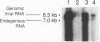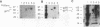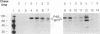Abstract
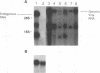
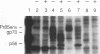
We have characterized the restriction mechanism for RD114 virus replication in embryonic feline cells (FeF). By comparing growth properties of the virus in FeF cells with its behavior in a fetal feline glial cell line (G355) permissive for RD114, we showed that both cell lines were readily infectible by virus grown in permissive cells and that no significant differences in viral integration or viral RNA expression could be detected. However, analysis of viral protein expression revealed differences in viral env gene processing in the two cell types. Envelope precursor pR85 was produced, but the expected processed gp70 product was detectable only in permissive (G355) cells. An envelope product of 85 kDa was packaged into virions produced by FeF cells, while virions produced by G355 cells contained the expected RD114 gp70. While the gp85 env-containing virions were infectious for permissive G355 cells, they were unable to infect FeF cells. The block to infection by the gp85-containing particles in FeF cells could be abrogated by treatment with the glycosylation inhibitor tunicamycin. Our results indicate that restriction of RD114 virus involves a novel mechanism dependent on two factors: altered glycosylation of the envelope to a gp85 form and an altered RD114 receptor in FeF cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Segregation of RD-114 AND FeL-V-related sequences in crosses between domestic cat and leopard cat. Nature. 1975 Oct 9;257(5526):506–508. doi: 10.1038/257506a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P., Olshevsky U., Baltimore D., Dolberg D., Fan H. Virus-like 30S RNA in mouse cells. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1168–1176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1168-1176.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., McClements W. L., Oskarsson M. K., Fischinger P. J., Vande Woude G. F. Biological activity of cloned Moloney sarcoma virus DNA: Terminally redundant sequences may enhance transformation efficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch M. P., Devi B. G., Soe L. H., Perbal B., Baluda M. A., Roy-Burman P. Characterization of the expression of cellular retrovirus genes and oncogenes in feline cells. Hematol Oncol. 1983 Jan-Mar;1(1):61–75. doi: 10.1002/hon.2900010108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Nomura S., Blevins C. S., Bolognesi D. P. Two levels of restriction by mouse or cat cells of murine sarcoma virus coated by endogenous xenotropic oncornavirus. J Gen Virol. 1975 Oct;29(1):51–62. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-29-1-51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., O'Conner T. E. Viral infection across species barriers: reversible alteration of murine sarcoma virus for growth in cat cells. Science. 1969 Aug 15;165(3894):714–716. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3894.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Peebles P. T., Nomura S., Haapala D. K. Isolation of RD-114-like oncornavirus from a cat cell line. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):978–985. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.978-985.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E. O., Risser R. The role of envelope glycoprotein processing in murine leukemia virus infection. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2852–2856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2852-2856.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haapala D. K., Robey W. G., Oroszlan S. D., Tsai W. P. Isolation from cats of an endogenous type C virus with a novel envelope glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):827–833. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.827-833.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhappan C., Vande Woude G. F., Robins T. S. Transduction of host cellular sequences by a retroviral shuttle vector. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):750–753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.750-753.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P. The Fv-1 gene of the mouse and its control of murine leukemia virus replication. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1979;86:67–122. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67341-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Jaenisch R. Integration of Moloney leukaemia virus into the germ line of mice: correlation between site of integration and virus activation. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):456–458. doi: 10.1038/287456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M., Todaro G. J. Endogenous type C virus from a cat cell clone with properties distinct from previously described feline type C virus. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):142–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90473-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. G., Miller A. D. Tunicamycin treatment of CHO cells abrogates multiple blocks to retrovirus infection, one of which is due to a secreted inhibitor. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):78–84. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.78-84.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. I., Casey J. W., Nicolson M. O., Burck K. B., Davidson N. Sequence arrangement and biological activity of cloned feline leukemia virus proviruses from a virus-productive human cell line. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):688–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.688-703.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niman H. L., Akhavi M., Gardner M. B., Stephenson J. R., Roy-Burman P. Differential expression of two distinct endogenous retrovisus genomes in developing tissues of the domestic cat. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Mar;64(3):587–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poss M. L., Mullins J. I., Hoover E. A. Posttranslational modifications distinguish the envelope glycoprotein of the immunodeficiency disease-inducing feline leukemia virus retrovirus. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):189–195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.189-195.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pryciak P. M., Varmus H. E. Fv-1 restriction and its effects on murine leukemia virus integration in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5959–5966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5959-5966.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reeves R. H., O'Brien S. J. Molecular genetic characterization of the RD-114 gene family of endogenous feline retroviral sequences. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.164-171.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Schultz A. M., Bader J. P., Bassin R. H. Inhibitors of glycosylation reverse retroviral interference. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma P. S., Tseng J., Lee Y. K., Gilden R. V. Virus similar to RD114 virus in cat cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 11;244(132):56–59. doi: 10.1038/newbio244056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Vass W. C., Howk R. S., Duesberg P. H. Defective retrovirus-like 30S RNA species of rat and mouse cells are infectious if packaged by type C helper virus. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):964–972. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.964-972.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwin S. A., Rapp U. R., Benveniste R. E., Sen A., Todaro G. J. Rescue of endogenous 30S retroviral sequences from mouse cells by baboon type C virus. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):257–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.257-264.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spodick D. A., Ghosh A. K., Parimoo S., Roy-Burman P. The long terminal repeat of feline endogenous RD-114 retroviral DNAs: analysis of transcription regulatory activity and nucleotide sequence. Virus Res. 1988 Feb;9(2-3):263–283. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(88)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spodick D. A., Soe L. H., Roy-Burman P. Genetic analysis of the feline RD-114 retrovirus-related endogenous elements. Virus Res. 1984 Oct;1(7):543–555. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk B., Kozloff L. M. A method for the efficient blotting of strongly basic proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose. Anal Biochem. 1985 Nov 1;150(2):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90528-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Benveniste R. E., Lieber M. M., Livingston D. M. Infectious type C viruses released by normal cat embryo cells. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):506–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W. K., Boone L. R., Tennant R. W., Brown A. Restriction of murine leukemia viruses by Fv-1: a model for studying host genetic control of retroviral gene movement and leukemogenesis. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;29:175–192. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]