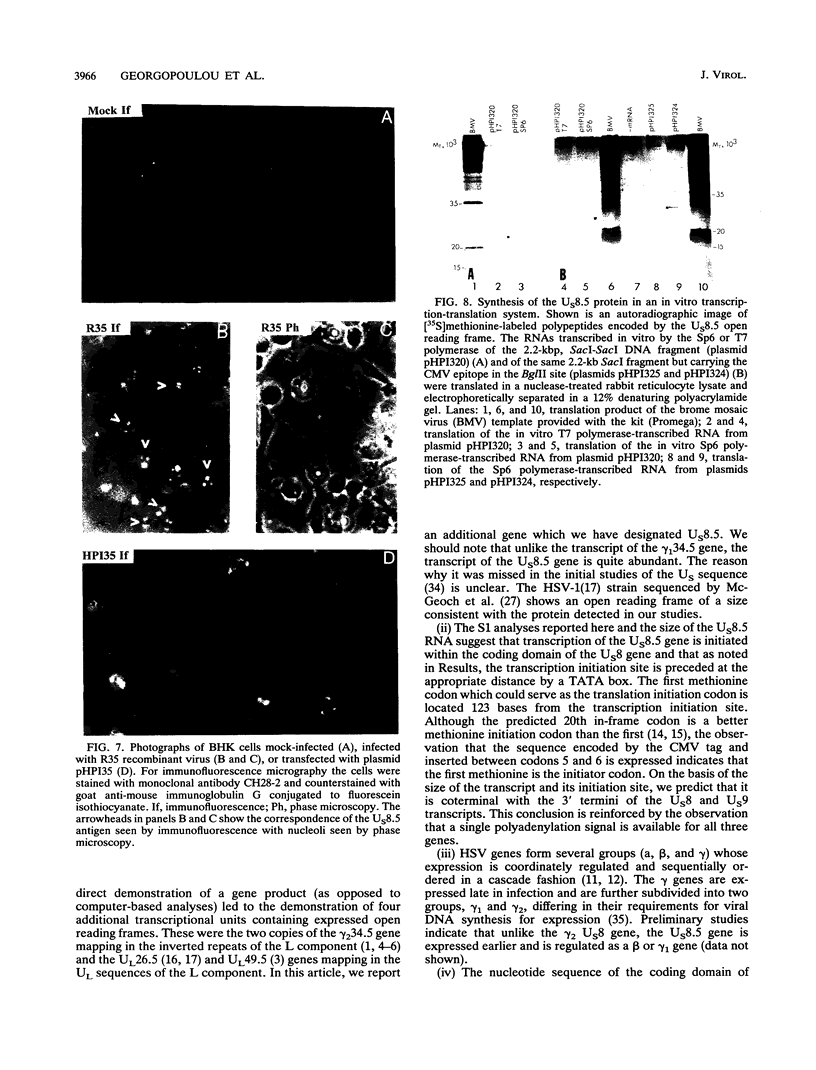
The herpes simplex virus genome 1 consists of two unique stretches, long (UL) and short (U(S)), each flanked by inverted repeat sequences. The U(S) sequence has been previously reported to contain 12 open reading frames designated U(S)1 through U(S)12. This report demonstrates the existence of a 13th open reading frame within the U(S) sequence, designated U(S)8.5. The U(S)8.5 sequence is located between, and overlaps in part with, the domains of the U(S)8 and U(S)9 genes. Its transcription is initiated within the coding sequence of U(S)8, and its transcript decays earlier than that of U(S)8. On the basis of the size of its RNA (1.2 kb) and map position, it is likely that the U(S)8.5 transcript is 3' coterminal with the U(S)8 and U(S)9 mRNAs at the single polyadenylation signal which serves these genes. The nucleotide sequence of the U(S)8.5 open reading frame predicts that its product is a 151-amino-acid basic, hydrophilic polypeptide. To determine whether the U(S)8.5 encodes a protein, a sequence encoding 23 amino acids that contains an epitope reacting with a known monoclonal antibody to human cytomegalovirus protein was inserted in frame after the predicted fifth codon of the U(S)8.5 gene. The recombinant virus carrying this epitope induced the synthesis of a protein reactive with the monoclonal antibody in immunoblots. The tagged protein localized in nucleoli of cells infected with the recombinant virus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Chou J., Sarmiento M., Lerner R. A., Roizman B. Identification by antibody to a synthetic peptide of a protein specified by a diploid gene located in the terminal repeats of the L component of herpes simplex virus genome. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):843–850. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.843-850.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsenakis M., Hubenthal-Voss J., Campadelli-Fiume G., Pereira L., Roizman B. Construction and properties of a cell line constitutively expressing the herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B dependent on functional alpha 4 protein synthesis. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.674-682.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D. E., Roizman B. The unique sequence of the herpes simplex virus 1 L component contains an additional translated open reading frame designated UL49.5. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):562–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.562-566.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Kern E. R., Whitley R. J., Roizman B. Mapping of herpes simplex virus-1 neurovirulence to gamma 134.5, a gene nonessential for growth in culture. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1262–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.2173860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 gene for ICP34.5, which maps in inverted repeats, is conserved in several limited-passage isolates but not in strain 17syn+. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1014–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1014-1020.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The terminal a sequence of the herpes simplex virus genome contains the promoter of a gene located in the repeat sequences of the L component. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):629–637. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.629-637.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ejercito P. M., Kieff E. D., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus strains differing in their effects on social behaviour of infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1968 May;2(3):357–364. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-2-3-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. 8. Characterization and composition of multiple capsid forms of subtypes 1 and 2. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):1044–1052. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.1044-1052.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W., Roizman B. Proteins specified by herpes simplex virus. Staining and radiolabeling properties of B capsid and virion proteins in polyacrylamide gels. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):155–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.155-165.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Jacob R. J., Wadsworth S. C., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA: evidence for four populations of molecules that differ in the relative orientations of their long and short components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins F. J., Howett M. K. Characterization of mRNAs that map in the BglII N fragment of the herpes simplex virus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.99-107.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 gene encoding a protease also contains within its coding domain the gene encoding the more abundant substrate. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5149–5156. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5149-5156.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. Y., Roizman B. The promoter, transcriptional unit, and coding sequence of herpes simplex virus 1 family 35 proteins are contained within and in frame with the UL26 open reading frame. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):206–212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.206-212.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Chatterjee S., Whitley R. J., Roizman B. Identification of a herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein gene within a gene cluster dispensable for growth in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4303–4307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Clustering of genes dispensable for growth in culture in the S component of the HSV-1 genome. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):573–576. doi: 10.1126/science.3033823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Generation of an inverting herpes simplex virus 1 mutant lacking the L-S junction a sequences, an origin of DNA synthesis, and several genes including those specifying glycoprotein E and the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.583-591.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matz B., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Preston V. G. Physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutations of herpes simplex virus type 1 using cloned restriction endonuclease fragments. J Gen Virol. 1983 Oct;64(Pt 10):2261–2270. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-10-2261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Rixon F. J. Sequence determination and genetic content of the short unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90320-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meignier B., Longnecker R., Mavromara-Nazos P., Sears A. E., Roizman B. Virulence of and establishment of latency by genetically engineered deletion mutants of herpes simplex virus 1. Virology. 1988 Jan;162(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90417-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse L. S., Pereira L., Roizman B., Schaffer P. A. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus (HSV) DNA. X. Mapping of viral genes by analysis of polypeptides and functions specified by HSV-1 X HSV-2 recombinants. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):389–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.389-410.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Conley A. J., Mocarski E. S., Roizman B. Cloning of reiterated and nonreiterated herpes simplex virus 1 sequences as BamHI fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4201–4205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Roizman B. A generalized technique for deletion of specific genes in large genomes: alpha gene 22 of herpes simplex virus 1 is not essential for growth. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90247-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Davison A. J., Marsden H. S., Timbury M. C., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Recombinants between herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2: analyses of genome structures and expression of immediate early polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):499–517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.499-517.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., McGeoch D. J. A 3' co-terminal family of mRNAs from the herpes simplex virus type 1 short region: two overlapping reading frames encode unrelated polypeptide one of which has highly reiterated amino acid sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 12;12(5):2473–2487. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.5.2473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rixon F. J., McGeoch D. J. Detailed analysis of the mRNAs mapping in the short unique region of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):953–973. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roller R. J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus 1 RNA binding protein US11 is a virion component and associates with ribosomal 60S subunits. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3624–3632. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3624-3632.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roller R. J., Roizman B. The herpes simplex virus Us11 open reading frame encodes a sequence-specific RNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3463–3470. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3463-3470.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick P., Berthelot N. Inverted repetitions in the chromosome of herpes simplex virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):667–678. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Roizman B. gamma 2-Thymidine kinase chimeras are identically transcribed but regulated a gamma 2 genes in herpes simplex virus genomes and as beta genes in cell genomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):518–528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]