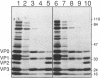
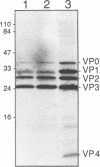
Abstract
During the entry of poliovirus into cells, a conformational transition occurs within the virion that is dependent upon its binding to the cell surface receptor. This conformational rearrangement generates an altered particle of 135S, results in the extrusion of capsid protein VP4 and the amino terminus of VP1 from the virion interior, and leads to the acquisition of membrane-binding properties by the 135S particle. Although the subsequent fate of VP4 is unknown, its apparent absence from purified 135S particles has long suggested that VP4 is not directly involved during virus entry. We report here the construction by site-specific mutagenesis of a nonviable VP4 mutant that upon transfection of the cDNA appears to form mature virus particles. These particles, upon interaction with the cellular receptor, undergo the 135S conformational transition but are defective at a subsequent stage in virus entry. The results demonstrate that the participation of VP4 is required during cell entry of poliovirus. In addition, these data indicate the existence of additional stages in the cell entry process beyond receptor binding and the transition to 135S particles. These post-135S stages must include the poorly understood processes by which nonenveloped viruses cross the cell membrane, uncoat, and deliver their genomes into the cytoplasm.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chow M., Newman J. F., Filman D., Hogle J. M., Rowlands D. J., Brown F. Myristylation of picornavirus capsid protein VP4 and its structural significance. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):482–486. doi: 10.1038/327482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sena J., Mandel B. Studies on the in vitro uncoating of poliovirus. II. Characteristics of the membrane-modified particle. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):554–566. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everaert L., Vrijsen R., Boeyé A. Eclipse products of poliovirus after cold-synchronized infection of HeLa cells. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90512-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENWICK M. L., COOPER P. D. Early interactions between poliovirus and ERK cells: some observations on the nature and significance of the rejected particles. Virology. 1962 Oct;18:212–223. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricks C. E., Hogle J. M. Cell-induced conformational change in poliovirus: externalization of the amino terminus of VP1 is responsible for liposome binding. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1934–1945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1934-1945.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K., DARNELL J. E., Jr The adsorption and early fate of purified poliovirus in HeLa cells. Virology. 1961 Apr;13:439–447. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90275-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Horie H., Ise I., Okitsu A., Yoshida M., Iizuka N., Takeuchi K., Takegami T., Nomoto A. The poliovirus receptor protein is produced both as membrane-bound and secreted forms. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3217–3224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07520.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg-Holm K., Gosser L. B., Kauer J. C. Early alteration of poliovirus in infected cells and its specific inhibition. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jun;27(3):329–342. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-27-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Infectious entry pathway of influenza virus in a canine kidney cell line. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):601–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscufo N., Chow M. Myristate-protein interactions in poliovirus: interactions of VP4 threonine 28 contribute to the structural conformation of assembly intermediates and the stability of assembled virions. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):6849–6857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.6849-6857.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscufo N., Simons J., Chow M. Myristoylation is important at multiple stages in poliovirus assembly. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2372–2380. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2372-2380.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons J., Rogove A., Moscufo N., Reynolds C., Chow M. Efficient analysis of nonviable poliovirus capsid mutants. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1734–1738. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1734-1738.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]