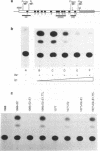
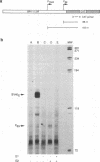
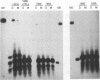
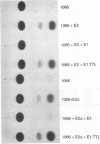
Abstract
Bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV-1) is the prototype virus for the study of papillomavirus gene regulation. The functions of the BPV-1 E2 proteins in transcriptional regulation have been well characterized. The BPV-1 E1 protein is required for viral DNA replication and can bind to the origin of replication alone or in a complex with the E2 transactivator protein. In this study, we demonstrated that the BPV-1 E1 protein is also involved in transcriptional regulation. The E1 protein significantly repressed E2-transactivated transcription from the major early promoter P89. This activity is consistent with the elevated level of P89 transcription observed in BPV-1 E1 open reading frame mutants. Transcriptional repression by E1 correlated with the ability of an E1-E2 protein complex to bind the replication origin but was not dependent on viral DNA replication. These studies identify a new mechanism involved in the regulation of papillomavirus transcription which has implications regarding expression of the viral transforming functions.
Full text
PDF


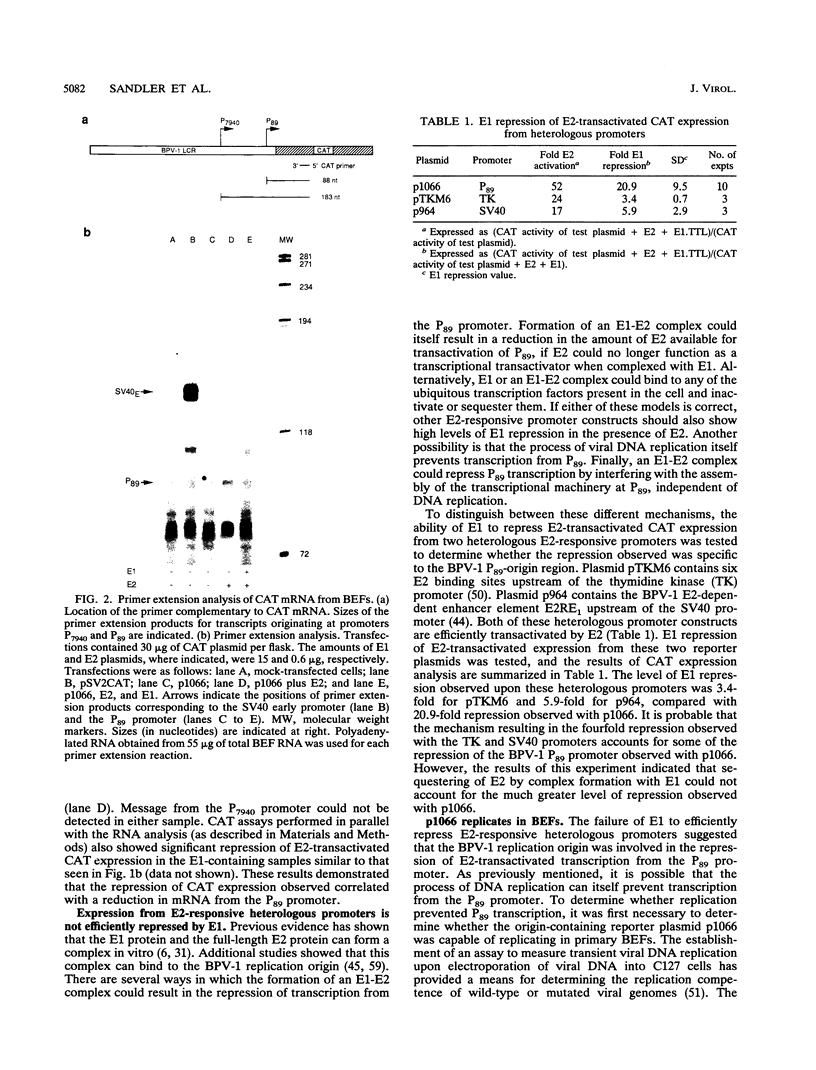





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahola H., Stenlund A., Moreno-López J., Pettersson U. Promoters and processing sites within the transforming region of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2240–2244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2240-2244.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Androphy E. J., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Bovine papillomavirus E2 trans-activating gene product binds to specific sites in papillomavirus DNA. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):70–73. doi: 10.1038/325070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Howley P. M. Differential promoter utilization by the bovine papillomavirus in transformed cells and productively infected wart tissues. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1027–1035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsoum J., Prakash S. S., Han P., Androphy E. J. Mechanism of action of the papillomavirus E2 repressor: repression in the absence of DNA binding. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3941–3945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3941-3945.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blitz I. L., Laimins L. A. The 68-kilodalton E1 protein of bovine papillomavirus is a DNA binding phosphoprotein which associates with the E2 transcriptional activator in vitro. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):649–656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.649-656.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett S., Moreno-Lopez J., Pettersson U. Messenger RNAs from the E1 region of bovine papillomavirus type 1 detected in virus-infected bovine cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):8607–8620. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.8607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D. Nonsense mutation in open reading frame E2 of bovine papillomavirus DNA. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):475–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.475-480.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostatni N., Lambert P. F., Sousa R., Ham J., Howley P. M., Yaniv M. The functional BPV-1 E2 trans-activating protein can act as a repressor by preventing formation of the initiation complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1657–1671. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostatni N., Thierry F., Yaniv M. A dimer of BPV-1 E2 containing a protease resistant core interacts with its DNA target. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3807–3816. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Knippers R. Structure and function of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:55–85. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.000415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Williams J. Mapping temperature-sensitive and host-range mutations of adenovirus type 5 by marker rescue. Virology. 1978 Nov;91(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90353-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Howard B. H., Reeves R. Expression of recombinant plasmids in mammalian cells is enhanced by sodium butyrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7631–7648. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley-Nelson P., Vousden K. H., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. HPV16 E6 and E7 proteins cooperate to immortalize human foreskin keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3905–3910. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Khoury G., Gorman C., Howard B., Gruss P. Host-specific activation of transcription by tandem repeats from simian virus 40 and Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6453–6457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 E1 replication-defective mutants are altered in their transcriptional regulation. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4009–4015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4009-4015.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Hubbert N. L., Howley P. M., Schiller J. T. Genetic assignment of multiple E2 gene products in bovine papillomavirus-transformed cells. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3151–3154. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3151-3154.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Howley P. M. Mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus contain only extrachromosomal viral DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2727–2731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Commitment and activation at pol II promoters: a tail of protein-protein interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1161–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90675-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J. D., Jackson S. P., Tjian R., Botchan M. R. Direct interaction between Sp1 and the BPV enhancer E2 protein mediates synergistic activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90467-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J., Bream G., Stenlund A., Botchan M. Specific recognition nucleotides and their DNA context determine the affinity of E2 protein for 17 binding sites in the BPV-1 genome. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):510–526. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride A. A., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. E2 polypeptides encoded by bovine papillomavirus type 1 form dimers through the common carboxyl-terminal domain: transactivation is mediated by the conserved amino-terminal domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):510–514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride A. A., Schlegel R., Howley P. M. The carboxy-terminal domain shared by the bovine papillomavirus E2 transactivator and repressor proteins contains a specific DNA binding activity. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):533–539. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr I. J., Clark R., Sun S., Androphy E. J., MacPherson P., Botchan M. R. Targeting the E1 replication protein to the papillomavirus origin of replication by complex formation with the E2 transactivator. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1694–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2176744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Münger K., Phelps W. C., Bubb V., Howley P. M., Schlegel R. The E6 and E7 genes of the human papillomavirus type 16 together are necessary and sufficient for transformation of primary human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4417–4421. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4417-4421.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neary K., DiMaio D. Open reading frames E6 and E7 of bovine papillomavirus type 1 are both required for full transformation of mouse C127 cells. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):259–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.259-266.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Philipson L. Regulation of adenovirus gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;97:157–203. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68318-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M. S., Yee C., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 3' early region transformation and plasmid maintenance functions. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):626–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.626-634.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanczuk H., Howley P. M. Disruption of either the E1 or the E2 regulatory gene of human papillomavirus type 16 increases viral immortalization capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3159–3163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Kleiner E., Androphy E. J., Lowy D. R., Pfister H. Identification of bovine papillomavirus E1 mutants with increased transforming and transcriptional activity. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1775–1782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1775-1782.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Identification of a second transforming region in bovine papillomavirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7880–7884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Lambert P. F., Yee C. L., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus transcriptional regulation: localization of the E2-responsive elements of the long control region. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2128–2137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2128-2137.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., McBride A. A., Sarafi T., Quintero J. Binding of bovine papillomavirus E1 to the origin is not sufficient for DNA replication. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):201–212. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Vande Pol S. B., Howley P. M. Characterization of the cis elements involved in basal and E2-transactivated expression of the bovine papillomavirus P2443 promoter. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):743–753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.743-753.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Transactivation of a bovine papilloma virus transcriptional regulatory element by the E2 gene product. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenlund A., Zabielski J., Ahola H., Moreno-Lopez J., Pettersson U. Messenger RNAs from the transforming region of bovine papilloma virus type I. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):541–554. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymanski P., Stenlund A. Regulation of early gene expression from the bovine papillomavirus genome in transiently transfected C127 cells. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5710–5720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5710-5720.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry F., Dostatni N., Arnos F., Yaniv M. Cooperative activation of transcription by bovine papillomavirus type 1 E2 can occur over a large distance. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4431–4437. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav M., Stenlund A. Transient replication of BPV-1 requires two viral polypeptides encoded by the E1 and E2 open reading frames. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):449–457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav M., Ustav E., Szymanski P., Stenlund A. Identification of the origin of replication of bovine papillomavirus and characterization of the viral origin recognition factor E1. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4321–4329. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Pol S. B., Howley P. M. A bovine papillomavirus constitutive enhancer is negatively regulated by the E2 repressor through competitive binding for a cellular factor. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5420–5429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5420-5429.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Pol S. B., Howley P. M. The bovine papillomavirus constitutive enhancer is essential for viral transformation, DNA replication, and the maintenance of latency. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2346–2358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2346-2358.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. G., Ludes-Meyers J. A bovine papillomavirus E1-related protein binds specifically to bovine papillomavirus DNA. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5314–5322. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5314-5322.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winokur P. L., McBride A. A. Separation of the transcriptional activation and replication functions of the bovine papillomavirus-1 E2 protein. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4111–4118. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05504.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Botchan M. Replication of bovine papillomavirus type 1 DNA initiates within an E2-responsive enhancer element. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5903–5911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5903-5911.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Li R., Mohr I. J., Clark R., Botchan M. R. Activation of BPV-1 replication in vitro by the transcription factor E2. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):628–632. doi: 10.1038/353628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Okayama H., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus contains multiple transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1030–1034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]