Abstract
The polyomavirus large T antigen promotes homologous recombination at high rates when expressed in rat cells carrying the viral replication origin and two repeats of viral DNA sequences stably integrated into the cellular genome. Recombination consists of both reciprocal and nonreciprocal events and is promoted by mutants defective in the initiation of viral DNA synthesis (L. St-Onge, L. Bouchard, and M. Bastin, J. Virol. 67:1788-1795, 1993). We have extended our studies to a rat cell line undergoing amplification of the viral insert. We show that large T antigen promotes amplification independently of its replicative function but that its origin-specific DNA binding activity is not sufficient to promote homologous recombination.
Full text
PDF
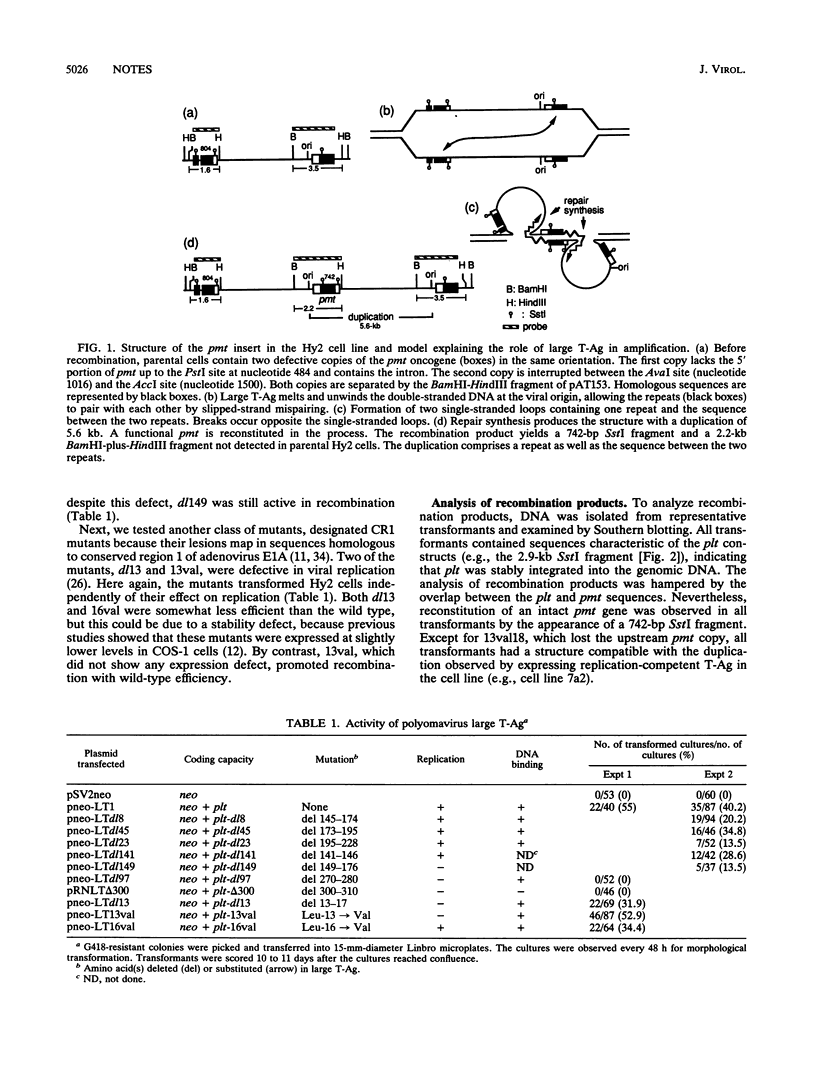
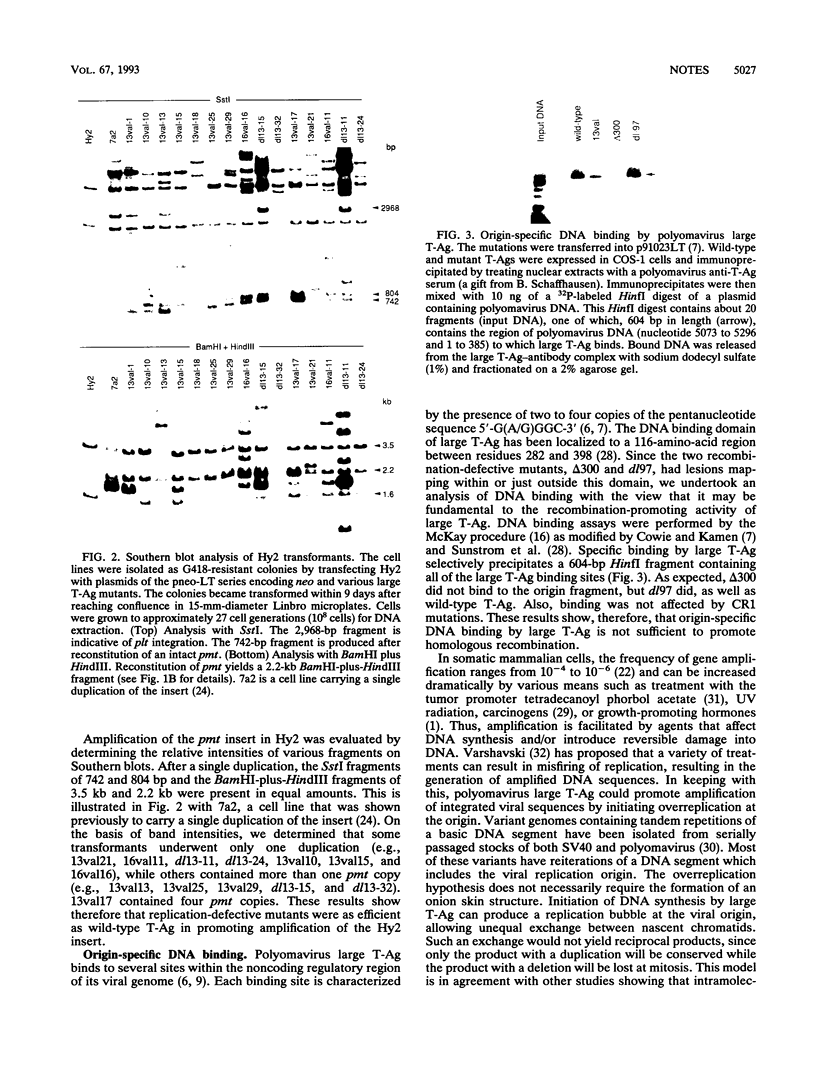


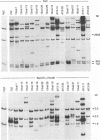
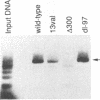
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsoum J., Varshavsky A. Mitogenic hormones and tumor promoters greatly increase the incidence of colony-forming cells bearing amplified dihydrofolate reductase genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5330–5334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett E. R., Naujokas M., Hassell J. A. Requirements for species-specific papovavirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5371–5385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5371-5385.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Topp W., Sambrook J. Studies on simian virus 40 excision from cellular chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):709–719. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Seidman M. M. Intramolecular recombination between transfected repeated sequences in mammalian cells is nonconservative. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2520–2526. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantuoni V., Dailey L., Valle G. D., Basilico C. Requirements for excision and amplification of integrated viral DNA molecules in polyoma virus-transformed cells. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):617–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.617-628.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Kamen R. Guanine nucleotide contacts within viral DNA sequences bound by polyomavirus large T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):505–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.505-514.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowie A., Kamen R. Multiple binding sites for polyomavirus large T antigen within regulatory sequences of polyomavirus DNA. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):750–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.750-760.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth S. M., Cowie A., Kamen R. I., Griffin B. E. DNA binding activity of polyoma virus large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1941–1945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dornreiter I., Höss A., Arthur A. K., Fanning E. SV40 T antigen binds directly to the large subunit of purified DNA polymerase alpha. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3329–3336. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan C., Jelsma T. N., Howe J. A., Bayley S. T., Ferguson B., Branton P. E. Mapping of cellular protein-binding sites on the products of early-region 1A of human adenovirus type 5. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3955–3959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larose A., Dyson N., Sullivan M., Harlow E., Bastin M. Polyomavirus large T mutants affected in retinoblastoma protein binding are defective in immortalization. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2308–2313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2308-2313.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larose A., St-Onge L., Bastin M. Mutations in polyomavirus large T affecting immortalization of primary rat embryo fibroblasts. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):98–105. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90234-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson G., Gutman G. A. Slipped-strand mispairing: a major mechanism for DNA sequence evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 May;4(3):203–221. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin F. L., Sperle K., Sternberg N. Model for homologous recombination during transfer of DNA into mouse L cells: role for DNA ends in the recombination process. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1020–1034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D. Binding of a simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 25;145(3):471–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Bullock P., Botchan M. Simian virus 40 T antigen is required for viral excision from chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7534–7538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pall M. L. Gene-amplification model of carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2465–2468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellegrini S., Dailey L., Basilico C. Amplification and excision of integrated polyoma DNA sequences require a functional origin of replication. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):943–949. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90044-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz B. J., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus and simian virus 40 large T antigens bind to common DNA sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):925–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.925-937.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller A., Prives C. Simian virus 40 and polyomavirus large tumor antigens have different requirements for high-affinity sequence-specific DNA binding. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):532–545. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.532-545.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C. The organization and amplification of two chromosomal domains containing Drosophila chorion genes. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90373-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Onge L., Bastin M. Amplification of polyomavirus DNA sequences stably integrated in rat cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6619–6625. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Onge L., Bouchard L., Bastin M. High-frequency recombination mediated by polyomavirus large T antigen defective in replication. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1788–1795. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1788-1795.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St-Onge L., Bouchard L., Laurent S., Bastin M. Intrachromosomal recombination mediated by papovavirus large T antigens. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2958–2966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2958-2966.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sunstrom N. A., Acheson N. H., Hassell J. A. Determination of the origin-specific DNA-binding domain of polyomavirus large T antigen. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6998–7003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6998-7003.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tlsty T. D., Brown P. C., Schimke R. T. UV radiation facilitates methotrexate resistance and amplification of the dihydrofolate reductase gene in cultured 3T6 mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1050–1056. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. On the possibility of metabolic control of replicon "misfiring": relationship to emergence of malignant phenotypes in mammalian cell lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3673–3677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. Phorbol ester dramatically increases incidence of methotrexate-resistant mouse cells: possible mechanisms and relevance to tumor promotion. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Buchkovich K. J., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Raybuck M., Weinberg R. A., Harlow E. Association between an oncogene and an anti-oncogene: the adenovirus E1A proteins bind to the retinoblastoma gene product. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):124–129. doi: 10.1038/334124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whyte P., Williamson N. M., Harlow E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90984-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]