Abstract
A polyprotein cleavage assay has been developed to assay the proteolytic activities in vitro of the 2A proteinases encoded by poliovirus and human rhinovirus 14, which are representative members of the Enterovirus and Rhinovirus genera of picornaviruses, respectively. The elastase-specific substrate-based inhibitors elastatinal and methoxysuccinyl-Ala-Ala-Pro-Val-chloromethylketone (MPCMK) inhibited both 2A proteinases in vitro. The electrophoretic mobilities of both 2A proteinases were reduced upon incubation with elastatinal, whereas the mobility of a Cys-109-->Ala poliovirus 2Apro mutant was unchanged, an observation suggesting that this inhibitor may have formed a covalent bond with the active-site Cys-109 nucleophile. Iodoacetamide, calpain inhibitor 1, and antipain inhibited poliovirus 2Apro. MPCMK caused a reduction in the yields of the enteroviruses poliovirus type 1 and coxsackievirus A21 and of human rhinovirus 2 in infected HeLa cells but did not affect the growth of encephalomyocarditis virus, a picornavirus of the Cardiovirus genus. MPCMK abrogated the shutoff of host cell protein synthesis that is induced by enterovirus and rhinovirus infection and reduced the synthesis of virus-encoded polypeptides in infected cells. These results indicate that the determinants of substrate recognition by 2A proteinases resemble those of pancreatic and leukocyte elastases. These results may be relevant to the development of broad-range chemotherapeutic agents against entero- and rhinoviruses.
Full text
PDF

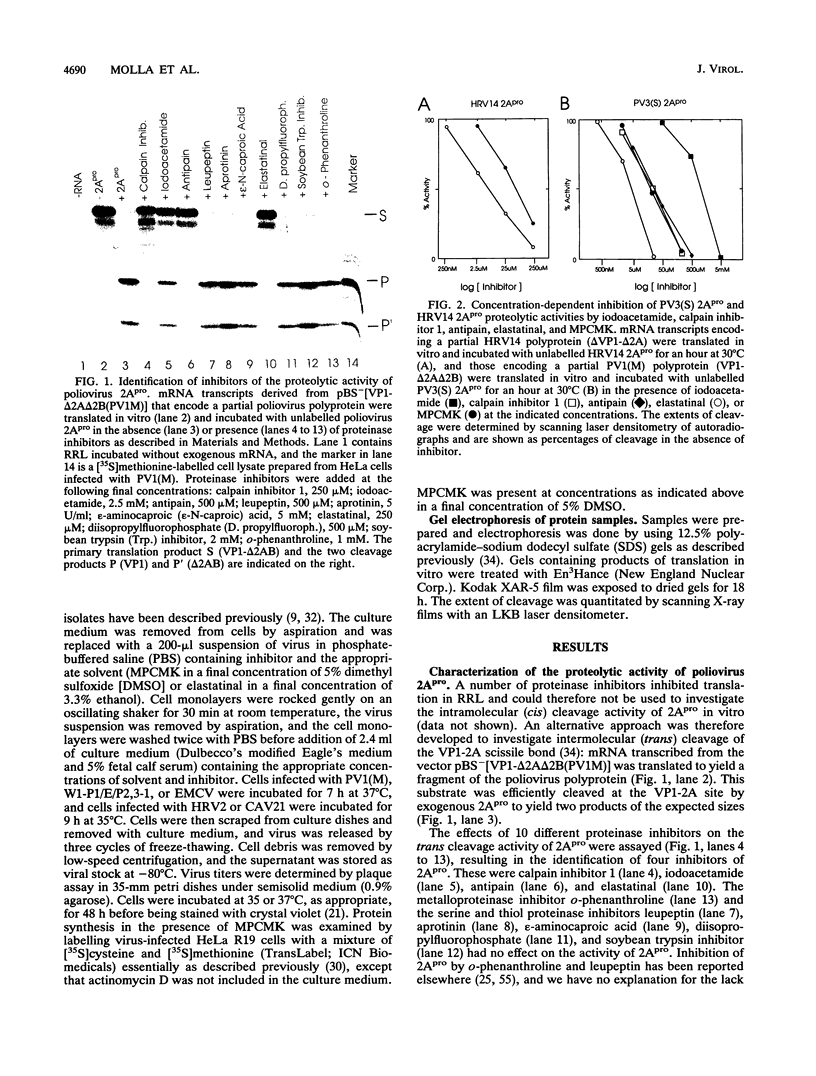
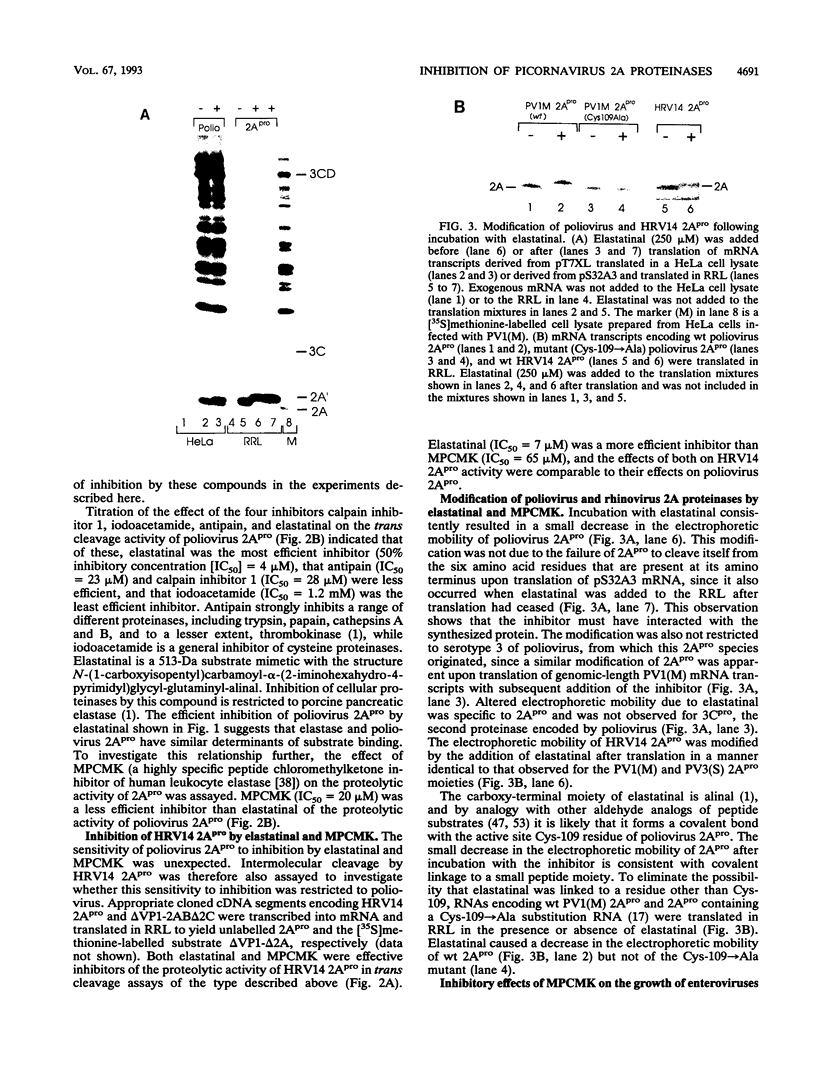
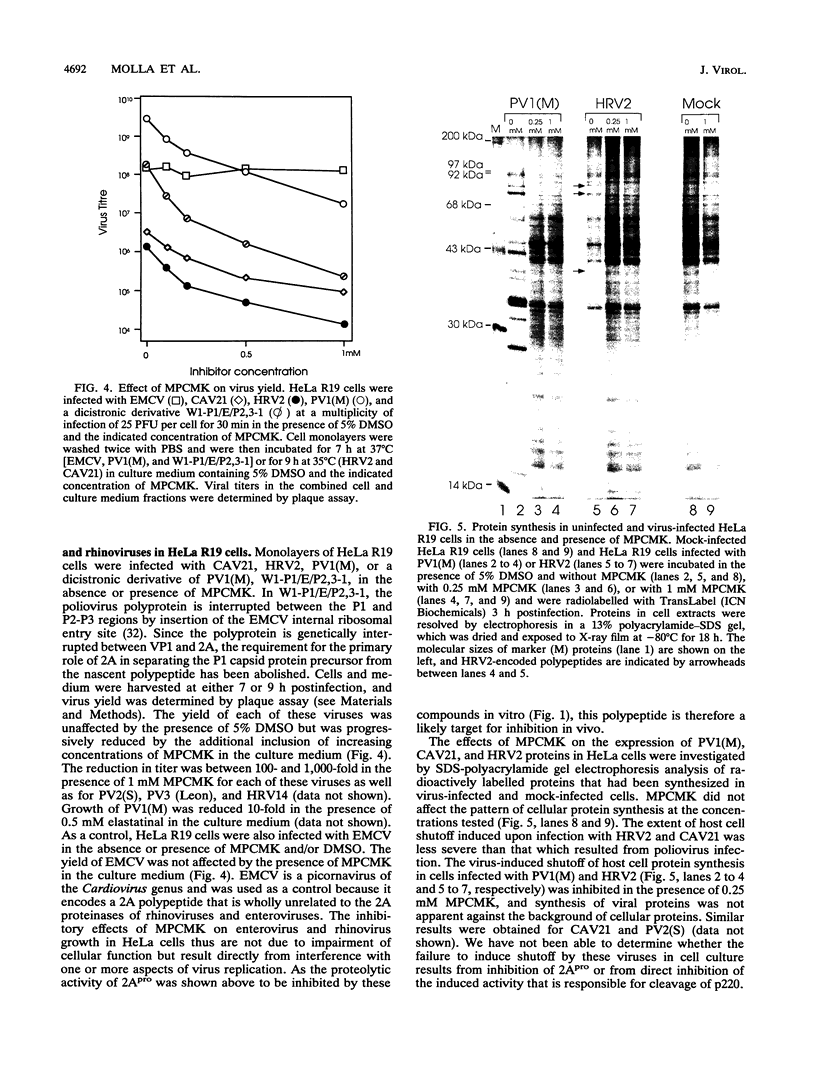



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauer C. A., Brayer G. D., Sielecki A. R., James M. N. Active site of alpha-lytic protease: enzyme-substrate interactions. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(2):289–294. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05702.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Viral cysteine proteases are homologous to the trypsin-like family of serine proteases: structural and functional implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7872–7876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger A., Schechter I. Mapping the active site of papain with the aid of peptide substrates and inhibitors. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Feb 12;257(813):249–264. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1970.0024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Sonenberg N., Baltimore D. Poliovirus mutant that does not selectively inhibit host cell protein synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2913–2923. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Meyer E., Jr, Powers J. C. Human leukocyte and porcine pancreatic elastase: X-ray crystal structures, mechanism, substrate specificity, and mechanism-based inhibitors. Biochemistry. 1989 Mar 7;28(5):1951–1963. doi: 10.1021/bi00431a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Elzinga M., Wimmer E. Carboxy-terminal analysis of poliovirus proteins: termination of poliovirus RNA translation and location of unique poliovirus polyprotein cleavage sites. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):194–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.194-199.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Schleif W. A., Colonno R. J., Wimmer E. Antigenic conservation and divergence between the viral-specific proteins of poliovirus type 1 and various picornaviruses. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90441-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Fout S. Human rhinovirus 14 infection of HeLa cells results in the proteolytic cleavage of the p220 cap-binding complex subunit and inactivates globin mRNA translation in vitro. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):634–638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.634-638.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groutas W. C. Inhibitors of leukocyte elastase and leukocyte cathepsin G. Agents for the treatment of emphysema and related ailments. Med Res Rev. 1987 Apr-Jun;7(2):227–241. doi: 10.1002/med.2610070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLLAND J. J., McLAREN L. C. Improved method for staining cell monolayers for virus plaque counts. J Bacteriol. 1959 Oct;78:596–597. doi: 10.1128/jb.78.4.596-597.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambidge S. J., Sarnow P. Translational enhancement of the poliovirus 5' noncoding region mediated by virus-encoded polypeptide 2A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10272–10276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamparian V. V., Colonno R. J., Cooney M. K., Dick E. C., Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Hughes J. H., Jordan W. S., Jr, Kapikian A. Z., Mogabgab W. J., Monto A. A collaborative report: rhinoviruses--extension of the numbering system from 89 to 100. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):191–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90367-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Fäcke M., Kräusslich H. G., Lee C. K., Wimmer E. Characterization of poliovirus 2A proteinase by mutational analysis: residues required for autocatalytic activity are essential for induction of cleavage of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4226–4231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4226-4231.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of polyproteins in the replication of RNA viruses. Biochemistry. 1989 Dec 26;28(26):9881–9890. doi: 10.1021/bi00452a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Lee C. K., Wimmer E. Determinants of substrate recognition by poliovirus 2A proteinase. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3330–3338. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3330-3338.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Wimmer E. Viral proteases as targets for chemotherapeutic intervention. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1992 Dec;3(6):643–649. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(92)90010-G. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Pestova T. V., Hellen C. U., Witherell G. W., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of picornavirus RNAs: structure and function of the internal ribosomal entry site. Enzyme. 1990;44(1-4):292–309. doi: 10.1159/000468766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski H., Maurer-Fogy I., Zorn M., Mischak H., Kuechler E., Blaas D. Cleavage site between VP1 and P2A of human rhinovirus is different in serotypes 2 and 14. J Gen Virol. 1987 Dec;68(Pt 12):3197–3200. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-12-3197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Viral proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:701–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Rosenwirth B. Purification and partial characterization of poliovirus protease 2A by means of a functional assay. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1243–1250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1243-1250.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein: elimination of 2Apro-mediated, alternative cleavage of polypeptide 3CD by in vitro mutagenesis. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. M., Monroe S. S., Rueckert R. R. Role of maturation cleavage in infectivity of picornaviruses: activation of an infectosome. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2110–2122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2110-2122.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A., Jang S. K., Paul A. V., Reuer Q., Wimmer E. Cardioviral internal ribosomal entry site is functional in a genetically engineered dicistronic poliovirus. Nature. 1992 Mar 19;356(6366):255–257. doi: 10.1038/356255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molla A., Paul A. V., Wimmer E. Cell-free, de novo synthesis of poliovirus. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1647–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.1661029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklin M. J., Kräusslich H. G., Toyoda H., Dunn J. J., Wimmer E. Poliovirus polypeptide precursors: expression in vitro and processing by exogenous 3C and 2A proteinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4002–4006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. E., Racaniello V. R. Inhibition of translation in cells infected with a poliovirus 2Apro mutant correlates with phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eucaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5069–5075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5069-5075.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestova T. V., Hellen C. U., Wimmer E. Translation of poliovirus RNA: role of an essential cis-acting oligopyrimidine element within the 5' nontranslated region and involvement of a cellular 57-kilodalton protein. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6194–6204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6194-6204.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. C., Gupton B. F., Harley A. D., Nishino N., Whitley R. J. Specificity of porcine pancreatic elastase, human leukocyte elastase and cathepsin G. Inhibition with peptide chloromethyl ketones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 23;485(1):156–166. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(77)90203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. C. Synthetic elastase inhibitors: prospects for use in the treatment of emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1983 Feb;127(2):S54–S58. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1983.127.2P2.S54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. C., Tuhy P. M. Active-site specific inhibitors of elastase. Biochemistry. 1973 Nov 6;12(23):4767–4774. doi: 10.1021/bi00747a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skern T., Sommergruber W., Auer H., Volkmann P., Zorn M., Liebig H. D., Fessl F., Blaas D., Kuechler E. Substrate requirements of a human rhinoviral 2A proteinase. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):46–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90468-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skiles J. W., Fuchs V., Miao C., Sorcek R., Grozinger K. G., Mauldin S. C., Vitous J., Mui P. W., Jacober S., Chow G. Inhibition of human leukocyte elastase (HLE) by N-substituted peptidyl trifluoromethyl ketones. J Med Chem. 1992 Feb 21;35(4):641–662. doi: 10.1021/jm00082a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommergruber W., Zorn M., Blaas D., Fessl F., Volkmann P., Maurer-Fogy I., Pallai P., Merluzzi V., Matteo M., Skern T. Polypeptide 2A of human rhinovirus type 2: identification as a protease and characterization by mutational analysis. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):68–77. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanway G. Structure, function and evolution of picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2483–2501. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein R. L., Strimpler A. M., Hori H., Powers J. C. Catalysis by human leukocyte elastase: mechanistic insights into specificity requirements. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1301–1305. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Blout E. R. Dependence of the kinetic parameters for elastase-catalyzed amide hydrolysis on the length of peptide substrates. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):57–65. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Blout E. R. Peptide chloromethyl ketones as irreversible inhibitors of elastase. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):44–47. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C. Use of peptide aldehydes to generate transition-state analogs of elastase. Biochemistry. 1973 Jan 2;12(1):47–51. doi: 10.1021/bi00725a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoda H., Nicklin M. J., Murray M. G., Anderson C. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W., Wimmer E. A second virus-encoded proteinase involved in proteolytic processing of poliovirus polyprotein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):761–770. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90790-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerik J. O., Wolfenden R. Aldehydes as inhibitors of papain. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8195–8197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff E. E., Hershey J. W., Ehrenfeld E. Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 is required for poliovirus 2A protease-induced cleavage of the p220 component of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9529–9533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu S. F., Lloyd R. E. Identification of essential amino acid residues in the functional activity of poliovirus 2A protease. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):615–625. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90602-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Werf S., Bradley J., Wimmer E., Studier F. W., Dunn J. J. Synthesis of infectious poliovirus RNA by purified T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]