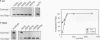Abstract
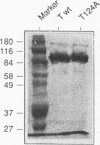
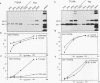
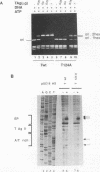
A mutant simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor (T) antigen bearing alanine instead of threonine at residue 124 (T124A) failed to replicate SV40 DNA in infected monkey cells (J. Schneider and E. Fanning, J. Virol. 62:1598-1605, 1988). We investigated the biochemical properties of T124A T antigen in greater detail by using purified protein from a baculovirus expression system. Purified T124A is defective in SV40 DNA replication in vitro, but does bind specifically to the viral origin under the conditions normally used for DNA replication. The mutant protein forms double-hexamer complexes at the origin in an ATP-dependent fashion, although the binding reaction requires somewhat higher protein concentrations than the wild-type protein. Binding of T124A protein results in local distortion of the origin DNA similar to that observed with the wild-type protein. These findings indicate that the replication defect of T124A protein is not due to failure to recognize and occupy the origin. Under some conditions T124A is capable of unwinding short origin DNA fragments. However, the mutant protein is almost completely defective in unwinding of circular plasmid DNA molecules containing the SV40 origin. Since the helicase activity of T124A is essentially identical to that of the wild-type protein, we conclude that the mutant is defective in the initial opening of the duplex at the origin, possibly as a result of altered hexamer-hexamer interactions. The phenotype of T124A suggests a possible role for phosphorylation of threonine 124 by cyclin-dependent kinases in controlling the origin unwinding activity of T antigen in infected cells.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell S. P., Stillman B. ATP-dependent recognition of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication by a multiprotein complex. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):128–134. doi: 10.1038/357128a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Bullock P. A., Hurwitz J. Binding and unwinding--how T antigen engages the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90730-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Differential induction of structural changes in the simian virus 40 origin of replication by T antigen. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1228–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1228-1235.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Hurwitz J. ATP stimulates the binding of simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor antigen to the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):64–68. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Hurwitz J. Localized melting and structural changes in the SV40 origin of replication induced by T-antigen. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3149–3158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A. Inhibition of structural changes in the simian virus 40 core origin of replication by mutation of essential origin sequences. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5248–5255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5248-5255.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowiec J. A., Zhang L., Sasse-Dwight S., Gralla J. D. DNA supercoiling promotes formation of a bent repression loop in lac DNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):101–111. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90513-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock P. A., Seo Y. S., Hurwitz J. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: pulse-chase experiments identify the first labeled species as topologically unwound. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3944–3948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock P. A., Seo Y. S., Hurwitz J. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA synthesis in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2350–2361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cegielska A., Virshup D. M. Control of simian virus 40 DNA replication by the HeLa cell nuclear kinase casein kinase I. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1202–1211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Sanghera J. S., Pelech S. L. Definition of a consensus sequence for peptide substrate recognition by p44mpk, the meiosis-activated myelin basic protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15180–15184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. L., Wright P. J., DeLucia A. L., Lewton B. A., Anderson M. E., Tegtmeyer P. Critical spatial requirement within the origin of simian virus 40 DNA replication. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):91–96. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.91-96.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins K. L., Kelly T. J. Effects of T antigen and replication protein A on the initiation of DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase alpha-primase. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2108–2115. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Deb S., Partin K., Tegtmeyer P. Functional interactions of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication with flanking regulatory sequences. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.138-144.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Borowiec J. A., Eki T., Hurwitz J. The simian virus 40 T antigen double hexamer assembles around the DNA at the replication origin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14129–14137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Bullock P., Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA replication: SV40 large T antigen unwinds DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Dodson M., Echols H., Hurwitz J. ATP-dependent formation of a specialized nucleoprotein structure by simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor antigen at the SV40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8981–8985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 large T antigen untwists DNA at the origin of DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5062–5071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S. P., Tegtmeyer P. ATP enhances the binding of simian virus 40 large T antigen to the origin of replication. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3649–3654. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3649-3654.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Nathans D. Regulatory mutants of simian virus 40. Effect of mutations at a T antigen binding site on DNA replication and expression of viral genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):531–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90265-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Cocker J. H. Protein-DNA interactions at a yeast replication origin. Nature. 1992 May 14;357(6374):169–172. doi: 10.1038/357169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F. Early events in eukaryotic DNA replication. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;2(10):298–303. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson M., Dean F. B., Bullock P., Echols H., Hurwitz J. Unwinding of duplex DNA from the SV40 origin of replication by T antigen. Science. 1987 Nov 13;238(4829):964–967. doi: 10.1126/science.2823389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Copeland W. C., Wang T. S. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication requires the interaction of a specific domain of human DNA polymerase alpha with large T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):809–820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Erdile L. F., Gilbert I. U., von Winkler D., Kelly T. J., Fanning E. Interaction of DNA polymerase alpha-primase with cellular replication protein A and SV40 T antigen. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):769–776. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Höss A., Arthur A. K., Fanning E. SV40 T antigen binds directly to the large subunit of purified DNA polymerase alpha. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3329–3336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdile L. F., Collins K. L., Russo A., Simancek P., Small D., Umbricht C., Virshup D., Cheng L., Randall S., Weinberg D. Initiation of SV40 DNA replication: mechanism and control. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:303–313. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes H. G., Robinson B. S., Eisenberg S. At least three distinct proteins are necessary for the reconstitution of a specific multiprotein complex at a eukaryotic chromosomal origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11156–11160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Knippers R. Structure and function of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:55–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E. Simian virus 40 large T antigen: the puzzle, the pieces, and the emerging picture. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1289–1293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1289-1293.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. Interactions between SV40 T antigen and DNA polymerase alpha. New Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):84–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill S. C., von Hippel P. H. Calculation of protein extinction coefficients from amino acid sequence data. Anal Biochem. 1989 Nov 1;182(2):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90602-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetz G. S., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J., Matson S. W. The unwinding of duplex regions in DNA by the simian virus 40 large tumor antigen-associated DNA helicase activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):383–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Mann K., Walter G. Removal of serine phosphates from simian virus 40 large T antigen increases its ability to stimulate DNA replication in vitro but has no effect on ATPase and DNA binding. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3373–3380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3373-3380.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo Z. S., Gutierrez C., Heine U., Sogo J. M., Depamphilis M. L. Origin auxiliary sequences can facilitate initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro as they do in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3593–3602. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. Summary: put out more flags. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:757–769. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1071–1074. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90028-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höss A., Moarefi I., Scheidtmann K. H., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L., Dornreiter I., Arthur A. K., Fanning E. Altered phosphorylation pattern of simian virus 40 T antigen expressed in insect cells by using a baculovirus vector. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4799–4807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4799-4807.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimi Y., Claude A., Bullock P., Hurwitz J. Complete enzymatic synthesis of DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19723–19733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny M. K., Lee S. H., Hurwitz J. Multiple functions of human single-stranded-DNA binding protein in simian virus 40 DNA replication: single-strand stabilization and stimulation of DNA polymerases alpha and delta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9757–9761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E. Expression of simian virus 40 T antigen in insect cells using a baculovirus expression vector. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):72–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Driving the cell cycle: M phase kinase, its partners, and substrates. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90181-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6973–6977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: specificity of initiation and evidence for bidirectional replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1238–1246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo I. A., Hough P. V., Wall J. S., Dodson M., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. ATP-dependent assembly of double hexamers of SV40 T antigen at the viral origin of DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):658–662. doi: 10.1038/338658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto T., Eki T., Hurwitz J. Studies on the initiation and elongation reactions in the simian virus 40 DNA replication system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9712–9716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Ewen M. E., Strom D. K., Kato J. Y., Hanks S. K., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Identification and properties of an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type G1 cyclins. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90360-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVey D., Brizuela L., Mohr I., Marshak D. R., Gluzman Y., Beach D. Phosphorylation of large tumour antigen by cdc2 stimulates SV40 DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):503–507. doi: 10.1038/341503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melendy T., Stillman B. An interaction between replication protein A and SV40 T antigen appears essential for primosome assembly during SV40 DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3389–3395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr I. J., Stillman B., Gluzman Y. Regulation of SV40 DNA replication by phosphorylation of T antigen. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):153–160. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Eki T., Hurwitz J. Studies on the initiation of simian virus 40 replication in vitro: RNA primer synthesis and its elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):952–956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nethanel T., Kaufmann G. Two DNA polymerases may be required for synthesis of the lagging DNA strand of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5912–5918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5912-5918.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nethanel T., Zlotkin T., Kaufmann G. Assembly of simian virus 40 Okazaki pieces from DNA primers is reversibly arrested by ATP depletion. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6634–6640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6634-6640.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. E., Stenger J. E., Ray S., Welker R., Anderson M. E., Tegtmeyer P. Cooperative assembly of simian virus 40 T-antigen hexamers on functional halves of the replication origin. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2798–2806. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2798-2806.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R., Anderson M. E., Tegtmeyer P. Three domains in the simian virus 40 core origin orchestrate the binding, melting, and DNA helicase activities of T antigen. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):509–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.509-518.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R., Tegtmeyer P. Spacing is crucial for coordination of domain functions within the simian virus 40 core origin of replication. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1933–1942. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1933-1942.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelech S. L., Sanghera J. S. Mitogen-activated protein kinases: versatile transducers for cell signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jun;17(6):233–238. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)80005-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. The replication functions of SV40 T antigen are regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):735–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90179-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. The role of p34 kinases in the G1 to S-phase transition. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:529–561. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. M. Simian virus 40 (SV40) large tumor antigen causes stepwise changes in SV40 origin structure during initiation of DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):3939–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.3939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruediger R., Van Wart Hood J. E., Mumby M., Walter G. Constant expression and activity of protein phosphatase 2A in synchronized cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;11(8):4282–4285. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.8.4282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Vakalopoulou E., Mertz R., Mastrangelo I., Hough P., Tegtmeyer P., Fanning E. Seventeen base pairs of region I encode a novel tripartite binding signal for SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):539–548. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90111-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H. Phosphorylation of simian virus 40 large T antigen: cytoplasmic and nuclear phophorylation sites differ in their metabolic stability. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):85–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Virshup D. M., Kelly T. J. Protein phosphatase 2A dephosphorylates simian virus 40 large T antigen specifically at residues involved in regulation of DNA-binding activity. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2098–2101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2098-2101.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Fanning E. Mutations in the phosphorylation sites of simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen alter its origin DNA-binding specificity for sites I or II and affect SV40 DNA replication activity. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1598–1605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1598-1605.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Tjian R. T-antigen-DNA polymerase alpha complex implicated in simian virus 40 DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4077–4087. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. W., Gluzman Y. Replication and supercoiling of simian virus 40 DNA in cell extracts from human cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2051–2060. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strausfeld U., Richter A. Simultaneous purification of DNA topoisomerase I and II from eukaryotic cells. Prep Biochem. 1989;19(1):37–48. doi: 10.1080/10826068908544895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. MAP kinase by any other name smells just as sweet. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):3–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90199-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traut W., Fanning E. Sequence-specific interactions between a cellular DNA-binding protein and the simian virus 40 origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):903–911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Fairman M. P., Stillman B. Simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: identification of multiple stages of initiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3839–3849. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Melendy T., Stillman B. Sequential initiation of lagging and leading strand synthesis by two different polymerase complexes at the SV40 DNA replication origin. Nature. 1990 Aug 9;346(6284):534–539. doi: 10.1038/346534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Replication factors required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. I. DNA structure-specific recognition of a primer-template junction by eukaryotic DNA polymerases and their accessory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1950–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurimoto T., Stillman B. Replication factors required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. II. Switching of DNA polymerase alpha and delta during initiation of leading and lagging strand synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1961–1968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virshup D. M., Kauffman M. G., Kelly T. J. Activation of SV40 DNA replication in vitro by cellular protein phosphatase 2A. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3891–3898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virshup D. M., Kelly T. J. Purification of replication protein C, a cellular protein involved in the initial stages of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3584–3588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virshup D. M., Russo A. A., Kelly T. J. Mechanism of activation of simian virus 40 DNA replication by protein phosphatase 2A. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4883–4895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Collins K. L., Simancek P., Russo A., Wold M. S., Virshup D. M., Kelly T. J. Reconstitution of simian virus 40 DNA replication with purified proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8692–8696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wessel R., Schweizer J., Stahl H. Simian virus 40 T-antigen DNA helicase is a hexamer which forms a binary complex during bidirectional unwinding from the viral origin of DNA replication. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):804–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.804-815.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold M. S., Li J. J., Kelly T. J. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro: large-tumor-antigen- and origin-dependent unwinding of the template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3643–3647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]