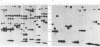
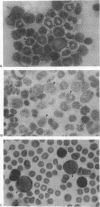
Abstract
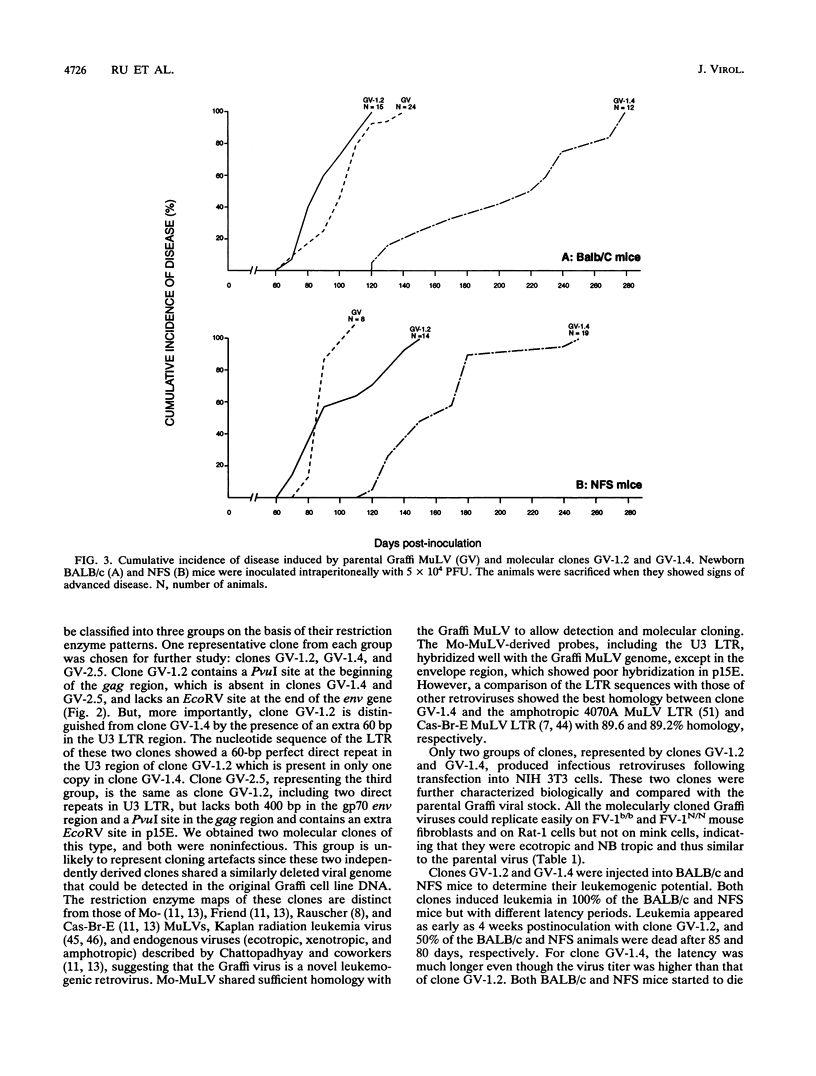
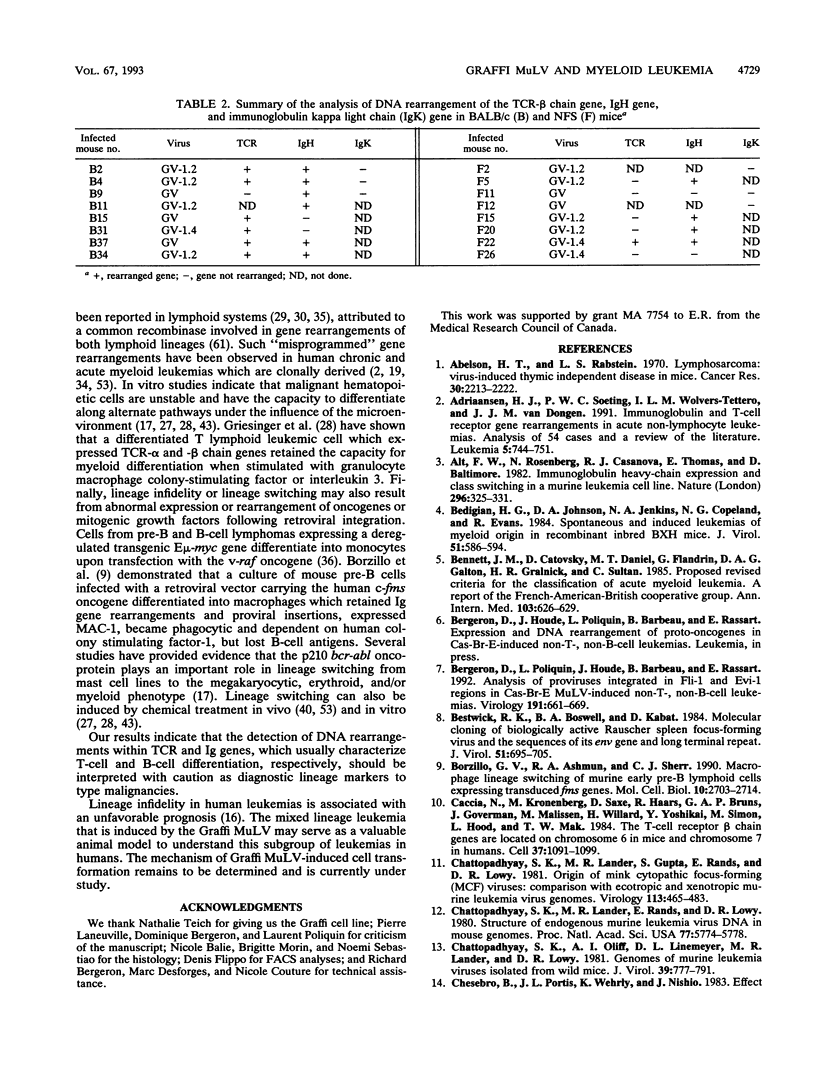
The Graffi murine leukemia virus (MuLV) is a retroviral mixture that induces predominantly myeloid leukemia in several inbred strains of mice. To analyze the viral component responsible for the myeloid leukemogenesis, we cloned several proviruses from a Graffi MuLV-infected cell line. Several infectious molecular clones were obtained that could be classified into two distinct groups of infectious MuLV. Both types of MuLV were nondefective, ecotropic, and NB tropic and induced granulocytic leukemia in BALB/c and NFS mice. Restriction enzyme analysis and molecular hybridization with several MuLV probes on one molecular clone from each group revealed that both groups are closely related to each other but are clearly distinct from all known retroviruses. One component of MuLV, however, induced leukemia with a shorter latency period and harbored a lengthier long terminal repeat. The long terminal repeat of the more leukemogenic component of MuLV had acquired a 60-bp perfect duplication in the U3 region. Analysis of the tumor DNAs with probes for the mouse T-cell receptor and immunoglobulin heavy chain genes revealed frequent rearrangements with one or both probes. This concomitant expression by leukemic cells of markers of different lineages, observed in human leukemias, has been termed "lineage infidelity" and confirms that the latter rearrangements are not restricted to hematopoietic precursors committed to lymphoid differentiation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson H. T., Rabstein L. S. Lymphosarcoma: virus-induced thymic-independent disease in mice. Cancer Res. 1970 Aug;30(8):2213–2222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adriaansen H. J., Soeting P. W., Wolvers-Tettero I. L., van Dongen J. J. Immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements in acute non-lymphocytic leukemias. Analysis of 54 cases and a review of the literature. Leukemia. 1991 Sep;5(9):744–751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alt F. W., Rosenberg N., Casanova R. J., Thomas E., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin heavy-chain expression and class switching in a murine leukaemia cell line. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):325–331. doi: 10.1038/296325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedigian H. G., Johnson D. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Evans R. Spontaneous and induced leukemias of myeloid origin in recombinant inbred BXH mice. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):586–594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.586-594.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron D., Poliquin L., Houde J., Barbeau B., Rassart E. Analysis of proviruses integrated in Fli-1 and Evi-1 regions in Cas-Br-E MuLV-induced non-T-, non-B-cell leukemias. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):661–669. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90241-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestwick R. K., Boswell B. A., Kabat D. Molecular cloning of biologically active Rauscher spleen focus-forming virus and the sequences of its env gene and long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.695-705.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borzillo G. V., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Macrophage lineage switching of murine early pre-B lymphoid cells expressing transduced fms genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2703–2714. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caccia N., Kronenberg M., Saxe D., Haars R., Bruns G. A., Goverman J., Malissen M., Willard H., Yoshikai Y., Simon M. The T cell receptor beta chain genes are located on chromosome 6 in mice and chromosome 7 in humans. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1091–1099. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90443-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Structure of endogenous murine leukemia virus DNA in mouse genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Oliff A. I., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Lowy D. R. Genomes of murine leukemia viruses isolated from wild mice. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):777–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.777-791.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drexler H. G., Thiel E., Ludwig W. D. Review of the incidence and clinical relevance of myeloid antigen-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 1991 Aug;5(8):637–645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elefanty A. G., Cory S. bcr-abl-Induced cell lines can switch from mast cell to erythroid or myeloid differentiation in vitro. Blood. 1992 Mar 1;79(5):1271–1281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIORE-DONATI L., CHIECO-BIANCHI L. INFLUENCE OF HOST FACTORS ON DEVELOPMENT AND TYPE OF LEUKEMIA INDUCED IN MICE BY GRAFFI VIRUS. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 May;32:1083–1107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEND C. Cell-free transmission in adult Swiss mice of a disease having the character of a leukemia. J Exp Med. 1957 Apr 1;105(4):307–318. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.4.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fialkow P. J., Jacobson R. J., Papayannopoulou T. Chronic myelocytic leukemia: clonal origin in a stem cell common to the granulocyte, erythrocyte, platelet and monocyte/macrophage. Am J Med. 1977 Jul;63(1):125–130. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(77)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiore-Donati L., Chieco-Bianchi L., Tridente G., Pennelli N. Studies on thymus-dependent mechanisms of mouse leukemogenesis by Graffi virus. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Sep;22:587–603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Dunlop N. M., Robey W. G. Pathogenesis and virus content of lymphomas induced by pure ecotropic Graffi murine leukemia virus. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1985 Feb;11(2):241–251. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(85)90145-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAFFI A. Chloroleukemia of mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Oct 21;68(2):540–558. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb56107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graffi A., Fey F., Schramm T. Experiments on the hematologic diversification of viral mouse leukemias. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Sep;22:21–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger J. S., Sakakeeny M. A., Humphries R. K., Eaves C. J., Eckner R. J. Demonstration of permanent factor-dependent multipotential (erythroid/neutrophil/basophil) hematopoietic progenitor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2931–2935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson C. A., Thamilarasan M., Ross C. W., Stoolman L. M., Schnitzer B. Kappa light chain gene rearrangement in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Apr;93(4):563–568. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/93.4.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara J., Benedict S. H., Champagne E., Mak T. W., Minden M., Gelfand E. W. Relationship between rearrangement and transcription of the T-cell receptor alpha, beta, and gamma genes in B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1989 Feb;73(2):500–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. At least four viral genes contribute to the leukemogenicity of murine retrovirus MCF 247 in AKR mice. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):158–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.158-165.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. L., Morse H. C., 3rd Murine hematopoietic cell surface antigen expression. Immunol Today. 1988 Nov;9(11):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91335-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Morse H. C., 3rd, Keller J., Holmes K. L. Interleukin 3 dependent retrovirus induced lymphomas: loss of the ability to terminally differentiate in response to differentiation factors. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;113:86–91. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69860-6_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersey J. H. Chronic myelocytic (multipotent-stem-cell) leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1983 Oct 6;309(14):851–852. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198310063091409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Rovigatti U., Mauer A. M., Melvin S., Murphy S. B., Stass S. Rearrangement of immunoglobulin heavy chain genes in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1985 Mar;65(3):725–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinken S. P., Alexander W. S., Adams J. M. Hemopoietic lineage switch: v-raf oncogene converts Emu-myc transgenic B cells into macrophages. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):857–867. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90309-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lithotripsy. Health and Public Policy Committee, American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Oct;103(4):626–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLONEY J. B. Biological studies on a lymphoid-leukemia virus extracted from sarcoma 37. I. Origin and introductory investigations. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1960 Apr;24:933–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The nucleotide sequence of a 5.5-kilobase DNA segment containing the mouse kappa immunoglobulin J and C region genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyaya R., Wolff L. New sites of proviral integration associated with murine promonocytic leukemias and evidence for alternate modes of c-myb activation. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6035–6044. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6035-6044.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. B., Stass S., Kalwinsky D., Rivera G. Phenotypic conversion of acute leukaemia from T-lymphoblastic to myeloblastic induced by therapy with 2'-deoxycoformycin. Br J Haematol. 1983 Oct;55(2):285–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb01249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Signorelli K., Collins L. The envelope gene and long terminal repeat sequences contribute to the pathogenic phenotype of helper-independent Friend viruses. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):788–794. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.788-794.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oster W., König K., Ludwig W. D., Ganser A., Lindemann A., Mertelsmann R., Herrmann F. Incidence of lineage promiscuity in acute myeloblastic leukemia: diagnostic implications of immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangement analysis and immunological phenotyping. Leuk Res. 1988;12(11-12):887–895. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(88)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo A., Minowada J., Erikson J., Croce C. M., Rovera G. Lineage infidelity of a human myelogenous leukemia cell line. Blood. 1984 Nov;64(5):1059–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAUSCHER F. J. A virus-induced disease of mice characterized by erythrocytopoiesis and lymphoid leukemia. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1962 Sep;29:515–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassart E., Nelbach L., Jolicoeur P. Cas-Br-E murine leukemia virus: sequencing of the paralytogenic region of its genome and derivation of specific probes to study its origin and the structure of its recombinant genomes in leukemic tissues. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):910–919. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.910-919.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassart E., Paquette Y., Jolicoeur P. Inability of Kaplan radiation leukemia virus to replicate on mouse fibroblasts is conferred by its long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3840–3848. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3840-3848.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassart E., Shang M., Boie Y., Jolicoeur P. Studies on emerging radiation leukemia virus variants in C57BL/Ka mice. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):96–106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.96-106.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saikevych I. A., Kerrigan D. P., McConnell T. S., Head D. R., Appelbaum F. R., Willman C. L. Multiparameter analysis of acute mixed lineage leukemia: correlation of a B/myeloid immunophenotype and immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements with the presence of the Philadelphia chromosome translocation in acute leukemias with myeloid morphology. Leukemia. 1991 May;5(5):373–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., Wright D., Erdman V. D., Cutting A. E. Amphotropic retrovirus vector system for human cell gene transfer. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1730–1737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stass S., Mirro J., Melvin S., Pui C. H., Murphy S. B., Williams D. Lineage switch in acute leukemia. Blood. 1984 Sep;64(3):701–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi T., Aicher W. K., Fujihashi K., Yamamoto M., McGhee J. R., Bluestone J. A., Kiyono H. Novel function for intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Murine CD3+, gamma/delta TCR+ T cells produce IFN-gamma and IL-5. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3736–3744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka T., Craig A. W. Cell-free transmission of murine myeloid leukaemia. Eur J Cancer. 1970 Aug;6(4):329–333. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(70)90098-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton A. C., Jenkins V. K., Walburg H. E., Jr, Tyndall R. L., Conklin J. W., Wald N. Observations on viral, chemical, and radiation-induced myeloid and lymphoid leukemias in RF mice. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1966 Sep;22:329–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe N., Nishi M., Ikawa Y., Amanuma H. A deletion in the Friend spleen focus-forming virus env gene is necessary for its product (gp55) to be leukemogenic. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2678–2686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2678-2686.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Koller R., Davidson W. Acute myeloid leukemia induction by amphotropic murine retrovirus (4070A): clonal integrations involve c-myb in some but not all leukemias. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3607–3616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3607-3616.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yancopoulos G. D., Blackwell T. K., Suh H., Hood L., Alt F. W. Introduced T cell receptor variable region gene segments recombine in pre-B cells: evidence that B and T cells use a common recombinase. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90759-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- di Celle P. F., Carbone A., Lo Coco F., Guerrasio A., Diverio D., Rosso C., Lopez M., Saglio G., Foà R. Identical utilization of T-cell receptor gene regions in B-lymphoid blast crisis of chronic myeloid leukemia and B-precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 1991 May;5(5):366–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]