Abstract
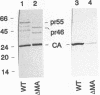
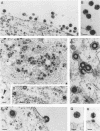
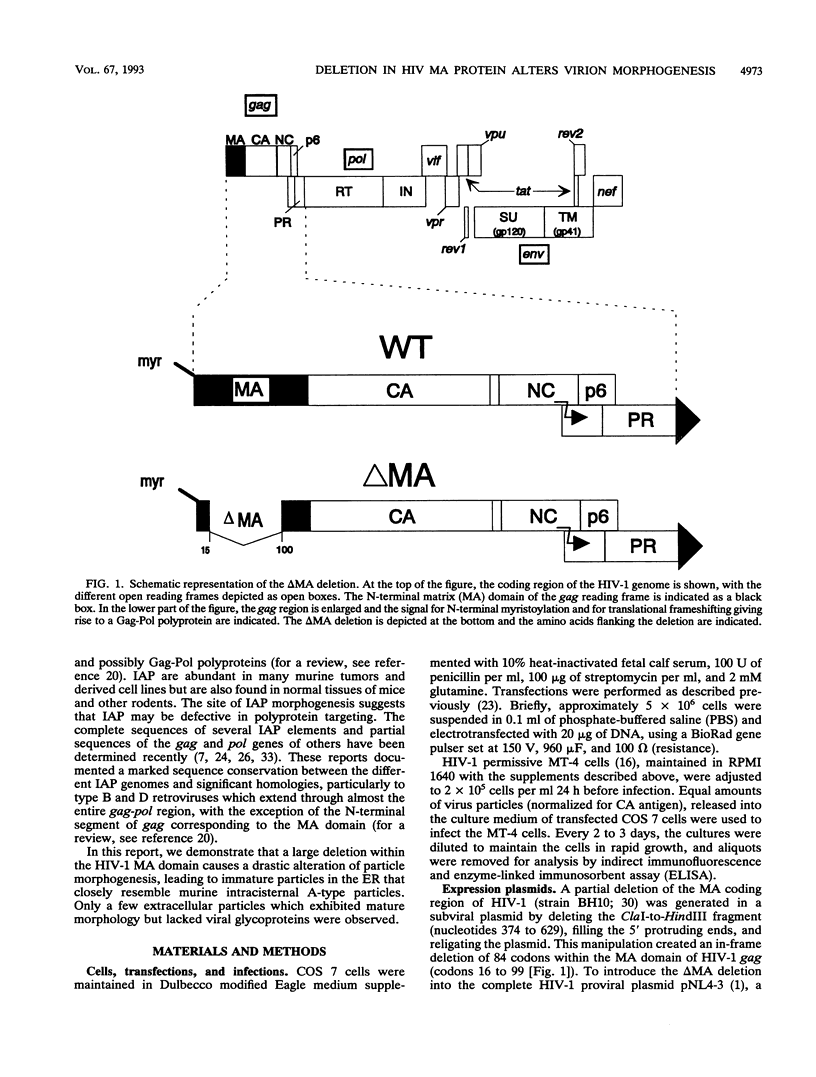
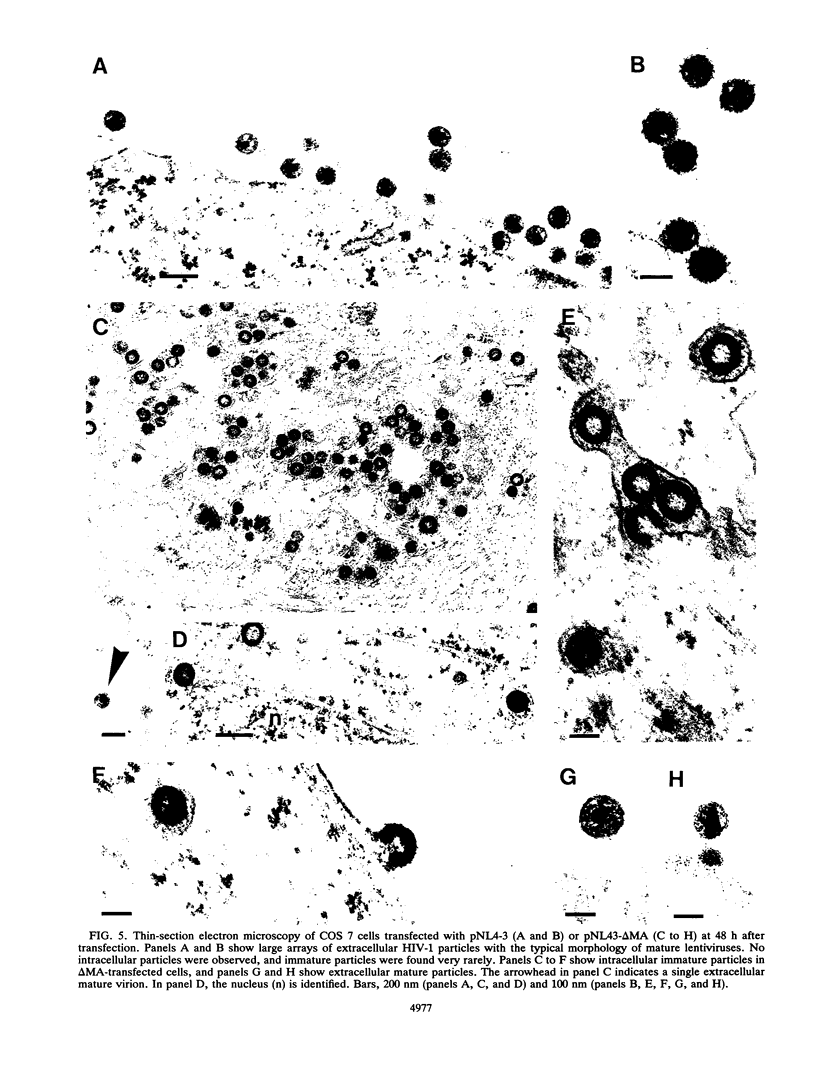
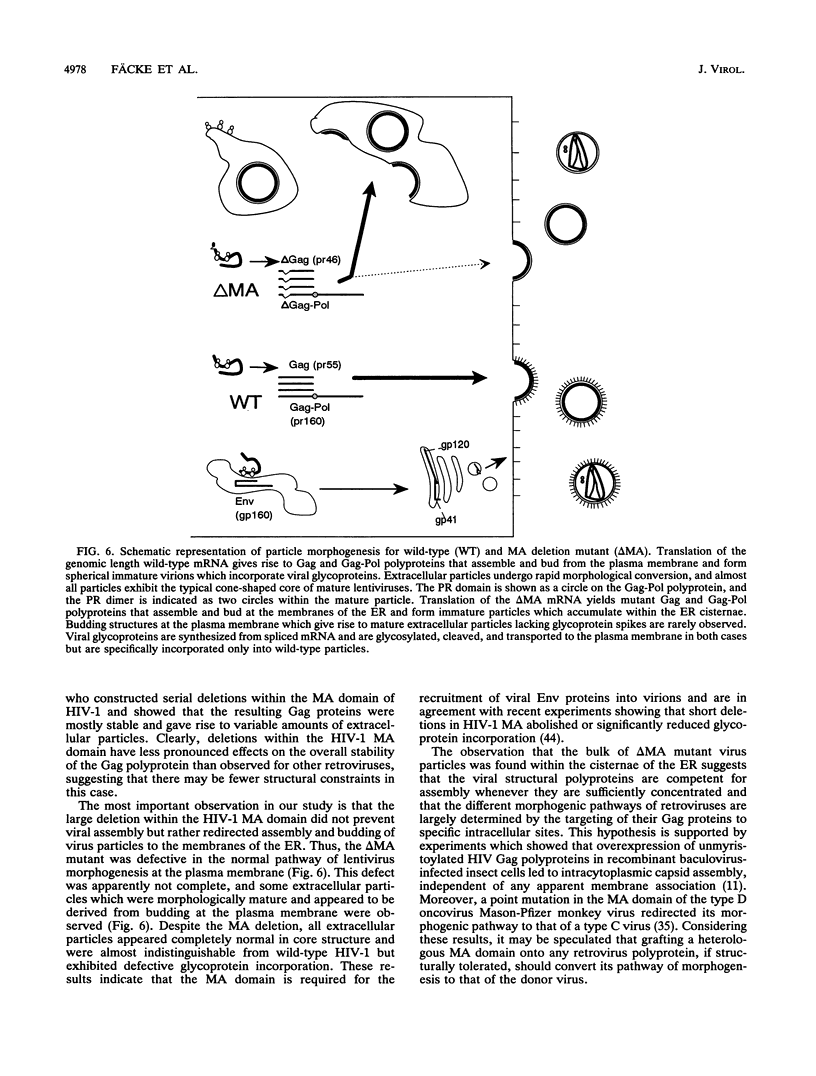
Morphogenesis of retroviruses involves assembly of the structural Gag and Gag-Pol polyproteins with subsequent budding of the virus particle from the plasma membrane and proteolytic cleavage by the viral proteinase. The matrix (MA) domain, representing the N-terminal segment of Gag, plays a critical role in this process. We constructed an in-frame deletion in the MA coding region (lacking codons 16 to 99) of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 gag gene. Following transient transfection of the complete proviral DNA carrying the deletion, the mutant polyprotein was synthesized and proteolytically processed like the wild-type polyprotein. However, release of virus particles was reduced approximately 10-fold. The extracellular particles that were released did not contain viral glycoproteins and were noninfectious. Electron micrographs revealed budding of virus particles into the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) of transfected cells and large numbers of particles within the ER. These particles were all immature and morphologically indistinguishable from intracisternal A-type particles, a class of murine endogenous retrovirus elements. Budding structures at the plasma membrane were rarely seen and only a few extracellular particles were observed, but in contrast to those in the ER, these particles had the morphology of mature particles, similar to that of wild-type HIV, except for the lack of surface projections.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosch J. V., Schwarz R. T. Processing of gPr92env, the precursor to the glycoproteins of Rous sarcoma virus: use of inhibitors of oligosaccharide trimming and glycoprotein transport. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):95–109. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M., Ratner L. Myristoylation-dependent replication and assembly of human immunodeficiency virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):523–527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Der C. J., Solski P. A. The six amino-terminal amino acids of p60src are sufficient to cause myristylation of p21v-ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3960–3963. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Bonneville F., Kriz R., Kelleher K., Bean K., Kaufman R. J. Molecular cloning and characterization of a complete Chinese hamster provirus related to intracisternal A particle genomes. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4713–4719. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4713-4719.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhardt A., Bosch J. V., Ziemiecki A., Friis R. R. Rous sarcoma virus p19 and gp35 can be chemically crosslinked to high molecular weight complexes. An insight into virus assembly. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 5;174(2):297–317. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90340-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R. Assembly and morphology of HIV: potential effect of structure on viral function. AIDS. 1991 Jun;5(6):617–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R., Hausmann E. H., Ozel M., Pauli G., Koch M. A. Fine structure of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and immunolocalization of structural proteins. Virology. 1987 Jan;156(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90449-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheysen D., Jacobs E., de Foresta F., Thiriart C., Francotte M., Thines D., De Wilde M. Assembly and release of HIV-1 precursor Pr55gag virus-like particles from recombinant baculovirus-infected insect cells. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):103–112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90873-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb D. S. Are the cytosolic components of the nuclear, ER, and mitochondrial import apparatus functionally related? Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90094-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grief C., Farrar G. H., Kent K. A., Berger E. G. The assembly of HIV within the Golgi apparatus and Golgi-derived vesicles of JM cell syncytia. AIDS. 1991 Dec;5(12):1433–1439. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199112000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlinger H. G., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Role of capsid precursor processing and myristoylation in morphogenesis and infectivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5781–5785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M., Jelinek L., Whiting S., Barklis E. Transport and assembly of gag proteins into Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5306–5316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5306-5316.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Koyanagi Y., Yamamoto N. Infection of HTLV-III/LAV in HTLV-I-carrying cells MT-2 and MT-4 and application in a plaque assay. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):563–566. doi: 10.1126/science.2992081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Blaug G., Hansen M., Barklis E. Assembly of gag-beta-galactosidase proteins into retrovirus particles. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2265–2279. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2265-2279.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen E. C., Pedersen F. S., Jørgensen P. Matrix protein of Akv murine leukemia virus: genetic mapping of regions essential for particle formation. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4479–4487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4479-4487.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimkait T., Strebel K., Hoggan M. D., Martin M. A., Orenstein J. M. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific protein vpu is required for efficient virus maturation and release. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):621–629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.621-629.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Wimmer E. Viral proteinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:701–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Lueders K. K. The intracisternal A-particle gene family: structure and functional aspects. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:183–276. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J., Baltimore D., Bishop J. M., Coffin J., Fleissner E., Goff S. P., Oroszlan S., Robinson H., Skalka A. M., Temin H. M. Standardized and simplified nomenclature for proteins common to all retroviruses. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1808–1809. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1808-1809.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald K. Osmium ferricyanide fixation improves microfilament preservation and membrane visualization in a variety of animal cell types. J Ultrastruct Res. 1984 Feb;86(2):107–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(84)80051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergener K., Fäcke M., Welker R., Brinkmann V., Gelderblom H. R., Kräusslich H. G. Analysis of HIV particle formation using transient expression of subviral constructs in mammalian cells. Virology. 1992 Jan;186(1):25–39. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90058-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Grossman Z., Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Nucleotide sequence of a complete mouse intracisternal A-particle genome: relationship to known aspects of particle assembly and function. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3020–3029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3020-3029.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedrig M., Hinkula J., Weigelt W., L'age-Stehr J., Pauli G., Rosen J., Wahren B. Epitope mapping of monoclonal antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 structural proteins by using peptides. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3525–3528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3525-3528.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Toh H., Miyata T., Awaya T. Nucleotide sequence of the Syrian hamster intracisternal A-particle gene: close evolutionary relationship of type A particle gene to types B and D oncovirus genes. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):387–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.387-394.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. J., Dubay J. W., Hunter E., Compans R. W. Human immunodeficiency virus envelope protein determines the site of virus release in polarized epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3987–3991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papsidero L. D., Sheu M., Ruscetti F. W. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-neutralizing monoclonal antibodies which react with p17 core protein: characterization and epitope mapping. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):267–272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.267-272.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. An N-terminal peptide from p60src can direct myristylation and plasma membrane localization when fused to heterologous proteins. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):374–377. doi: 10.1038/314374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D., Ling H. P. Identification of a 32K plasma membrane protein that binds to the myristylated amino-terminal sequence of p60v-src. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):84–86. doi: 10.1038/346084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Specific and saturable binding of pp60v-src to plasma membranes: evidence for a myristyl-src receptor. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):281–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90842-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuss F. U., Schaller H. C. cDNA sequence and genomic characterization of intracisternal A-particle-related retroviral elements containing an envelope gene. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5702–5709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5702-5709.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. A single amino acid substitution within the matrix protein of a type D retrovirus converts its morphogenesis to that of a type C retrovirus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):77–86. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90289-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. Amino acid substitutions within the matrix protein of type D retroviruses affect assembly, transport and membrane association of a capsid. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):535–546. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. Myristylation is required for intracellular transport but not for assembly of D-type retrovirus capsids. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1045–1053. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1045-1053.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. Structural role of the matrix protein of type D retroviruses in gag polyprotein stability and capsid assembly. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4383–4389. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4383-4389.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer W. E., Jr, Love W. E., Fenderson F. F. Cooperative dimeric and tetrameric clam haemoglobins are novel assemblages of myoglobin folds. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):277–280. doi: 10.1038/316277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer J. B., Palade G. E. Effects of Brefeldin A on the Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum and viral envelope glycoproteins in murine erythroleukemia cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;54(1):38–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verner K., Schatz G. Protein translocation across membranes. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1307–1313. doi: 10.1126/science.2842866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Craven R. C. Form, function, and use of retroviral gag proteins. AIDS. 1991 Jun;5(6):639–654. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199106000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Craven R. C., Weldon R. A., Jr, Nelle T. D., Erdie C. R. Suppression of retroviral MA deletions by the amino-terminal membrane-binding domain of p60src. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3804–3812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3804-3812.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X., Yu Q. C., Lee T. H., Essex M. The C terminus of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 matrix protein is involved in early steps of the virus life cycle. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5667–5670. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5667-5670.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X., Yuan X., Matsuda Z., Lee T. H., Essex M. The matrix protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is required for incorporation of viral envelope protein into mature virions. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4966–4971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4966-4971.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Transcending the impenetrable: how proteins come to terms with membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jun 9;947(2):307–333. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(88)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]