Abstract
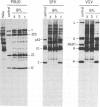
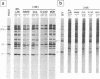
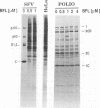
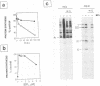
The requirement of a low-pH step during poliovirus entry was investigated by using the macrolide antibiotic bafilomycin A1, which is a powerful and selective inhibitor of the vacuolar proton-ATPases. Thus, viruses such as Semliki Forest virus and vesicular stomatitis virus that enter cells through endosomes and need their acidification, are potently inhibited by bafilomycin A1, whereas poliovirus infection is not affected by the antibiotic. The presence of lysosomotropic agents such as chloroquine, amantadine, dansylcadaverine, and monensin during poliovirus entry did not inhibit infection, further supporting the idea that poliovirus does not depend on a low-pH step to enter the cytoplasm. The effect of bafilomycin A1 on other members of the Picornaviridae family was also assayed. Encephalomyocarditis virus entry into HeLa cells was not affected by the macrolide antibiotic, whereas rhinovirus was sensitive. Coentry of toxins, such as alpha-sarcin, with viral particles was potently inhibited by bafilomycin A1, indicating that an active vacuolar proton-ATPase is necessary for the early membrane permeabilization (coentry of alpha-sarcin) induced by poliovirus to take place.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almela M. J., González M. E., Carrasco L. Inhibitors of poliovirus uncoating efficiently block the early membrane permeabilization induced by virus particles. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2572–2577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2572-2577.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxt B. Effect of lysosomotropic compounds on early events in foot-and-mouth disease virus replication. Virus Res. 1987 May;7(3):257–271. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman E. J., Siebers A., Altendorf K. Bafilomycins: a class of inhibitors of membrane ATPases from microorganisms, animal cells, and plant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7972–7976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L. Modification of membrane permeability induced by animal viruses early in infection. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):623–629. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90190-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasco L., Otero M. J., Castrillo J. L. Modification of membrane permeability by animal viruses. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;40(2):171–212. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90096-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo E. C., Giachetti C., Campos R. H. Effect of lysosomotropic agents on the foot-and-mouth disease virus replication. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):542–545. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrillo E. C., Giachetti C., Campos R. Early steps in FMDV replication: further analysis on the effects of chloroquine. Virology. 1985 Nov;147(1):118–125. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunnebacke T. H., Levinthal J. D., Williams R. C. Entry and release of poliovirus as observed by electron microscopy of cultured cells. J Virol. 1969 Oct;4(4):505–513. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.4.505-513.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Puentes C., Carrasco L. Viral infection permeabilizes mammalian cells to protein toxins. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):769–775. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald D. J., Padmanabhan R., Pastan I., Willingham M. C. Adenovirus-induced release of epidermal growth factor and pseudomonas toxin into the cytosol of KB cells during receptor-mediated endocytosis. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90480-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricks C. E., Hogle J. M. Cell-induced conformational change in poliovirus: externalization of the amino terminus of VP1 is responsible for liposome binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1934–1945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1934-1945.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gromeier M., Wetz K. Kinetics of poliovirus uncoating in HeLa cells in a nonacidic environment. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3590–3597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3590-3597.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebsch R. R., Raub T. J., Wattenberg B. W. Primaquine blocks transport by inhibiting the formation of functional transport vesicles. Studies in a cell-free assay of protein transport through the Golgi apparatus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20323–20328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., Kok J. W. Entry mechanisms of enveloped viruses. Implications for fusion of intracellular membranes. Biosci Rep. 1989 Jun;9(3):273–305. doi: 10.1007/BF01114682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Different pH requirements for entry of the two picornaviruses, human rhinovirus 2 and murine encephalomyocarditis virus. Virology. 1984 Dec;139(2):346–357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Mechanism of entry into the cytosol of poliovirus type 1: requirement for low pH. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1194–1200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madshus I. H., Olsnes S., Sandvig K. Requirements for entry of poliovirus RNA into cells at low pH. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):1945–1950. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02074.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Taiz L. The evolution of H+-ATPases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubauer C., Frasel L., Kuechler E., Blaas D. Mechanism of entry of human rhinovirus 2 into HeLa cells. Virology. 1987 May;158(1):255–258. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90264-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otero M. J., Carrasco L. Proteins are cointernalized with virion particles during early infection. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Johnson J. E. Icosahedral RNA virus structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:533–573. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. L. The proton pump ATPase of lysosomes and related organelles of the vacuolar apparatus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987;895(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4173(87)80013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seglen P. O. Inhibitors of lysosomal function. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:737–764. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96063-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Viral and cellular membrane fusion proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:675–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Skehel J. J. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. A., Collier R. J. Diphtheria toxin and Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A: active-site structure and enzymic mechanism. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;175:27–41. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76966-5_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeichhardt H., Wetz K., Willingmann P., Habermehl K. O. Entry of poliovirus type 1 and Mouse Elberfeld (ME) virus into HEp-2 cells: receptor-mediated endocytosis and endosomal or lysosomal uncoating. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):483–492. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeuzem S., Feick P., Zimmermann P., Haase W., Kahn R. A., Schulz I. Intravesicular acidification correlates with binding of ADP-ribosylation factor to microsomal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6619–6623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]