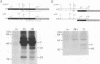Abstract
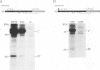
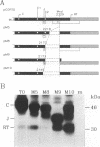
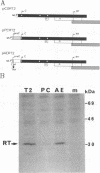
The hepatitis B virus (HBV) P gene which encodes the reverse transcriptase and other proteins required for replication is expressed on the bicistronic mRNA pregenome which also encodes the capsid protein in its first cistron. Recent results have suggested that the hepadnaviral P gene is translated by internal entry of ribosomes upstream from the P gene, in the overlapping C gene. Using a reporter gene fused to the HBV C or P gene, we demonstrate that the C sequence does not allow internal initiation of translation. Alternatively, our results support a model in which the HBV P gene is translated by ribosomes which scan from the capped extremity of the bicistronic mRNA pregenome. The mechanism by which the ribosomes scan past four AUGs before they initiate translation at the P AUG was analyzed. Our results show that these AUGs are skipped via two mechanisms: leaky scanning on AUGs in a weak or suboptimal initiation context and translation of an out-of-C-frame minicistron followed by reinitiation at P AUG. The minicistron translation allows ribosomes to bypass an AUG in a favorable context that would otherwise be used as a start codon for translation of a truncated capsid protein. Our results suggest that this elaborated scanning mechanism permits the coordinate expression of the HBV C and P genes on the viral bicistronic mRNA pregenome.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abastado J. P., Miller P. F., Jackson B. M., Hinnebusch A. G. Suppression of ribosomal reinitiation at upstream open reading frames in amino acid-starved cells forms the basis for GCN4 translational control. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):486–496. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An G., Hidaka K., Siminovitch L. Expression of bacterial beta-galactosidase in animal cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1628–1632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. Hepadnaviral assembly is initiated by polymerase binding to the encapsidation signal in the viral RNA genome. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3413–3420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05420.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. The amino-terminal domain of the hepadnaviral P-gene encodes the terminal protein (genome-linked protein) believed to prime reverse transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4185–4192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates B., Hardin J., Zhan X., Drickamer K., Goldfarb M. Biosynthesis of human fibroblast growth factor-5. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1840–1845. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belsham G. J. Dual initiation sites of protein synthesis on foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA are selected following internal entry and scanning of ribosomes in vivo. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):1105–1110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05150.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Mechanism of translation of the hepadnaviral polymerase (P) gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5158–5162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Hirsch R. C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Effects of insertional and point mutations on the functions of the duck hepatitis B virus polymerase. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5553–5558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5553-5558.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang L. J., Pryciak P., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Biosynthesis of the reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B viruses involves de novo translational initiation not ribosomal frameshifting. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):364–368. doi: 10.1038/337364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Scanning independent ribosomal initiation of the Sendai virus X protein. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2869–2874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J. The sequence context of the initiation codon in the encephalomyocarditis virus leader modulates efficiency of internal translation initiation. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1924–1932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1924-1932.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Huang J. T., Schneider R. J. Translation by the adenovirus tripartite leader: elements which determine independence from cap-binding protein complex. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2669–2677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2669-2677.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolph P. J., Racaniello V., Villamarin A., Palladino F., Schneider R. J. The adenovirus tripartite leader may eliminate the requirement for cap-binding protein complex during translation initiation. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2059–2066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2059-2066.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fütterer J., Hohn T. Role of an upstream open reading frame in the translation of polycistronic mRNAs in plant cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):3851–3857. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.3851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison T., Graham F., Williams J. Host-range mutants of adenovirus type 5 defective for growth in HeLa cells. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90428-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Fäcke M., Kräusslich H. G., Lee C. K., Wimmer E. Characterization of poliovirus 2A proteinase by mutational analysis: residues required for autocatalytic activity are essential for induction of cleavage of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4226–4231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4226-4231.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman G. E., O'Brien W. E., Beaudet A. L. An E. coli beta-galactosidase cassette suitable for study of eukaryotic expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7130–7130. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch R. C., Lavine J. E., Chang L. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Polymerase gene products of hepatitis B viruses are required for genomic RNA packaging as wel as for reverse transcription. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):552–555. doi: 10.1038/344552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Howell M. T., Kaminski A. The novel mechanism of initiation of picornavirus RNA translation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90302-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J., Wimmer E. Initiation of protein synthesis by internal entry of ribosomes into the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1651–1660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1651-1660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean-Jean O., Levrero M., Will H., Perricaudet M., Rossignol J. M. Expression mechanism of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) C gene and biosynthesis of HBe antigen. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90356-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jean-Jean O., Weimer T., de Recondo A. M., Will H., Rossignol J. M. Internal entry of ribosomes and ribosomal scanning involved in hepatitis B virus P gene expression. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5451–5454. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5451-5454.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminski A., Howell M. T., Jackson R. J. Initiation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA translation: the authentic initiation site is not selected by a scanning mechanism. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3753–3759. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. G., Lo S. J. Evidence for involvement of a ribosomal leaky scanning mechanism in the translation of the hepatitis B virus pol gene from the viral pregenome RNA. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):342–352. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90763-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macejak D. G., Sarnow P. Internal initiation of translation mediated by the 5' leader of a cellular mRNA. Nature. 1991 Sep 5;353(6339):90–94. doi: 10.1038/353090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Imai M., Shimozaki M., Hoshi Y., Iizuka H., Gotanda T., Tsuda F., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned hepatitis B virus genome, subtype ayr: comparison with genomes of the other three subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2305–2314. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Tsuda F., Sakugawa H., Sastrosoewignjo R. I., Imai M., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Typing hepatitis B virus by homology in nucleotide sequence: comparison of surface antigen subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2575–2583. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasek M., Goto T., Gilbert W., Zink B., Schaller H., MacKay P., Leadbetter G., Murray K. Hepatitis B virus genes and their expression in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Dec 6;282(5739):575–579. doi: 10.1038/282575a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peabody D. S., Berg P. Termination-reinitiation occurs in the translation of mammalian cell mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2695–2703. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Insertion mutagenesis to increase secondary structure within the 5' noncoding region of a eukaryotic mRNA reduces translational efficiency. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty I. T., Edwards M. C., Jackson A. O. Systemic movement of an RNA plant virus determined by a point substitution in a 5' leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8894–8897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radziwill G., Tucker W., Schaller H. Mutational analysis of the hepatitis B virus P gene product: domain structure and RNase H activity. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):613–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.613-620.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury S., Shih C. cis rescue of a mutated reverse transcriptase gene of human hepatitis B virus by creation of an internal ATG. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1063–1069. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1063-1069.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santantonio T., Jung M. C., Miska S., Pastore G., Pape G. R., Will H. Prevalence and type of pre-C HBV mutants in anti-HBe positive carriers with chronic liver disease in a highly endemic area. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):840–844. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)91022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Radziwill G., Schaller H. Synthesis and encapsidation of duck hepatitis B virus reverse transcriptase do not require formation of core-polymerase fusion proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90986-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleigh M. J. A nonchromatographic assay for expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in eucaryotic cells. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90180-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Masiarz F. R., Rutter W. J. A signal peptide encoded within the precore region of hepatitis B virus directs the secretion of a heterogeneous population of e antigens in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8405–8409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. Human immunodeficiency virus tat-activated expression of poliovirus protein 2A inhibits mRNA translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2143–2146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. P., Li J. S., Vitvitski L., Trépo C. Replication capacities of natural and artificial precore stop codon mutants of hepatitis B virus: relevance of pregenome encapsidation signal. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90185-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudin M., Wolstenholme A. J., Tsiquaye K. N., Zuckerman A. J., Harrison T. J. The complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of a hepatitis B virus isolated from a naturally infected chimpanzee. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1383–1389. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]