Abstract
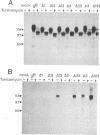
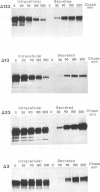
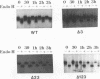
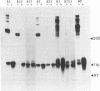
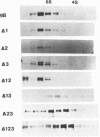
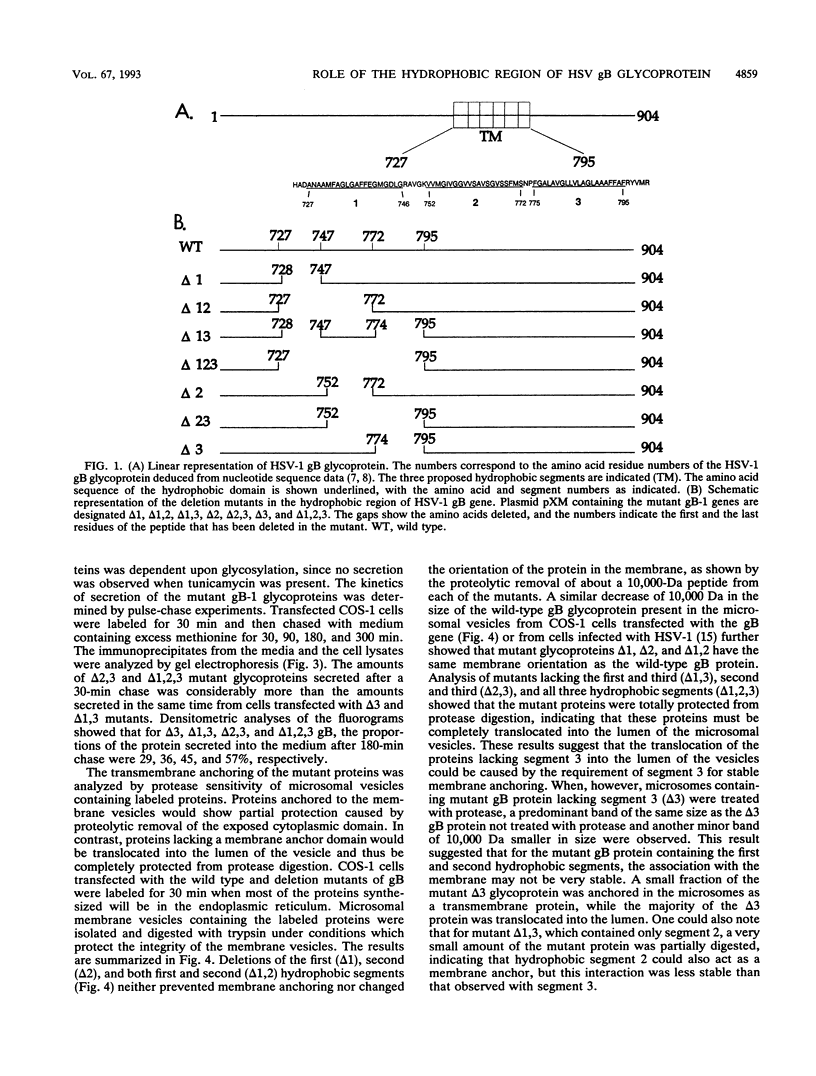
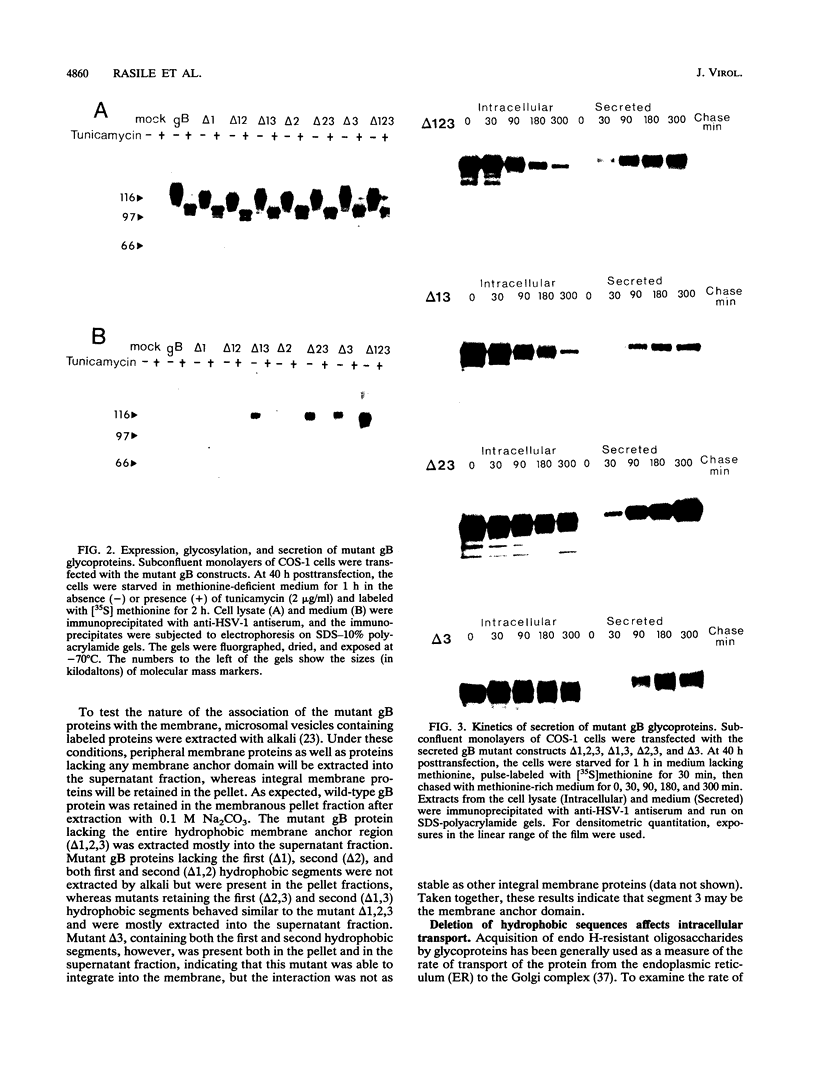
The gB glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1 is involved in viral entry and fusion and contains a predicted membrane-anchoring sequence of 69 hydrophobic amino acids, which can span the membrane three times, near the carboxy terminus. To define the membrane-anchoring sequence and the role of this hydrophobic stretch, we have constructed deletion mutants of gB-1, lacking one, two, or three predicted membrane-spanning segments within the 69 amino acids. Expression of the wild-type and mutant glycoproteins in COS-1 cells show that mutant glycoproteins lacking segment 3 (amino acids 774 to 795 of the gB-1 protein) were secreted from the cells. Protease digestion and alkaline extraction of microsomes containing labeled mutant proteins further showed that segment 3 was sufficient for stable membrane anchoring of the glycoproteins, indicating that this segment may specify the transmembrane domain of the gB glycoprotein. Also, the mutant glycoproteins containing segment 3 were localized in the nuclear envelop, which is the site of virus budding. Deletion of any of the hydrophobic segments, however, affected the intracellular transport and processing of the mutant glycoproteins. The mutant glycoproteins, although localized in the nuclear envelope, failed to complement the gB-null virus (K082). These results suggest that the carboxy-terminal hydrophobic region contains essential structural determinants of the functional gB glycoprotein.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams G. A., Rose J. K. Structural requirements of a membrane-spanning domain for protein anchoring and cell surface transport. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1007–1015. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali M. A., Butcher M., Ghosh H. P. Expression and nuclear envelope localization of biologically active fusion glycoprotein gB of herpes simplex virus in mammalian cells using cloned DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5675–5679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali M. A. Oligomerization of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and a 102 amino acid cytosolic domain is dispensable for dimer assembly. Virology. 1990 Oct;178(2):588–592. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90359-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann C. C., Maass D., Poruchynsky M. S., Atkinson P. H., Bellamy A. R. Topology of the non-structural rotavirus receptor glycoprotein NS28 in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1695–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bole D. G., Hendershot L. M., Kearney J. F. Posttranslational association of immunoglobulin heavy chain binding protein with nascent heavy chains in nonsecreting and secreting hybridomas. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1558–1566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher M., Raviprakash K., Ghosh H. P. Acid pH-induced fusion of cells by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins gB an gD. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5862–5868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Debroy C., Fox B. A., Pederson N. E., Person S. The nucleotide sequence of the gB glycoprotein gene of HSV-2 and comparison with the corresponding gene of HSV-1. Virology. 1986 Dec;155(2):322–333. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90196-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Fox B. A., DeLuca N. A., Person S. Nucleotide sequence of a region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 gB glycoprotein gene: mutations affecting rate of virus entry and cell fusion. Virology. 1984 Aug;137(1):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Fox B. A., DeLuca N. A., Person S. Nucleotide sequence specifying the glycoprotein gene, gB, of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90397-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. H., Gu B., Person S. Role of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1 in viral entry and cell fusion. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2596–2604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2596-2604.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. Z., Person S., DebRoy C., Gu B. H. Functional regions and structural features of the gB glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1. An analysis of linker insertion mutants. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):575–588. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90639-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai W. Z., Person S., Warner S. C., Zhou J. H., DeLuca N. A. Linker-insertion nonsense and restriction-site deletion mutations of the gB glycoprotein gene of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):714–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.714-721.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Au K. S., Estes M. K. Topography of the simian rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein (NS28) in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90557-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapsal J. M., Pereira L. Characterization of epitopes on native and denatured forms of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B. Virology. 1988 Jun;164(2):427–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90556-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson-Welsh L., Spear P. G. Amino-terminal sequence, synthesis, and membrane insertion of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.1-7.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson-Welsh L., Spear P. G. Oligomerization of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein B. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):803–806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.803-806.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton T., Courtney R. J. Virus-specific glycoproteins associated with the nuclear fraction of herpes simplex virus type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):594–597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.594-597.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Zimmer K. P., Wagner K. R., Healey G. A., Mellman I., Helenius A. Folding, trimerization, and transport are sequential events in the biogenesis of influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90381-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crise B., Ruusala A., Zagouras P., Shaw A., Rose J. K. Oligomerization of glycolipid-anchored and soluble forms of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5328–5333. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5328-5333.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlington R. W., Moss L. H., 3rd Herpesvirus envelopment. J Virol. 1968 Jan;2(1):48–55. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.1.48-55.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Ruusala A., Machamer C., Helenius J., Helenius A., Rose J. K. Differential effects of mutations in three domains on folding, quaternary structure, and intracellular transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):89–99. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einfeld D., Hunter E. Oligomeric structure of a prototype retrovirus glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8688–8692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garoff H. Using recombinant DNA techniques to study protein targeting in the eucaryotic cell. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:403–445. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gompels U., Minson A. The properties and sequence of glycoprotein H of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1986 Sep;153(2):230–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan J. L., Rose J. K. Conversion of a secretory protein into a transmembrane protein results in its transport to the Golgi complex but not to the cell surface. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffey M. L., Spear P. G. Alterations in glycoprotein gB specified by mutants and their partial revertants in herpes simplex virus type 1 and relationship to other mutant phenotypes. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):114–128. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.114-128.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Highlander S. L., Goins W. F., Person S., Holland T. C., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Oligomer formation of the gB glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4275–4283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4275-4283.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson L., Browne H., Wargent V., Davis-Poynter N., Primorac S., Goldsmith K., Minson A. C., Johnson D. C. A novel herpes simplex virus glycoprotein, gL, forms a complex with glycoprotein H (gH) and affects normal folding and surface expression of gH. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2240–2250. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2240-2250.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson L., Goldsmith K., Snoddy D., Ghosh H., Graham F. L., Johnson D. C. Identification and characterization of a novel herpes simplex virus glycoprotein, gK, involved in cell fusion. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5603–5609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5603-5609.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Ghosh-Choudhury G., Smiley J. R., Fallis L., Graham F. L. Abundant expression of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein gB using an adenovirus vector. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90613-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga J., Chatterjee S., Whitley R. J. Studies on herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins using monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):385–389. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Assembly of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:631–664. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarovits J., Shia S. P., Ktistakis N., Lee M. S., Bird C., Roth M. G. The effects of foreign transmembrane domains on the biosynthesis of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4760–4767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little S. P., Jofre J. T., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. A virion-associated glycoprotein essential for infectivity of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1981 Nov;115(1):149–160. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F. Multi-spanning membrane proteins: how accurate are the models? Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Sep;13(9):332–334. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90101-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Chatterjee S., Whitley R. J., Roizman B. Identification of a herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein gene within a gene cluster dispensable for growth in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4303–4307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Rose J. K. A specific transmembrane domain of a coronavirus E1 glycoprotein is required for its retention in the Golgi region. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1205–1214. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manservigi R., Spear P. G., Buchan A. Cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus is promoted and suppressed by different viral glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro D., Qadri I., Pereira L. A mutation in the ectodomain of herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein B causes defective processing and retention in the endoplasmic reticulum. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90842-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro D., Qadri I., Pereira L. Transport and secretion of truncated derivatives of herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein B. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):234–245. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks G. D., Lamb R. A. Defective assembly and intracellular transport of mutant paramyxovirus hemagglutinin-neuraminidase proteins containing altered cytoplasmic domains. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3605–3616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3605-3616.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., Kousoulas K. G., Pereira L., Roizman B. Anatomy of the herpes simplex virus 1 strain F glycoprotein B gene: primary sequence and predicted protein structure of the wild type and of monoclonal antibody-resistant mutants. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):243–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.243-253.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez L. G., Davis G. L., Hunter E. Mutants of the Rous sarcoma virus envelope glycoprotein that lack the transmembrane anchor and cytoplasmic domains: analysis of intracellular transport and assembly into virions. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):2981–2988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.2981-2988.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qadri I., Gimeno C., Navarro D., Pereira L. Mutations in conformation-dependent domains of herpes simplex virus 1 glycoprotein B affect the antigenic properties, dimerization, and transport of the molecule. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):135–152. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan M. P., Chen L. B., Knipe D. M. The intranuclear location of a herpes simplex virus DNA-binding protein is determined by the status of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):857–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviprakash K., Rasile L., Ghosh K., Ghosh H. P. Shortened cytoplasmic domain affects intracellular transport but not nuclear localization of a viral glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1777–1782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Buckmaster A., Bell S., Hodgman C., Minson A. C. Identification of a new glycoprotein of herpes simplex virus type 1 and genetic mapping of the gene that codes for it. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):647–655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.647-655.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doms R. W. Regulation of protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:257–288. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Haffey M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. III. Role of glycoprotein VP7(B2) in virion infectivity. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1149–1158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1149-1158.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarmiento M., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. IV. Conformation of the virion glycoprotein designated VP7(B2). J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1159–1167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1159-1167.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Schlesinger S. Domains of virus glycoproteins. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:1–44. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60315-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter S. D., Zweig M., Hampar B. Monoclonal antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 proteins, including the immediate-early protein ICP 4. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):684–692. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.684-692.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh I., Doms R. W., Wagner K. R., Helenius A. Intracellular transport of soluble and membrane-bound glycoproteins: folding, assembly and secretion of anchor-free influenza hemagglutinin. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):631–639. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon K. A., Robbins A. K., Enquist L. W. Mutations in the C-terminal hydrophobic domain of pseudorabies virus gIII affect both membrane anchoring and protein export. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5952–5960. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5952-5960.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens E. B., Compans R. W. Assembly of animal viruses at cellular membranes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:489–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrisi M. R., Di Lazzaro C., Pavan A., Pereira L., Campadelli-Fiume G. Herpes simplex virus envelopment and maturation studied by fracture label. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):554–561. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.554-561.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Ciarletta A. B., Temple P. A., Chung M. P., Kovacic S., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Leary A. C., Kriz R., Donahue R. E., Wong G. G. Human IL-3 (multi-CSF): identification by expression cloning of a novel hematopoietic growth factor related to murine IL-3. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Q., Courtney R. J. Chemical crosslinking of glycoproteins on the envelope of herpes simplex virus. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):377–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]