Abstract
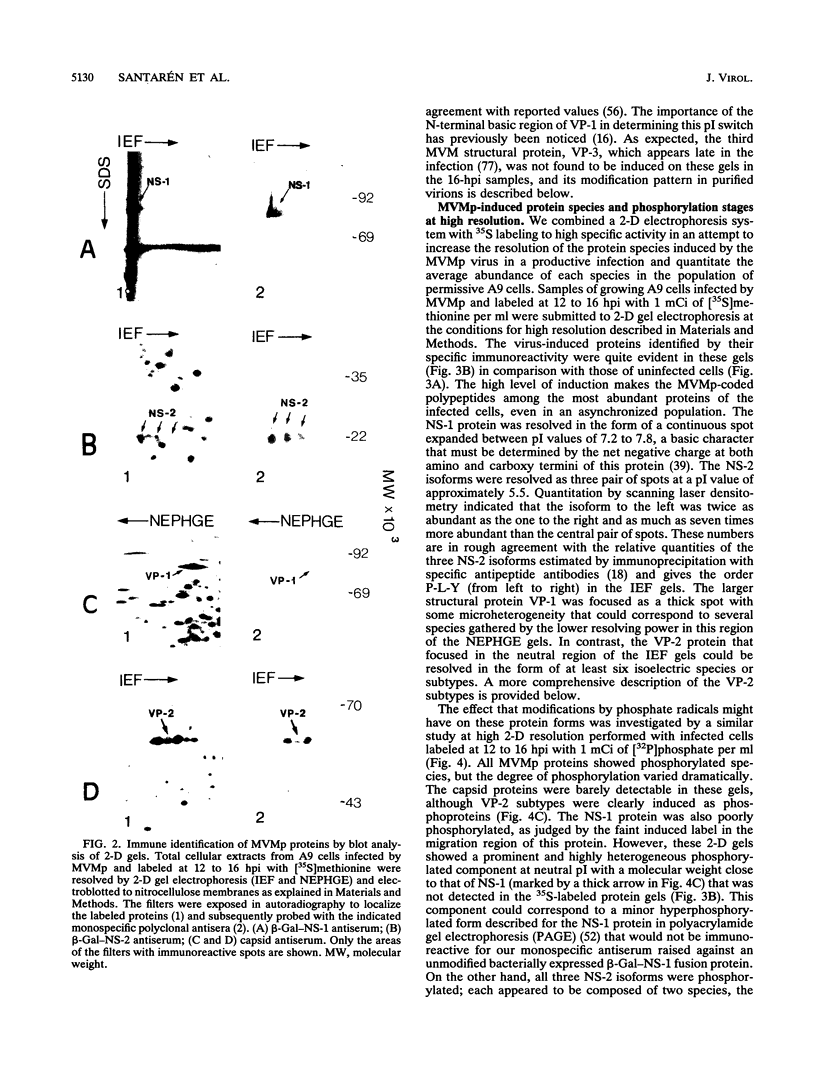
The pattern of induced protein species of the prototype strain of the parvovirus minute virus of mice was determined in permissive A9 mouse fibroblast cells by high-resolution two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Identities of the viral proteins in the gels were assigned by probing two-dimensional blots with antisera raised against either purified capsids (recognizing VP-1 and VP-2) or specific coding regions of the nonstructural proteins (NS-1 and NS-2) expressed as beta-galactosidase fusion products in bacteria. All viral proteins showed posttranslational modifications, phosphate being a common substituent. The NS-1 protein migrated as a basic polypeptide in the pI range of 7.4 to 7.8 with multiple stages of modification and as a likely minor but hyperphosphorylated component in the neutral region of the gel. The NS-2 isoforms were resolved at a pI value close to 5.5 as three groups of unevenly phosphorylated polypeptides, each composed of at least two protein species. Both VP-1 and VP-2 structural polypeptides were induced as heterogeneous phosphoproteins. The major VP-2 protein could be resolved in the form of a consistent pattern of three abundant (a to c), two intermediate (d and e), and one meager (f) neutral isoelectric focusing species or subtypes. This posttranslational modification precedes and is uncoupled from viral assembly, and all of the VP-2 subtypes are packaged into empty capsids at the induced stoichiometry. However, intracellular full virions harbored additional phosphorylated subtypes (g to l) and a subtle rearrangement in the whole VP-2 composition, while mature virions purified from lysed cultures lacked these subtypes, coordinately with the emergence of six neutral VP-3 subtypes. Thus, the virion coat undergoes a chemical transition entailed by genome encapsidation, in which phosphates seem to play a major role, triggering the preferential proteolytic cleavage of the more acidic VP-2 subtypes to VP-3. Parvoviruses, with small coding capacity, may regulate some morphogenetic steps, such as assembly, genome encapsidation, and maturation, by posttranslational modifications of their structural proteins.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders D. G., Consigli R. A. Comparison of nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated species of polyomavirus major capsid protein VP1 and identification of the major phosphorylation region. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):206–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.206-217.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonietti J. P., Sahli R., Beard P., Hirt B. Characterization of the cell type-specific determinant in the genome of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):552–557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.552-557.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Gardiner E. M., Tattersall P. DNA sequence of the lymphotropic variant of minute virus of mice, MVM(i), and comparison with the DNA sequence of the fibrotropic prototype strain. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):656–669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.656-669.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Smith M., Chow M. B., Ward D. C. Structure of the 3' hairpin termini of four rodent parvovirus genomes: nucleotide sequence homology at origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):691–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90276-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball-Goodrich L. J., Moir R. D., Tattersall P. Parvoviral target cell specificity: acquisition of fibrotropism by a mutant of the lymphotropic strain of minute virus of mice involves multiple amino acid substitutions within the capsid. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):175–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90834-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball-Goodrich L. J., Tattersall P. Two amino acid substitutions within the capsid are coordinately required for acquisition of fibrotropism by the lymphotropic strain of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3415–3423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3415-3423.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Anders D. G., Trempy J., Consigli R. A. Differences in the subpopulations of the structural proteins of polyoma virions and capsids: biological functions of the multiple VP1 species. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):80–91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.80-91.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D., Salzman L. A. Sequence homology between the structural proteins of Kilham rat virus. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):1018–1020. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.1018-1020.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caillet-Fauquet P., Perros M., Brandenburger A., Spegelaere P., Rommelaere J. Programmed killing of human cells by means of an inducible clone of parvoviral genes encoding non-structural proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2989–2995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07491.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens K. E., Cerutis D. R., Burger L. R., Yang C. Q., Pintel D. J. Cloning of minute virus of mice cDNAs and preliminary analysis of individual viral proteins expressed in murine cells. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3967–3973. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3967-3973.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis J. J., Becquart P., Duponchel N., Salomé N., Avalosse B. L., Namba M., Rommelaere J. Transformation of human fibroblasts by ionizing radiation, a chemical carcinogen, or simian virus 40 correlates with an increase in susceptibility to the autonomous parvoviruses H-1 virus and minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1679–1686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1679-1686.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelis J. J., Chen Y. Q., Spruyt N., Duponchel N., Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P., Rommelaere J. Susceptibility of human cells to killing by the parvoviruses H-1 and minute virus of mice correlates with viral transcription. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2537–2544. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2537-2544.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Sturzenbecker L. J., Tattersall P. The autonomous parvovirus MVM encodes two nonstructural proteins in addition to its capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. A genome-linked copy of the NS-1 polypeptide is located on the outside of infectious parvovirus particles. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3902–3911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3902-3911.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. Alternate splicing in a parvoviral nonstructural gene links a common amino-terminal sequence to downstream domains which confer radically different localization and turnover characteristics. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90512-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. In vivo resolution of circular plasmids containing concatemer junction fragments from minute virus of mice DNA and their subsequent replication as linear molecules. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):420–431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.420-431.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. Organization of nonstructural genes of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):724–732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.724-732.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The NS-1 polypeptide of the autonomous parvovirus MVM is a nuclear phosphoprotein. Virus Res. 1986 May;4(3):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:91–174. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V. A minute virus of mice. Virology. 1966 Aug;29(4):605–612. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90284-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerig C., Hirt B., Antonietti J. P., Beard P. Nonstructural protein of parvoviruses B19 and minute virus of mice controls transcription. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):387–396. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.387-396.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerig C., Hirt B., Beard P., Antonietti J. P. Minute virus of mice non-structural protein NS-1 is necessary and sufficient for trans-activation of the viral P39 promoter. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2563–2573. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust E. A., Brudzynska K., Morgan J. Characterization of novel populations of MVM virions containing covalent DNA-protein complexes. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):128–137. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Ballmer-Hofer K., Benjamin T. L. Virion assembly defect of polyomavirus hr-t mutants: underphosphorylation of major capsid protein VP1 before viral DNA encapsidation. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):311–316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.311-316.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Benjamin T. L. Host range transforming gene of polyoma virus plays a role in virus assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3613–3617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Talmage D. A., Harmatz A., Freund R., Benjamin T. L. Separation of host range from transformation functions of the hr-t gene of polyomavirus. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):312–319. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner E. M., Tattersall P. Evidence that developmentally regulated control of gene expression by a parvoviral allotropic determinant is particle mediated. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1713–1722. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1713-1722.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner E. M., Tattersall P. Mapping of the fibrotropic and lymphotropic host range determinants of the parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2605–2613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2605-2613.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghabrial S. A., Havens W. M. The Helminthosporium victoriae 190S mycovirus has two forms distinguishable by capsid protein composition and phosphorylation state. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):657–665. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90520-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes J. I., 2nd, Consigli R. A. Phosphorylation of the budgerigar fledgling disease virus major capsid protein VP1. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4551–4555. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4551-4555.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jongeneel C. V., Sahli R., McMaster G. K., Hirt B. A precise map of splice junctions in the mRNAs of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):564–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.564-573.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A. Architectural design of spherical viruses. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):378–379. doi: 10.1038/303378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles W. J., Bologna M. L. Isolation of the chemical domains of human erythrocyte spectrin. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:305–313. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labieniec-Pintel L., Pintel D. The minute virus of mice P39 transcription unit can encode both capsid proteins. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1163–1167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1163-1167.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Santos E., Notario V., Barbacid M., Yamazaki S., Kung H., Seamans C., McAndrew S., Crowl R. Expression of normal and transforming H-ras genes in Escherichia coli and purification of their encoded p21 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5305–5309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Katan M. Viral aspects of protein phosphorylation. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1441–1464. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legendre D., Rommelaere J. Terminal regions of the NS-1 protein of the parvovirus minute virus of mice are involved in cytotoxicity and promoter trans inhibition. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5705–5713. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5705-5713.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Rhode S. L., 3rd Nonstructural protein NS2 of parvovirus H-1 is required for efficient viral protein synthesis and virus production in rat cells in vivo and in vitro. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90828-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liddington R. C., Yan Y., Moulai J., Sahli R., Benjamin T. L., Harrison S. C. Structure of simian virus 40 at 3.8-A resolution. Nature. 1991 Nov 28;354(6351):278–284. doi: 10.1038/354278a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molitor T. W., Joo H. S., Collett M. S. Identification and characterization of a porcine parvovirus nonstructural polypeptide. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):554–559. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.554-559.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. R., Ward D. C. Three splicing patterns are used to excise the small intron common to all minute virus of mice RNAs. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1170–1174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1170-1174.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mousset S., Rommelaere J. Minute virus of mice inhibits cell transformation by simian virus 40. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):537–539. doi: 10.1038/300537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeger L. K., Cater J., Pintel D. J. The small nonstructural protein (NS2) of the parvovirus minute virus of mice is required for efficient DNA replication and infectious virus production in a cell-type-specific manner. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6166–6175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6166-6175.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeger L. K., Salomé N., Pintel D. J. NS2 is required for efficient translation of viral mRNA in minute virus of mice-infected murine cells. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):1034–1043. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.1034-1043.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M. Resolution of simian virus 40 proteins in whole cell extracts by two-dimensional electrophoresis: heterogeneity of the major capsid protein. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso P. R. Analysis of the protein-protein interactions in the parvovirus H-1 capsid. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):94–102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.94-102.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso P. R. Identification of multiple forms of the noncapsid parvovirus protein NCVP1 in H-1 parvovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):82–87. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.82-87.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso P. R. Infectious process of the parvovirus H-1: correlation of protein content, particle density, and viral infectivity. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):800–807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.800-807.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradiso P. R., Williams K. R., Costantino R. L. Mapping of the amino terminus of the H-1 parvovirus major capsid protein. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.77-81.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish C. R., Carmichael L. E. Characterization and recombination mapping of an antigenic and host range mutation of canine parvovirus. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish C. R. Mapping specific functions in the capsid structure of canine parvovirus and feline panleukopenia virus using infectious plasmid clones. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):195–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90132-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintel D., Dadachanji D., Astell C. R., Ward D. C. The genome of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus, encodes two overlapping transcription units. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):1019–1038. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponder B. A., Robbins A. K., Crawford L. V. Phophorylation of polyoma and SV40 virus proteins. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):75–83. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Both excision and replication of cloned autonomous parvovirus DNA require the NS1 (rep) protein. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4249–4256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4249-4256.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd trans-Activation of parvovirus P38 promoter by the 76K noncapsid protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):886–889. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.886-889.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards R., Linser P., Armentrout R. W. Kinetics of assembly of a parvovirus, minute virus of mice, in synchronized rat brain cells. J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):778–793. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.778-793.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell W. C., Webster A., Leith I. R., Kemp G. D. Phosphorylation of adenovirus DNA-binding protein. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3249–3259. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomé N., van Hille B., Duponchel N., Meneguzzi G., Cuzin F., Rommelaere J., Cornelis J. J. Sensitization of transformed rat cells to parvovirus MVMp is restricted to specific oncogenes. Oncogene. 1990 Jan;5(1):123–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salunke D. M., Caspar D. L., Garcea R. L. Self-assembly of purified polyomavirus capsid protein VP1. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segovia J. C., Real A., Bueren J. A., Almendral J. M. In vitro myelosuppressive effects of the parvovirus minute virus of mice (MVMi) on hematopoietic stem and committed progenitor cells. Blood. 1991 Mar 1;77(5):980–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Bates R. C., Berns K. I., Carter B. J., Kelly D. C., Kurstak E., Tattersall P. Characteristics and taxonomy of Parvoviridae. Intervirology. 1985;23(2):61–73. doi: 10.1159/000149587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Tattersall P. Interaction of minute virus of mice with differentiated cells: strain-dependent target cell specificity is mediated by intracellular factors. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):937–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.937-943.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spegelaere P., van Hille B., Spruyt N., Faisst S., Cornelis J. J., Rommelaere J. Initiation of transcription from the minute virus of mice P4 promoter is stimulated in rat cells expressing a c-Ha-ras oncogene. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4919–4928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4919-4928.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Bratton J. Reciprocal productive and restrictive virus-cell interactions of immunosuppressive and prototype strains of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):944–955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.944-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Cawte P. J., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Three structural polypeptides coded for by minite virus of mice, a parvovirus. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):273–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.273-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Sequence homology between the structural polypeptides of minute virus of mice. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr 25;111(4):375–394. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80060-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao J., Chapman M. S., Agbandje M., Keller W., Smith K., Wu H., Luo M., Smith T. J., Rossmann M. G., Compans R. W. The three-dimensional structure of canine parvovirus and its functional implications. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1456–1464. doi: 10.1126/science.2006420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis G. E., Burger L. R., Pintel D. J. The minor capsid protein VP1 of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice is dispensable for encapsidation of progeny single-stranded DNA but is required for infectivity. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):131–141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.131-141.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevacharya J., Compans R. W. The NS and capsid genes determine the host range of porcine parvovirus. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):515–524. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90454-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willwand K., Hirt B. The minute virus of mice capsid specifically recognizes the 3' hairpin structure of the viral replicative-form DNA: mapping of the binding site by hydroxyl radical footprinting. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4629–4635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4629-4635.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. M., Jindal H. K., Yeung D. E., Chen W., Astell C. R. Expression of minute virus of mice major nonstructural protein in insect cells: purification and identification of ATPase and helicase activities. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):90–98. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90757-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









