Abstract
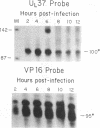
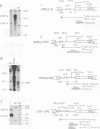
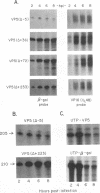
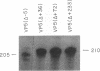
Transient expression assays with the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) promoter/leader controlling the beta gamma (leaky-late) VP5 (UL19) mRNA encoding the major capsid protein showed that no more than 36 to 72 bases of VP5 leader are required for full-level expression. Constructs lacking the viral leader and the transcription initiation site expressed the reporter gene at about 20% of the maximum level. We confirmed this observation by using recombinant viruses in which VP5 promoter/leader deletions controlling the bacterial beta-galactosidase gene were inserted into the nonessential glycoprotein C (UL44) locus of the genome. Sequences within +36 are required for full-level expression, and removal of all leader sequences including the cap site resulted in a 10-fold decrease in reporter mRNA accumulation. The removal of the leader sequence had a measurable effect upon the kinetics of reporter mRNA accumulation, but insertion of the entire VP5 leader and cap site into a construct in which the reporter gene was controlled by the kinetically early (beta) dUTPase (UL50) promoter did not result in any significant change in the kinetics of dUTPase promoter expression. These results suggest that DNA sequences both 5' and 3' of the TATA box are important determinants of the beta gamma kinetics and levels of VP5 mRNA accumulation in the infected cell.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair E. D., Blair C. C., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus virion stimulatory protein mRNA leader contains sequence elements which increase both virus-induced transcription and mRNA stability. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2499–2508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2499-2508.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair E. D., Wagner E. K. A single regulatory region modulates both cis activation and trans activation of the herpes simplex virus VP5 promoter in transient-expression assays in vivo. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):460–469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.460-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Mills L., Perry P., Riddle S., Wobig R., Lown R., Millette R. L. Transactivation of the major capsid protein gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 requires a cellular transcription factor. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4304–4314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4304-4314.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Cohen G., Eisenberg R., Long D., Wagner E. Direct demonstration that the abundant 6-kilobase herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA mapping between 0.23 and 0.27 map units encodes the major capsid protein VP5. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):287–292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.287-292.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson A. T., Sederati F., Devi-Rao G., Flanagan W. M., Farrell M. J., Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Feldman L. T. Identification of the latency-associated transcript promoter by expression of rabbit beta-globin mRNA in mouse sensory nerve ganglia latently infected with a recombinant herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3844–3851. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3844-3851.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan W. M., Papavassiliou A. G., Rice M., Hecht L. B., Silverstein S., Wagner E. K. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter controlling the expression of UL38, a true late gene involved in capsid assembly. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):769–786. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.769-786.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Nelson J. A. Enhancement of RNA polymerase II initiation complexes by a novel DNA control domain downstream from the cap site of the cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2299–2307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2299-2307.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodart S. A., Guzowski J. F., Rice M. K., Wagner E. K. Effect of genomic location on expression of beta-galactosidase mRNA controlled by the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL38 promoter. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2973–2981. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2973-2981.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guzowski J. F., Wagner E. K. Mutational analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 strict late UL38 promoter/leader reveals two regions critical in transcriptional regulation. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5098–5108. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5098-5108.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern M. E., Smiley J. R. Effects of deletions on expression of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene from the intact viral genome: the amino terminus of the enzyme is dispensable for catalytic activity. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):733–738. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.733-738.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Shibata M., Kuzushima K., Nishikawa K., Nishiyama Y., Morishima T. Detection and direct typing of herpes simplex virus by polymerase chain reaction. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1990;179(4):177–184. doi: 10.1007/BF00195248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J. D., Jackson S. P., Tjian R., Botchan M. R. Direct interaction between Sp1 and the BPV enhancer E2 protein mediates synergistic activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90467-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mavromara-Nazos P., Roizman B. Delineation of regulatory domains of early (beta) and late (gamma 2) genes by construction of chimeric genes expressed in herpes simplex virus 1 genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4071–4075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J. The genome of herpes simplex virus: structure, replication and evolution. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;7:67–94. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1987.supplement_7.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakatani Y., Horikoshi M., Brenner M., Yamamoto T., Besnard F., Roeder R. G., Freese E. A downstream initiation element required for efficient TATA box binding and in vitro function of TFIID. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):86–88. doi: 10.1038/348086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pederson N. E., Person S., Homa F. L. Analysis of the gB promoter of herpes simplex virus type 1: high-level expression requires both an 89-base-pair promoter fragment and a nontranslated leader sequence. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6226–6232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6226-6232.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. L., Wilcox K. W. The conserved DNA-binding domains encoded by the herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4, pseudorabies virus IE180, and varicella-zoster virus ORF62 genes recognize similar sites in the corresponding promoters. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1149-1159.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]