Abstract
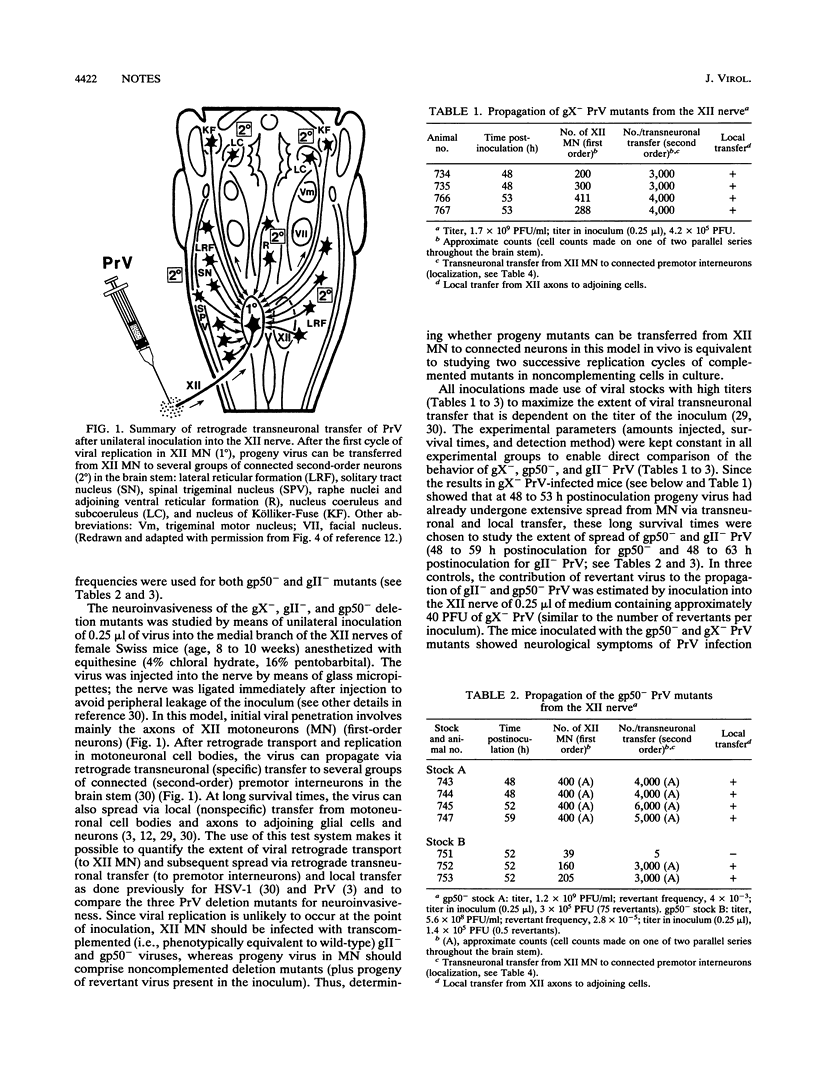
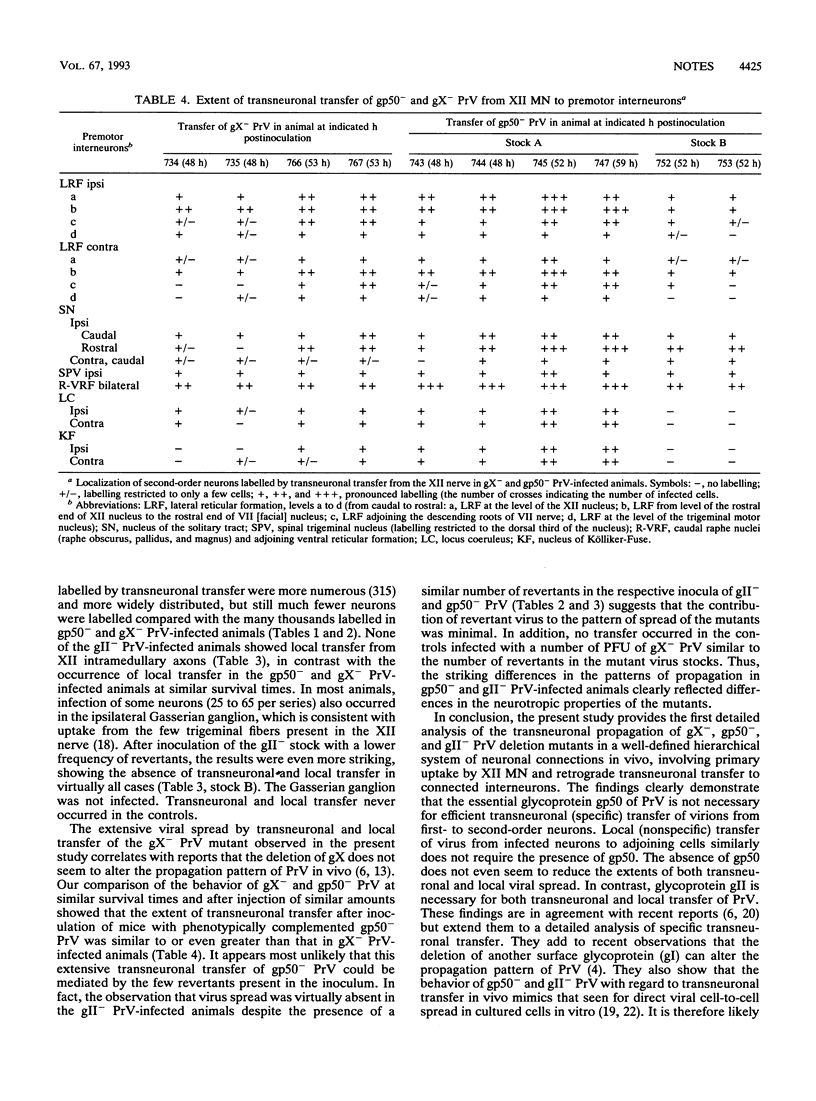
The propagation of pseudorabies virus (PrV) mutants deficient in essential glycoproteins gp50 and gII was studied after inoculation of transcomplemented gp50- and gII- PrV into the motor hypoglossal (XII) nerves of mice. In this model, viral spread from the infected XII motoneurons involves specific transneuronal transfer to connected cells and local, nonspecific transfer. For comparison, a PrV mutant lacking the nonessential nonstructural glycoprotein gX was included. Although the efficiencies of first-cycle replication were similar for the three viruses, only gX- and gp50- progeny mutants could spread from XII motoneurons via transneuronal and local transfer. The extents of transfer of gX- and gp50- PrV were comparable. The results show that the absence of gp50 does not alter the pattern of transneuronal or local spread of PrV, whereas gII is essential for both processes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldes L. D., Boone T. B. Organization of projections from the principal sensory trigeminal nucleus to the hypoglossal nucleus in the rat: an experimental light and electron microscopic study with axonal tracer techniques. Exp Brain Res. 1985;59(1):16–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00237661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borke R. C., Nau M. E., Ringler R. L., Jr Brain stem afferents of hypoglossal neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1983 Jun 13;269(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90961-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card J. P., Rinaman L., Schwaber J. S., Miselis R. R., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Neurotropic properties of pseudorabies virus: uptake and transneuronal passage in the rat central nervous system. J Neurosci. 1990 Jun;10(6):1974–1994. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-06-01974.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Pseudorabies virus envelope glycoprotein gI influences both neurotropism and virulence during infection of the rat visual system. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3032–3041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3032-3041.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Card J. P., Whealy M. E., Robbins A. K., Moore R. Y., Enquist L. W. Two alpha-herpesvirus strains are transported differentially in the rodent visual system. Neuron. 1991 Jun;6(6):957–969. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90236-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffner S., Kovács F., Klupp B. G., Mettenleiter T. C. Glycoprotein gp50-negative pseudorabies virus: a novel approach toward a nonspreading live herpesvirus vaccine. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1529–1537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1529-1537.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones B. E., Yang T. Z. The efferent projections from the reticular formation and the locus coeruleus studied by anterograde and retrograde axonal transport in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Dec 1;242(1):56–92. doi: 10.1002/cne.902420105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN A. S., VATTER A. E. A comparison of herpes simplex and pseudorabies viruses. Virology. 1959 Apr;7(4):394–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimman T. G., de Wind N., Oei-Lie N., Pol J. M., Berns A. J., Gielkens A. L. Contribution of single genes within the unique short region of Aujeszky's disease virus (suid herpesvirus type 1) to virulence, pathogenesis and immunogenicity. J Gen Virol. 1992 Feb;73(Pt 2):243–251. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovács F., Mettenleiter T. C. Firefly luciferase as a marker for herpesvirus (pseudorabies virus) replication in vitro and in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1991 Dec;72(Pt 12):2999–3008. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-12-2999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krammer E. B., Rath T., Lischka M. F. Somatotopic organization of the hypoglossal nucleus: a HRP study in the rat. Brain Res. 1979 Jul 20;170(3):533–537. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90970-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuypers H. G., Ugolini G. Viruses as transneuronal tracers. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Feb;13(2):71–75. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90071-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewy A. D., Bridgman P. C., Mettenleiter T. C. beta-Galactosidase expressing recombinant pseudorabies virus for light and electron microscopic study of transneuronally labeled CNS neurons. Brain Res. 1991 Aug 2;555(2):346–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manaker S., Tischler L. J., Morrison A. R. Raphespinal and reticulospinal axon collaterals to the hypoglossal nucleus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Aug 1;322(1):68–78. doi: 10.1002/cne.903220106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Kern H., Rauh I. Isolation of a viable herpesvirus (pseudorabies virus) mutant specifically lacking all four known nonessential glycoproteins. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):498–503. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90324-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C. Molecular biology of pseudorabies (Aujeszky's disease) virus. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991;14(2):151–163. doi: 10.1016/0147-9571(91)90128-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mettenleiter T. C., Rauh I. A glycoprotein gX-beta-galactosidase fusion gene as insertional marker for rapid identification of pseudorabies virus mutants. J Virol Methods. 1990 Oct;30(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(90)90043-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazruddin, Suemune S., Shirana Y., Yamauchi K., Shigenaga Y. The cells of origin of the hypoglossal afferent nerves and central projections in the cat. Brain Res. 1989 Jun 26;490(2):219–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90240-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B., Pol J., Gielkens A., Moormann R. Envelope glycoprotein gp50 of pseudorabies virus is essential for virus entry but is not required for viral spread in mice. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):170–177. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.170-177.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peeters B., de Wind N., Hooisma M., Wagenaar F., Gielkens A., Moormann R. Pseudorabies virus envelope glycoproteins gp50 and gII are essential for virus penetration, but only gII is involved in membrane fusion. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):894–905. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.894-905.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehaud C., Coulon P., LaFay F., Thiers C., Flamand A. Antigenic site II of the rabies virus glycoprotein: structure and role in viral virulence. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.1-7.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauh I., Mettenleiter T. C. Pseudorabies virus glycoproteins gII and gp50 are essential for virus penetration. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5348–5356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5348-5356.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauh I., Weiland F., Fehler F., Keil G. M., Mettenleiter T. C. Pseudorabies virus mutants lacking the essential glycoprotein gII can be complemented by glycoprotein gI of bovine herpesvirus 1. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):621–631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.621-631.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strack A. M., Loewy A. D. Pseudorabies virus: a highly specific transneuronal cell body marker in the sympathetic nervous system. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2139–2147. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02139.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strack A. M., Sawyer W. B., Hughes J. H., Platt K. B., Loewy A. D. A general pattern of CNS innervation of the sympathetic outflow demonstrated by transneuronal pseudorabies viral infections. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 3;491(1):156–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada M., Itoh K., Yasui Y., Mitani A., Nomura S., Mizuno N. Distribution of premotor neurons for the hypoglossal nucleus in the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Nov 23;52(1-2):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90364-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen D. R., Marchioli C. C., Yancey R. J., Jr, Post L. E. Replication and virulence of pseudorabies virus mutants lacking glycoprotein gX. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):229–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.229-232.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers J. B., Norgren R. Afferent projections to the oral motor nuclei in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Nov 1;220(3):280–298. doi: 10.1002/cne.902200303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugolini G., Kuypers H. G., Simmons A. Retrograde transneuronal transfer of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV 1) from motoneurones. Brain Res. 1987 Oct 6;422(2):242–256. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90931-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugolini G., Kuypers H. G., Strick P. L. Transneuronal transfer of herpes virus from peripheral nerves to cortex and brainstem. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):89–91. doi: 10.1126/science.2536188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugolini G. Transneuronal transfer of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV 1) from mixed limb nerves to the CNS. I. Sequence of transfer from sensory, motor, and sympathetic nerve fibres to the spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Dec 22;326(4):527–548. doi: 10.1002/cne.903260404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]