Abstract
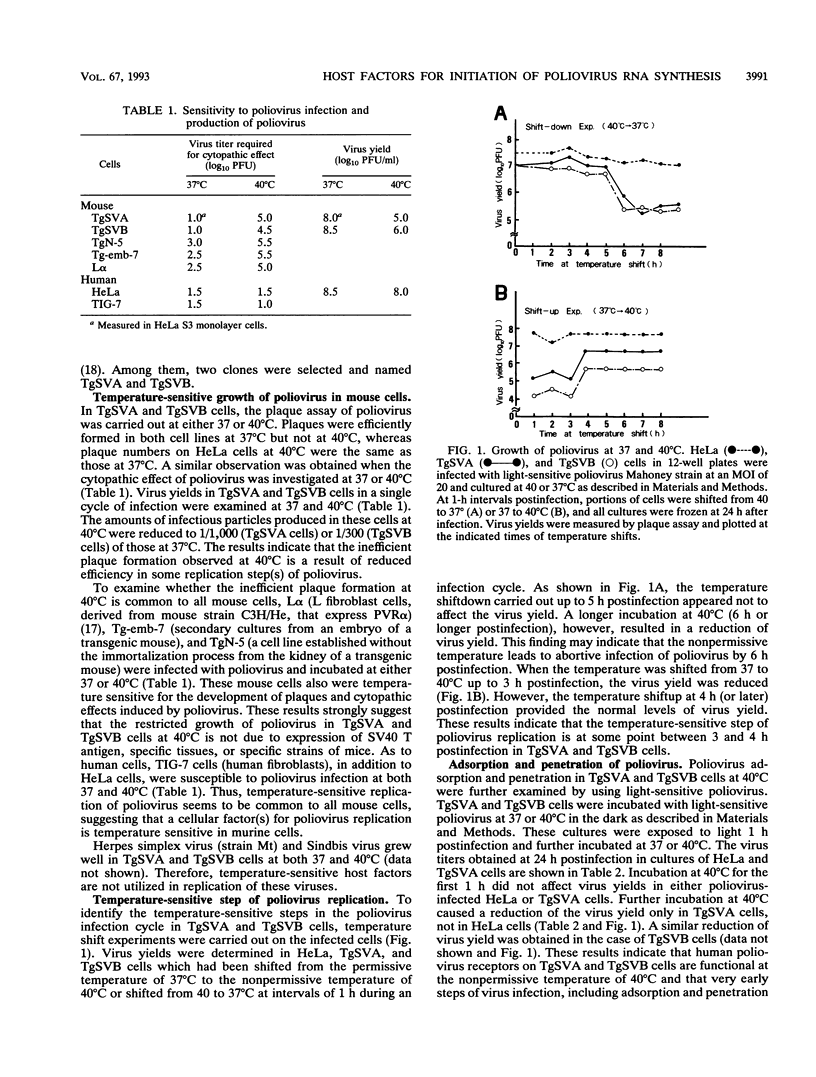
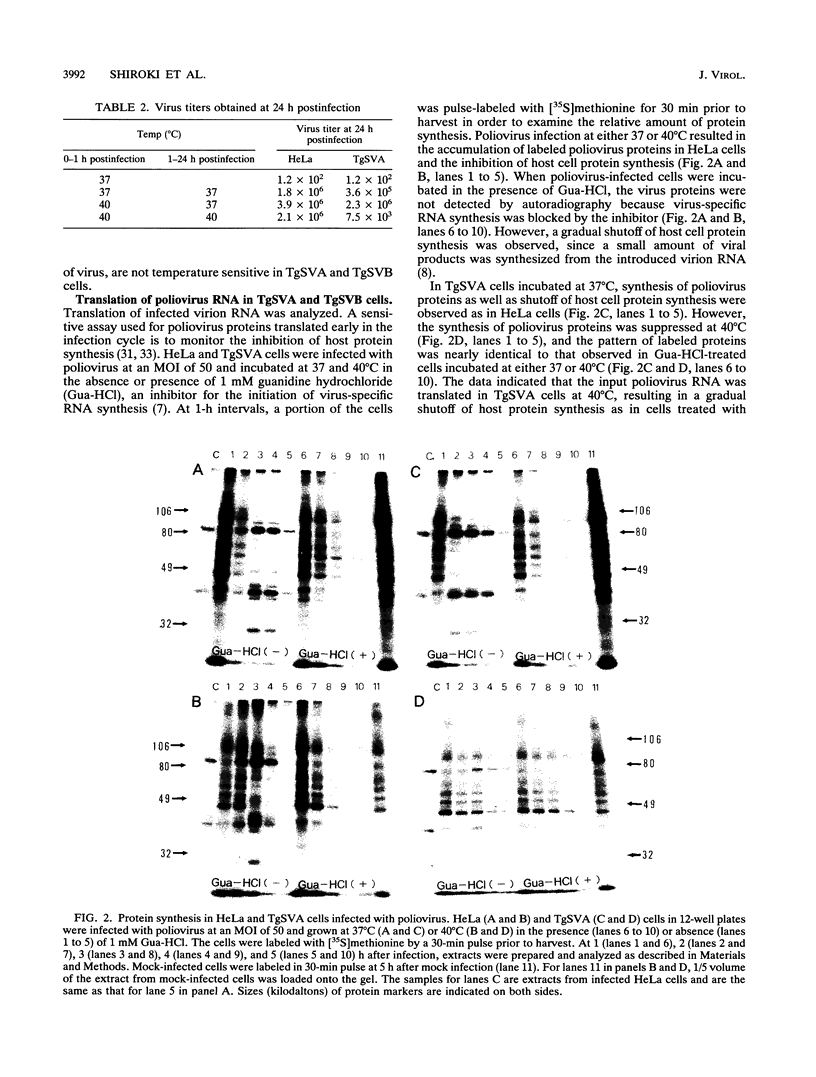
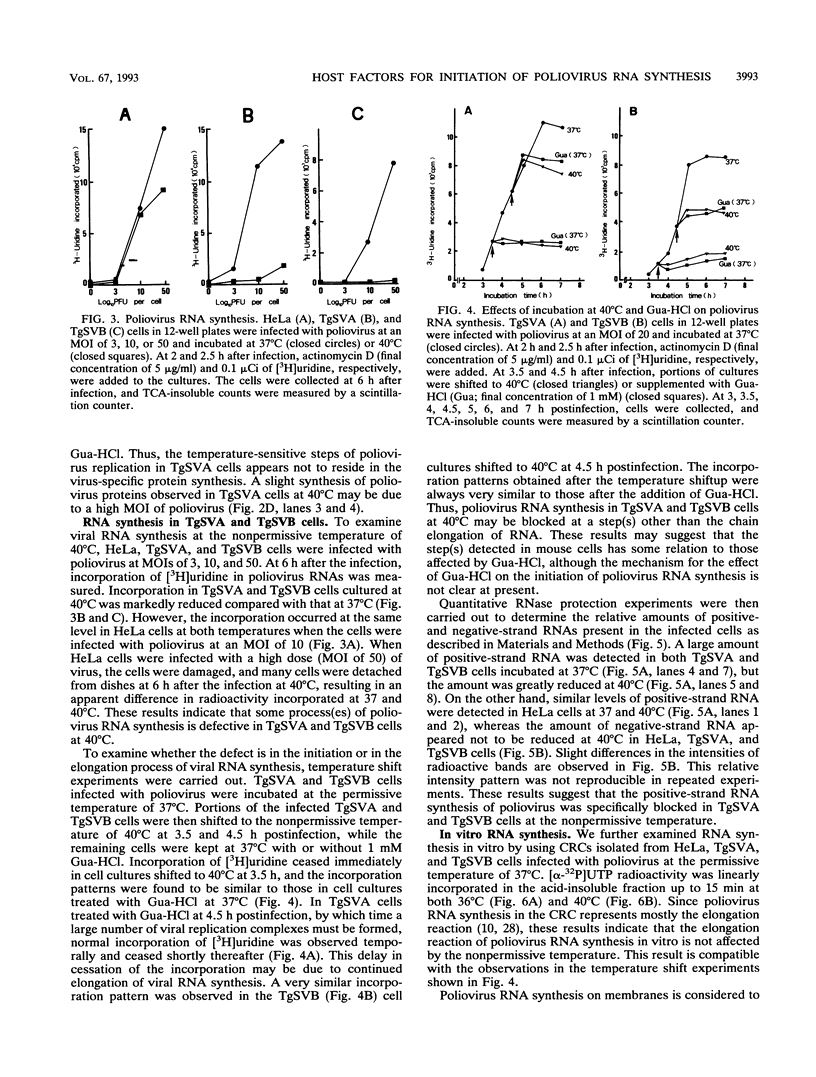
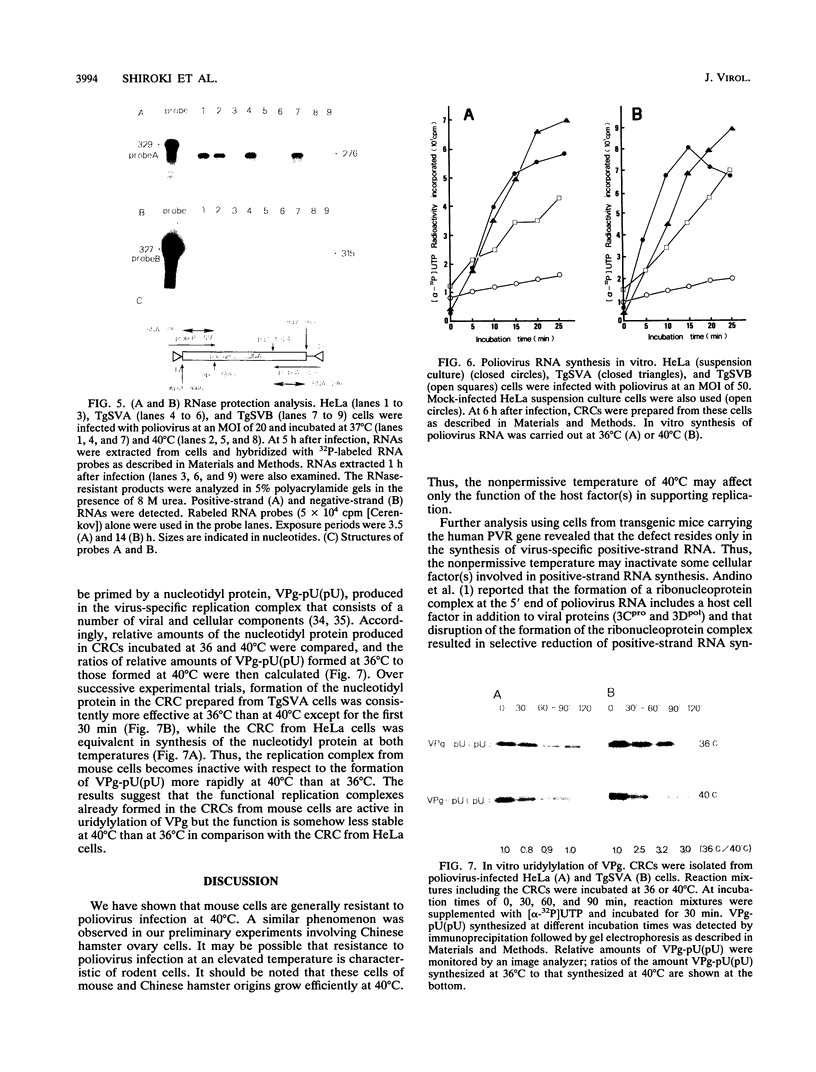
Two cell lines, TgSVA and TgSVB, were established from the kidneys of transgenic mice carrying the human gene encoding poliovirus receptor. The cells were highly susceptible to poliovirus infection, and a large amount of infectious particles was produced in the infected cells at 37 degrees C. However, the virus yield was greatly reduced at 40 degrees C. This phenomenon was common to all mouse cells tested. To identify the temperature-sensitive step(s) of the virus infection cycle, different steps of the infection cycle were examined for temperature sensitivity. The results strongly suggested that the growth restriction observed at 40 degrees C was due to reduced efficiency of the initiation process of virus-specific RNA synthesis. Furthermore, this restriction appeared to occur only on the synthesis of positive-strand RNA. Virus-specific RNA synthesis in crude replication complexes was not affected by the nonpermissive temperature of 40 degrees C. In vitro uridylylation of VPg seemed to be temperature sensitive only after prolonged incubation at 40 degrees C. These results indicate that a specific host factor(s) is involved in the efficient initiation process of positive-strand RNA synthesis of poliovirus and that the host factor(s) is temperature sensitive in TgSVA and TgSVB cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Baltimore D. A functional ribonucleoprotein complex forms around the 5' end of poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90170-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltera R. F., Jr, Tershak D. R. Guanidine-resistant mutants of poliovirus have distinct mutations in peptide 2C. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4441–4444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4441-4444.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Anti-VPg antibody inhibition of the poliovirus replicase reaction and production of covalent complexes of VPg-related proteins and RNA. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):745–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Pfister T., Troxler M. Structural and functional characterization of the poliovirus replication complex. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2740–2747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2740-2747.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz K., Egger D., Troxler M., Pasamontes L. Structural organization of poliovirus RNA replication is mediated by viral proteins of the P2 genomic region. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1156-1163.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Action of guanidine on the replication of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):408–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Characterization of poliovirus-specific structures associated with cytoplasmic membranes. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):112–122. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90243-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Membranous structures associated with translation and transcription of poliovirus RNA. Science. 1969 Nov 14;166(3907):885–886. doi: 10.1126/science.166.3907.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsch-Häsler K., Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Replication of picornaviruses. I. Evidence from in vitro RNA synthesis that poly(A) of the poliovirus genome is genetically coded. J Virol. 1975 Dec;16(6):1512–1517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.6.1512-1517.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Petterson R. F., Ambros V., Hewlett N. J., Baltimore D. Covalent linkage of a protein to a defined nucleotide sequence at the 5'-terminus of virion and replicative intermediate RNAs of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giachetti C., Semler B. L. Role of a viral membrane polypeptide in strand-specific initiation of poliovirus RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2647–2654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2647-2654.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinea R., Carrasco L. Phospholipid biosynthesis and poliovirus genome replication, two coupled phenomena. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):2011–2016. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajigaya S., Arakawa H., Kuge S., Koi T., Imura N., Nomoto A. Isolation and characterization of defective-interfering particles of poliovirus Sabin 1 strain. Virology. 1985 Apr 30;142(2):307–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90339-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Sumimoto H., Pognonec P., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Roeder R. G. HIV-1 Tat acts as a processivity factor in vitro in conjunction with cellular elongation factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):655–666. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Horie H., Ise I., Okitsu A., Yoshida M., Iizuka N., Takeuchi K., Takegami T., Nomoto A. The poliovirus receptor protein is produced both as membrane-bound and secreted forms. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3217–3224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Taya C., Kurata T., Abe S., Ise I., Yonekawa H., Nomoto A. Transgenic mice susceptible to poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):951–955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson M. A., Semler B. L. Picornavirus protein processing--enzymes, substrates, and genetic regulation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;161:49–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. P., Baltimore D. Isolation of poliovirus 2C mutants defective in viral RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4016–4021. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4016-4021.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser A. G., Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Incorporation of lipid precursors into cytoplasmic membranes of poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90236-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus S. E., Diamond D. C., Emini E. A., Wimmer E. Guanidine-selected mutants of poliovirus: mapping of point mutations to polypeptide 2C. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):638–646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.638-646.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransone L. J., Dasgupta A. Multiple isoelectric forms of poliovirus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase: evidence for phosphorylation. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4563–4568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4563-4568.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R. B., Costantini F., Gorgacz E. J., Lee J. J., Racaniello V. R. Transgenic mice expressing a human poliovirus receptor: a new model for poliomyelitis. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90168-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Poliovirus RNA replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;161:89–119. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75602-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Jacobson S. J., Najita L. Poliovirus genetics. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;161:155–188. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75602-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Impact of virus infection on host cell protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:317–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Hanecak R., Dorner L. F., Wimmer E. A membrane-associated precursor to poliovirus VPg identified by immunoprecipitation with antibodies directed against a synthetic heptapeptide. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):405–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroki K., Hamaguchi M., Kawai S. Highly efficient focus formation by Rous sarcoma virus on adenovirus type 12 E1A-transformed rat 3Y1 cells. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1449–1457. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1449-1457.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Regulation of translation by poliovirus. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:175–204. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60318-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda N., Kuhn R. J., Yang C. F., Takegami T., Wimmer E. Initiation of poliovirus plus-strand RNA synthesis in a membrane complex of infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):43–53. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.43-53.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Kuhn R. J., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane-dependent uridylylation of the genome-linked protein VPg of poliovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7447–7451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegami T., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Membrane fractions active in poliovirus RNA replication contain VPg precursor polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):33–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90316-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin G. J., Young D. C., Flanegan J. B. Self-catalyzed linkage of poliovirus terminal protein VPg to poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):511–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Yang C. F., Takeda N., Nomoto A., Wimmer E. Analysis of RNA synthesis of type 1 poliovirus by using an in vitro molecular genetic approach. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2816–2822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2816-2822.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmer E., Kuhn R. J., Pincus S., Yang C. F., Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Takeda N. Molecular events leading to picornavirus genome replication. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;7:251–276. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_7.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Wimmer E. Polyadenylic acid at the 3'-terminus of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1877–1882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]