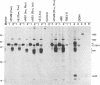
Abstract
Two new chimeric flaviviruses were constructed from full-length cDNAs that contained tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) CME or ME structural protein genes and the remaining genes derived from dengue type 4 virus (DEN4). Studies involving mice inoculated intracerebrally with the ME chimeric virus indicated that it retained the neurovirulence of its TBEV parent from which its pre-M and E genes were derived. However, unlike parental TBEV, the chimeric virus did not produce encephalitis when mice were inoculated peripherally, indicating a loss of neuroinvasiveness. In the present study, the ME chimeric virus (vME) was subjected to mutational analysis in an attempt to reduce or ablate neurovirulence measured by direct inoculation of virus into the brain. We identified three distinct mutations that were each associated independently with a significant reduction of mouse neurovirulence of vME. These mutations ablated (i) the TBEV pre-M cleavage site, (ii) the TBEV E glycosylation site, or (iii) the first DEN4 NS1 glycosylation site. In contrast, ablation of the second DEN4 NS1 glycosylation site or the TBE pre-M glycosylation site or amino acid substitution at two positions in the TBEV E protein increased neurovirulence. The only conserved feature of the three attenuated mutants was restriction of virus yield in both simian and mosquito cells. Following parenteral inoculation, these attenuated mutants induced complete resistance in mice to fatal encephalitis caused by the highly neurovirulent vME.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aihara S., Rao C. M., Yu Y. X., Lee T., Watanabe K., Komiya T., Sumiyoshi H., Hashimoto H., Nomoto A. Identification of mutations that occurred on the genome of Japanese encephalitis virus during the attenuation process. Virus Genes. 1991 Apr;5(2):95–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00571925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blok J., McWilliam S. M., Butler H. C., Gibbs A. J., Weiller G., Herring B. L., Hemsley A. C., Aaskov J. G., Yoksan S., Bhamarapravati N. Comparison of a dengue-2 virus and its candidate vaccine derivative: sequence relationships with the flaviviruses and other viruses. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):573–590. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90460-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch F. X., Orlich M., Klenk H. D., Rott R. The structure of the hemagglutinin, a determinant for the pathogenicity of influenza viruses. Virology. 1979 May;95(1):197–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90414-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray M., Lai C. J. Construction of intertypic chimeric dengue viruses by substitution of structural protein genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10342–10346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bray M., Zhao B. T., Markoff L., Eckels K. H., Chanock R. M., Lai C. J. Mice immunized with recombinant vaccinia virus expressing dengue 4 virus structural proteins with or without nonstructural protein NS1 are protected against fatal dengue virus encephalitis. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2853–2856. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2853-2856.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falgout B., Bray M., Schlesinger J. J., Lai C. J. Immunization of mice with recombinant vaccinia virus expressing authentic dengue virus nonstructural protein NS1 protects against lethal dengue virus encephalitis. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4356–4363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4356-4363.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirakhoo F., Bolin R. A., Roehrig J. T. The Murray Valley encephalitis virus prM protein confers acid resistance to virus particles and alters the expression of epitopes within the R2 domain of E glycoprotein. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):921–931. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90267-S. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirakhoo F., Heinz F. X., Kunz C. Epitope model of tick-borne encephalitis virus envelope glycoprotein E: analysis of structural properties, role of carbohydrate side chain, and conformational changes occurring at acidic pH. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):90–99. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guirakhoo F., Heinz F. X., Mandl C. W., Holzmann H., Kunz C. Fusion activity of flaviviruses: comparison of mature and immature (prM-containing) tick-borne encephalitis virions. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jun;72(Pt 6):1323–1329. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-6-1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Dalrymple J. M., Strauss J. H., Rice C. M. Comparison of the virulent Asibi strain of yellow fever virus with the 17D vaccine strain derived from it. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2019–2023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Zhao B. T., Hori H., Bray M. Infectious RNA transcribed from stably cloned full-length cDNA of dengue type 4 virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5139–5143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackow E., Makino Y., Zhao B. T., Zhang Y. M., Markoff L., Buckler-White A., Guiler M., Chanock R., Lai C. J. The nucleotide sequence of dengue type 4 virus: analysis of genes coding for nonstructural proteins. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl C. W., Heinz F. X., Kunz C. Sequence of the structural proteins of tick-borne encephalitis virus (western subtype) and comparative analysis with other flaviviruses. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl C. W., Iacono-Connors L., Wallner G., Holzmann H., Kunz C., Heinz F. X. Sequence of the genes encoding the structural proteins of the low-virulence tick-borne flaviviruses Langat TP21 and Yelantsev. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):891–895. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90567-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitayaphan S., Grant J. A., Chang G. J., Trent D. W. Nucleotide sequence of the virulent SA-14 strain of Japanese encephalitis virus and its attenuated vaccine derivative, SA-14-14-2. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90519-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletnev A. G., Bray M., Huggins J., Lai C. J. Construction and characterization of chimeric tick-borne encephalitis/dengue type 4 viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10532–10536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletnev A. G., Yamshchikov V. F., Blinov V. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome and complete amino acid sequence of the polyprotein of tick-borne encephalitis virus. Virology. 1990 Jan;174(1):250–263. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90073-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pletnev A. G., Yamshchikov V. F., Blinov V. M. Tick-borne encephalitis virus genome. The nucleotide sequence coding for virion structural proteins. FEBS Lett. 1986 May 12;200(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81160-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph V. B., Winkler G., Stollar V. Acidotropic amines inhibit proteolytic processing of flavivirus prM protein. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):450–458. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90099-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiu S. Y., Ayres M. D., Gould E. A. Genomic sequence of the structural proteins of louping ill virus: comparative analysis with tick-borne encephalitis virus. Virology. 1991 Jan;180(1):411–415. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90048-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsekhanovskaia N. A., Matveev L. E., Pletnev A. G., Rubin S. G., Safronov I. V., Pressman E. K. Lokalizatsiia antigennogo uchstka belka obolochki virusa kleshchevogo éntsefalita s ispol'zovaniem monoklonal'nykh antitel. Bioorg Khim. 1991 Mar;17(3):334–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venugopal K., Buckley A., Reid H. W., Gould E. A. Nucleotide sequence of the envelope glycoprotein of Negishi virus shows very close homology to louping ill virus. Virology. 1992 Sep;190(1):515–521. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)91245-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler G., Heinz F. X., Kunz C. Studies on the glycosylation of flavivirus E proteins and the role of carbohydrate in antigenic structure. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90460-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao B., Mackow E., Buckler-White A., Markoff L., Chanock R. M., Lai C. J., Makino Y. Cloning full-length dengue type 4 viral DNA sequences: analysis of genes coding for structural proteins. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90169-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]