Abstract
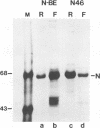
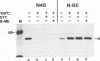
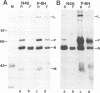
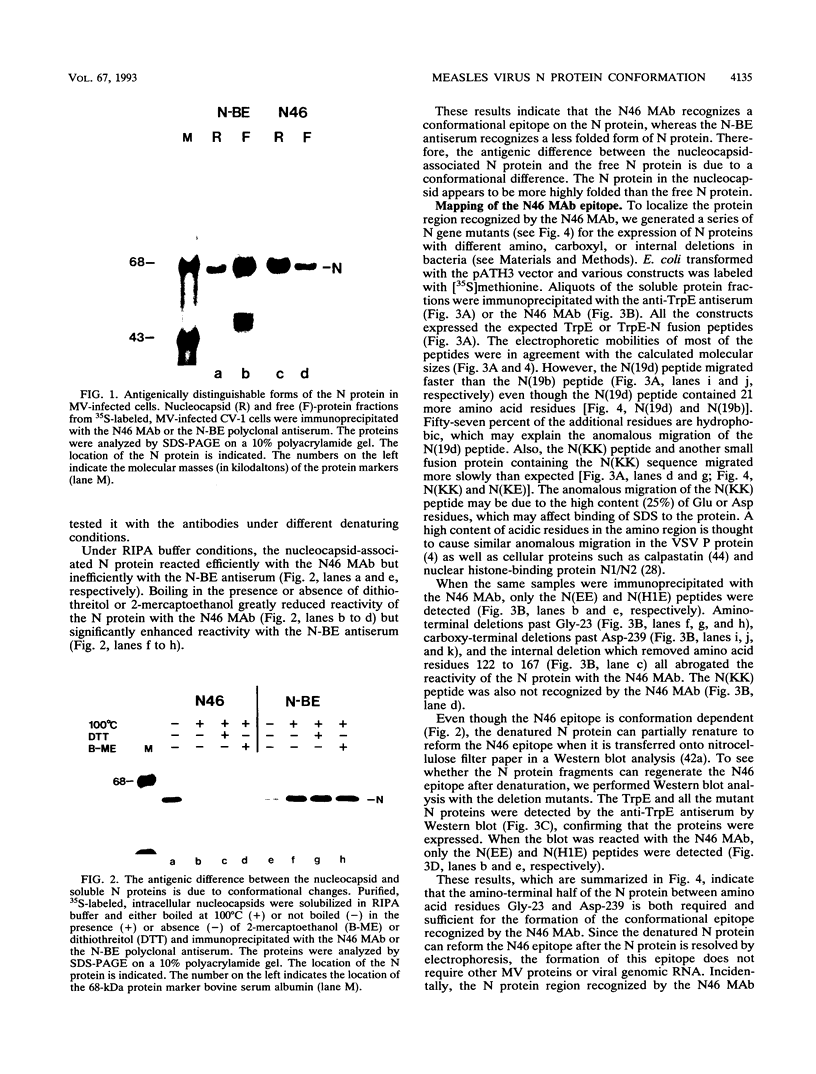
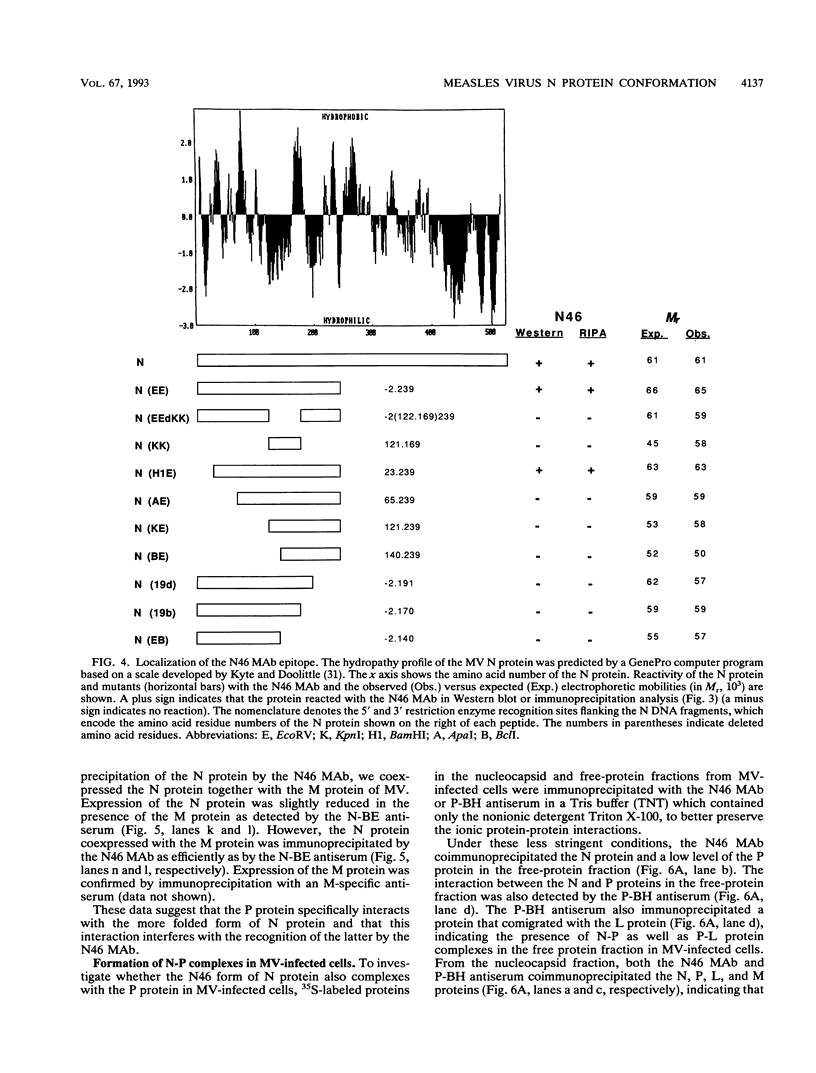
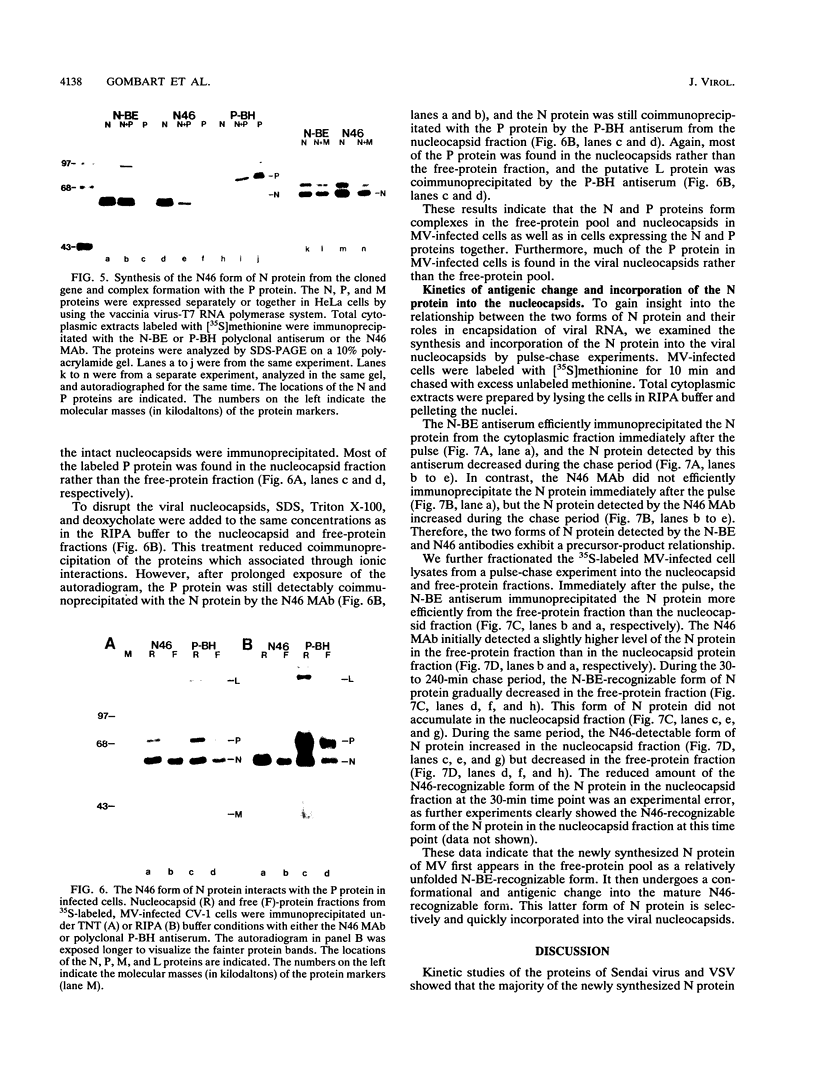
We have obtained a polyclonal antiserum, N-BE, against the denatured, amino-terminal half of the measles virus (MV) nucleocapsid (N) protein and a monoclonal antibody (MAb), N46, which recognizes a conformation-dependent epitope in the same region. Amino acid residues 23 to 239 were required and sufficient for the formation of the conformational epitope. Using these antibodies, we show that the N protein of MV is synthesized as a relatively unfolded protein which first appears in the free-protein pool. This nascent N protein undergoes a conformational change into a more folded mature form. This change does not require the participation of other viral proteins or genomic RNA. The mature N protein does not accumulate in the free-protein pool but is quickly and selectively incorporated into the viral nucleocapsids. The mature N protein is a target for interaction with the phosphoprotein (P protein) of MV. This interaction interferes with the recognition of the N protein by the N46 MAb. This suggests that the association with the P protein may mask the binding site for the N46 MAb or that it induces a conformational change in the N protein.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnheiter H., Davis N. L., Wertz G., Schubert M., Lazzarini R. A. Role of the nucleocapsid protein in regulating vesicular stomatitis virus RNA synthesis. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayata M., Hirano A., Wong T. C. Structural defect linked to nonrandom mutations in the matrix gene of biken strain subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus defined by cDNA cloning and expression of chimeric genes. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1162–1173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1162-1173.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee A. K. Transcription and replication of rhabdoviruses. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):66–87. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.66-87.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barik S., Banerjee A. K. Cloning and expression of the vesicular stomatitis virus phosphoprotein gene in Escherichia coli: analysis of phosphorylation status versus transcriptional activity. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1719–1726. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1719-1726.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland R., Giraudon P., Wild F. Expression of measles virus nucleoprotein in Escherichia coli: use of deletion mutants to locate the antigenic sites. J Gen Virol. 1989 Feb;70(Pt 2):435–441. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-2-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaneda S. J., Wong T. C. Leader sequence distinguishes between translatable and encapsidated measles virus RNAs. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):222–230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.222-230.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Schmid A., Billeter M. A., Sheppard R. D., Udem S. A. Multiple viral mutations rather than host factors cause defective measles virus gene expression in a subacute sclerosing panencephalitis cell line. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1388–1397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1388-1397.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Boeck R., Kolakofsky D. The Sendai virus P gene expresses both an essential protein and an inhibitor of RNA synthesis by shuffling modules via mRNA editing. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3079–3085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das T., Banerjee A. K. Role of the phosphoprotein (P) in the encapsidation of presynthesized and de novo synthesized vesicular stomatitis virus RNA by the nucleocapsid protein (N) in vitro. Cell Mol Biol. 1992 Feb;38(1):17–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. L., Arnheiter H., Wertz G. W. Vesicular stomatitis virus N and NS proteins form multiple complexes. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):751–754. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.751-754.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande K. L., Portner A. Structural and functional analysis of Sendai virus nucleocapsid protein NP with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):32–42. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. S., Takai S., Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Mapping of antigenic domains of Sendai virus nucleocapsid protein expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4805–4808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4805-4808.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraudon P., Jacquier M. F., Wild T. F. Antigenic analysis of African measles virus field isolates: identification and localisation of one conserved and two variable epitope sites on the NP protein. Virus Res. 1988 May;10(2-3):137–152. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gombart A. F., Hirano A., Wong T. C. Expression and properties of the V protein in acute measles virus and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus strains. Virus Res. 1992 Sep 1;25(1-2):63–78. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90100-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gombart A. F., Pearson M. N., Rohrmann G. F., Beaudreau G. S. A baculovirus polyhedral envelope-associated protein: genetic location, nucleotide sequence, and immunocytochemical characterization. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):182–193. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross C. H., Rohrmann G. F. Mapping unprocessed epitopes using deletion mutagenesis of gene fusions. Biotechniques. 1990 Feb;8(2):196–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Yoshida T., Nishikawa K., Naruse H., Nagai Y. Transcriptive complex of Newcastle disease virus. I. Both L and P proteins are required to constitute an active complex. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Wang A. H., Gombart A. F., Wong T. C. The matrix proteins of neurovirulent subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus and its acute measles virus progenitor are functionally different. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8745–8749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homann H. E., Willenbrink W., Buchholz C. J., Neubert W. J. Sendai virus protein-protein interactions studied by a protein-blotting protein-overlay technique: mapping of domains on NP protein required for binding to P protein. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1304–1309. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1304-1309.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikami S. M., Curran J., Kolakofsky D., Moyer S. A. Complexes of Sendai virus NP-P and P-L proteins are required for defective interfering particle genome replication in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4901–4908. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4901-4908.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard M., Wertz G. Vesicular stomatitis virus RNA replication: a role for the NS protein. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2683–2694. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. H., Kingsbury D. W., Murti K. G. Assembly of vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsids in vivo: a kinetic analysis. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):304–313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.304-313.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber M., Cattaneo R., Spielhofer P., Orvell C., Norrby E., Messerli M., Perriard J. C., Billeter M. A. Measles virus phosphoprotein retains the nucleocapsid protein in the cytoplasm. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90777-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsbury D. W., Hsu C. H., Murti K. G. Intracellular metabolism of sendai virus nucleocapside. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):86–94. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90357-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Dingwall C., Maier G., Franke W. W. Molecular characterization of a karyophilic, histone-binding protein: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence and expression of nuclear protein N1/N2 of Xenopus laevis. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3547–3552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04681.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Separate pathways of maturation of the major structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1128–1139. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1128-1139.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Ferla F. M., Peluso R. W. The 1:1 N-NS protein complex of vesicular stomatitis virus is essential for efficient genome replication. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3852–3857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3852-3857.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters P. S., Banerjee A. K. Complex formation with vesicular stomatitis virus phosphoprotein NS prevents binding of nucleocapsid protein N to nonspecific RNA. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2658–2664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2658-2664.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters P. S., Banerjee A. K. Resolution of multiple complexes of phosphoprotein NS with nucleocapsid protein N of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2651–2657. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2651-2657.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peluso R. W. Kinetic, quantitative, and functional analysis of multiple forms of the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid protein in infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2799–2807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2799-2807.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peluso R. W., Moyer S. A. Viral proteins required for the in vitro replication of vesicular stomatitis virus defective interfering particle genome RNA. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):369–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90477-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Regulatory events in the synthesis of Sendai virus polypeptides and their assembly into virions. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozenblatt S., Eizenberg O., Ben-Levy R., Lavie V., Bellini W. J. Sequence homology within the morbilliviruses. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):684–690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.684-690.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan K. W., Portner A., Murti K. G. Antibodies to paramyxovirus nucleoproteins define regions important for immunogenicity and nucleocapsid assembly. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):376–384. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spehner D., Kirn A., Drillien R. Assembly of nucleocapsidlike structures in animal cells infected with a vaccinia virus recombinant encoding the measles virus nucleoprotein. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6296–6300. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6296-6300.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano E., Maki M., Mori H., Hatanaka M., Marti T., Titani K., Kannagi R., Ooi T., Murachi T. Pig heart calpastatin: identification of repetitive domain structures and anomalous behavior in polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):1964–1972. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. C., Ayata M., Ueda S., Hirano A. Role of biased hypermutation in evolution of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis virus from progenitor acute measles virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2191–2199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2191-2199.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. C., Hirano A. Functional cDNA library for efficient expression of measles virus-specific gene products in primate cells. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):343–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.343-348.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. C., Hirano A. Structure and function of bicistronic RNA encoding the phosphoprotein and matrix protein of measles virus. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):584–589. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.584-589.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. C., Wipf G., Hirano A. The measles virus matrix gene and gene product defined by in vitro and in vivo expression. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):497–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]