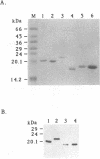
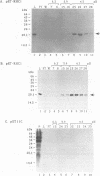
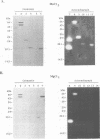
Abstract
We have expressed and purified from Escherichia coli a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNase H domain consisting of amino acids 400 to 560 of reverse transcriptase with either an N- or C-terminal polyhistidine tag. The native protease cleavage site of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase is between amino acids 440 and 441. Purification on Ni(2+)-nitrilotriacetate agarose resulted in a highly active RNase H domain dependent on MnCl2 rather than MgCl2. Activity was unambiguously attributed to the purified proteins by an in situ RNase H gel assay. Residues 400 to 426, which include a stretch of tryptophans, did not contribute to RNase H activity, and the polyhistidine tag was essential for activity. Despite the requirement for a histidine tag, the recombinant RNase H proteins retained characteristics of the wild-type heterodimer, as determined by examining activity in the presence of several known inhibitors of HIV-1 RNase H, including ribonucleoside vanadyl complexes, dAMP, and a monoclonal antibody. Importantly, the isolated RNase H domain produced the same specific cleavage in tRNA(3Lys) removal as HIV-1 heterodimer, leaving the 3'-rA (adenosine 5' phosphate) residue of a model tRNA attached to the adjacent U5 sequence. This HIV-1 RNase H domain sedimented as a monomer in a glycerol gradient.
Full text
PDF


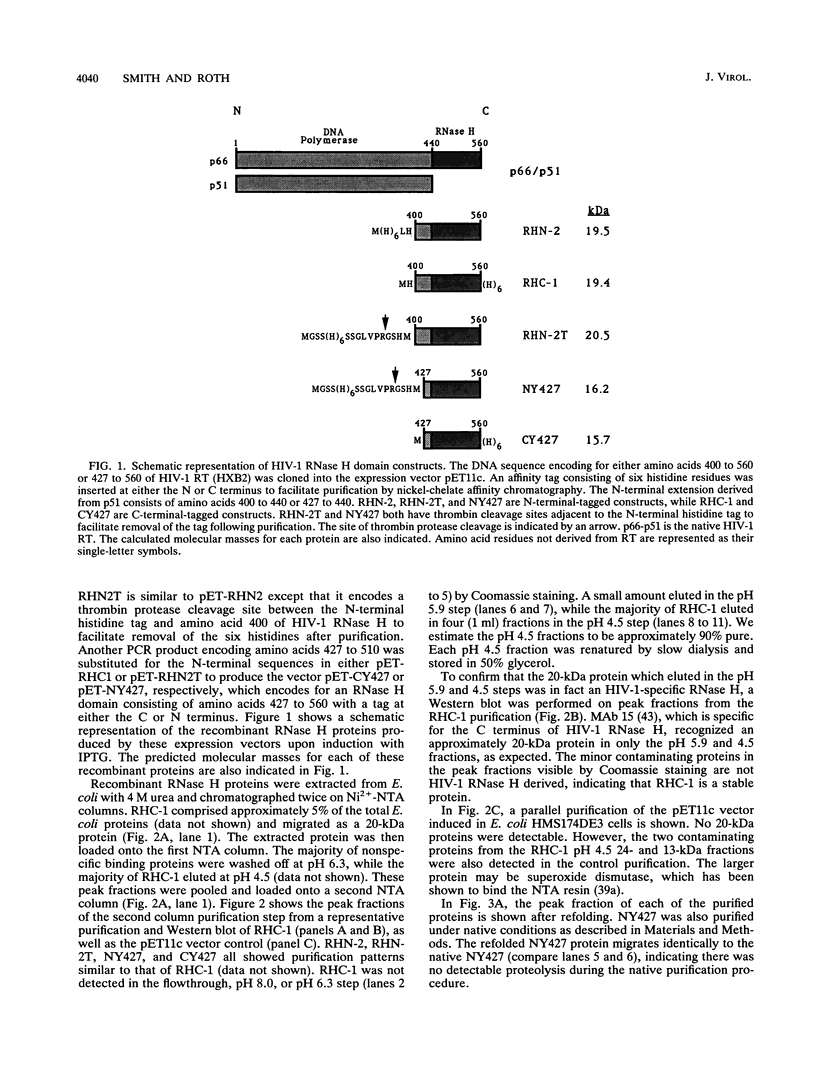




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold E., Jacobo-Molina A., Nanni R. G., Williams R. L., Lu X., Ding J., Clark A. D., Jr, Zhang A., Ferris A. L., Clark P. Structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase/DNA complex at 7 A resolution showing active site locations. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):85–89. doi: 10.1038/357085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becerra S. P., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Karlström A. R., Stahl S. J., Wilson S. H., Wingfield P. T. Purification and characterization of the RNase H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase expressed in recombinant Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81238-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Artzi H., Zeelon E., Gorecki M., Panet A. Double-stranded RNA-dependent RNase activity associated with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):927–931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Artzi H., Zeelon E., Le-Grice S. F., Gorecki M., Panet A. Characterization of the double stranded RNA dependent RNase activity associated with recombinant reverse transcriptases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Oct 11;20(19):5115–5118. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.19.5115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. L., Ferris A. L., Hughes S. H. Cassette mutagenesis of the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1031–1039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1031-1039.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. F., 2nd, Hostomska Z., Hostomsky Z., Jordan S. R., Matthews D. A. Crystal structure of the ribonuclease H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):88–95. doi: 10.1126/science.1707186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J. RNase III cleavage of single-stranded RNA. Effect of ionic strength on the fideltiy of cleavage. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jun 25;251(12):3807–3814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. B., Brawn K., Deibel M. R., Jr, Tarpley W. G., Sharma S. K. A recombinant ribonuclease H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase that is enzymatically active. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20583–20585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furfine E. S., Reardon J. E. Human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase ribonuclease H: specificity of tRNA(Lys3)-primer excision. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 23;30(29):7041–7046. doi: 10.1021/bi00243a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furfine E. S., Reardon J. E. Reverse transcriptase.RNase H from the human immunodeficiency virus. Relationship of the DNA polymerase and RNA hydrolysis activities. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):406–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan V., Peliska J. A., Benkovic S. J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase: spatial and temporal relationship between the polymerase and RNase H activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10763–10767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J., Schulze T., Mellert W., Moelling K. Identification and characterization of HIV-specific RNase H by monoclonal antibody. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):239–243. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., Hughes S. H., Shaharabany M. Mutational analysis of the ribonuclease H activity of human immunodeficiency virus 1 reverse transcriptase. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):575–580. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90444-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann A., Roeder R. G. Purification of his-tagged proteins in non-denaturing conditions suggests a convenient method for protein interaction studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6337–6338. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong T., Drlica K., Pinter A., Murphy E. Circular DNA of human immunodeficiency virus: analysis of circle junction nucleotide sequences. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):551–555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.551-555.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostomsky Z., Hostomska Z., Hudson G. O., Moomaw E. W., Nodes B. R. Reconstitution in vitro of RNase H activity by using purified N-terminal and C-terminal domains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1148–1152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson C. B., Donzella G. A., Roth M. J. Characterization of the forward and reverse integration reactions of the Moloney murine leukemia virus integrase protein purified from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):1462–1469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanaya S., Katsuda-Nakai C., Ikehara M. Importance of the positive charge cluster in Escherichia coli ribonuclease HI for the effective binding of the substrate. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):11621–11627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayanagi K., Miyagawa M., Matsushima M., Ishikawa M., Kanaya S., Ikehara M., Matsuzaki T., Morikawa K. Three-dimensional structure of ribonuclease H from E. coli. Nature. 1990 Sep 20;347(6290):306–309. doi: 10.1038/347306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Wang J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1377403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug M. S., Berger S. L. Reverse transcriptase from human immunodeficiency virus: a single template-primer binding site serves two physically separable catalytic functions. Biochemistry. 1991 Nov 5;30(44):10614–10623. doi: 10.1021/bi00108a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krug M. S., Berger S. L. Ribonuclease H activities associated with viral reverse transcriptases are endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3539–3543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulkosky J., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M. Terminal nucleotides of the preintegrative linear form of HIV-1 DNA deduced from the sequence of circular DNA junctions. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(9):852–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Grice S. F., Naas T., Wohlgensinger B., Schatz O. Subunit-selective mutagenesis indicates minimal polymerase activity in heterodimer-associated p51 HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3905–3911. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04960.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoote M. M., Coligan J. E., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Martin M. A., Venkatesan S. Structural characterization of reverse transcriptase and endonuclease polypeptides of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):771–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.771-775.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March P. E., Gonzalez M. A. Characterization of the biochemical properties of recombinant ribonuclease III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3293–3298. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi V., Lazarus G. M., Miles L. M., Meyers C. A., Debouck C. Recombinant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase: purification, primary structure, and polymerase/ribonuclease H activities. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Sep;273(2):347–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90493-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mous J., Heimer E. P., Le Grice S. F. Processing protease and reverse transcriptase from human immunodeficiency virus type I polyprotein in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1433–1436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1433-1436.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda Y., Yoshida M., Kanaya S. Role of histidine 124 in the catalytic function of ribonuclease HI from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):88–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza C. D. Two bases are deleted from the termini of HIV-1 linear DNA during integrative recombination. Virology. 1990 Dec;179(2):886–889. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90161-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R., Clore G. M., Bax A., Garrett D. S., Stahl S. J., Wingfield P. T., Gronenborn A. M. Secondary structure of the ribonuclease H domain of the human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase in solution using three-dimensional double and triple resonance heteronuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90920-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers R., Clore G. M., Stahl S. J., Wingfield P. T., Gronenborn A. Analysis of the backbone dynamics of the ribonuclease H domain of the human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase using 15N relaxation measurements. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 29;31(38):9150–9157. doi: 10.1021/bi00153a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad V. R., Goff S. P. Linker insertion mutagenesis of the human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase expressed in bacteria: definition of the minimal polymerase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3104–3108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen K. A., Ishimoto L. K., Champoux J. J. Incomplete removal of the RNA primer for minus-strand DNA synthesis by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):367–373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.367-373.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restle T., Müller B., Goody R. S. Dimerization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. A target for chemotherapeutic intervention. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):8986–8988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restle T., Müller B., Goody R. S. RNase H activity of HIV reverse transcriptases is confined exclusively to the dimeric forms. FEBS Lett. 1992 Mar 23;300(1):97–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80172-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restle T., Pawlita M., Sczakiel G., Müller B., Goody R. S. Structure-function relationships of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase determined using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):14654–14661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Tanese N., Goff S. P. Purification and characterization of murine retroviral reverse transcriptase expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9326–9335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar M., Champoux J. J., Reid B. R. Sugar conformations at hybrid duplex junctions in HIV-1 and Okazaki fragments. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 26;32(3):739–744. doi: 10.1021/bi00054a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz O., Cromme F. V., Grüninger-Leitch F., Le Grice S. F. Point mutations in conserved amino acid residues within the C-terminal domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase specifically repress RNase H function. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81559-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Kim S. Y., Roth M. J. Analysis of long terminal repeat circle junctions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6286–6290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6286-6290.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., Roth M. J. Specificity of human immunodeficiency virus-1 reverse transcriptase-associated ribonuclease H in removal of the minus-strand primer, tRNA(Lys3). J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15071–15079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stammers D. K., Tisdale M., Court S., Parmar V., Bradley C., Ross C. K. Rapid purification and characterisation of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and RNaseH engineered to incorporate a C-terminal tripeptide alpha-tubulin epitope. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jun 3;283(2):298–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80613-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starnes M. C., Cheng Y. C. Human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase-associated RNase H activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7073–7077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szilvay A. M., Nornes S., Haugan I. R., Olsen L., Prasad V. R., Endresen C., Goff S. P., Helland D. E. Epitope mapping of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with monoclonal antibodies that inhibit polymerase and RNase H activities. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(7):647–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. K., Zhang J., Li Z. Y., Tarpley W. G., Downey K. M., So A. G. Functional characterization of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase and RNase H activities of a recombinant HIV reverse transcriptase. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 12;30(10):2651–2655. doi: 10.1021/bi00224a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanese N., Goff S. P. Domain structure of the Moloney murine leukemia virus reverse transcriptase: mutational analysis and separate expression of the DNA polymerase and RNase H activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1777–1781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb J. M., Hughes S. H. Retroviral reverse transcription and integration: progress and problems. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:275–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitcomb J. M., Kumar R., Hughes S. H. Sequence of the circle junction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: implications for reverse transcription and integration. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4903–4906. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4903-4906.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöhrl B. M., Moelling K. Interaction of HIV-1 ribonuclease H with polypurine tract containing RNA-DNA hybrids. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 6;29(44):10141–10147. doi: 10.1021/bi00496a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wöhrl B. M., Volkmann S., Moelling K. Mutations of a conserved residue within HIV-1 ribonuclease H affect its exo- and endonuclease activities. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):801–818. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90119-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W., Hendrickson W. A., Crouch R. J., Satow Y. Structure of ribonuclease H phased at 2 A resolution by MAD analysis of the selenomethionyl protein. Science. 1990 Sep 21;249(4975):1398–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.2169648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Marzo Veronese F., Copeland T. D., DeVico A. L., Rahman R., Oroszlan S., Gallo R. C., Sarngadharan M. G. Characterization of highly immunogenic p66/p51 as the reverse transcriptase of HTLV-III/LAV. Science. 1986 Mar 14;231(4743):1289–1291. doi: 10.1126/science.2418504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]