Abstract
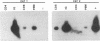
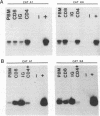
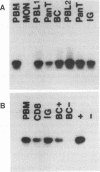
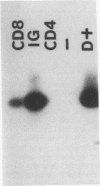
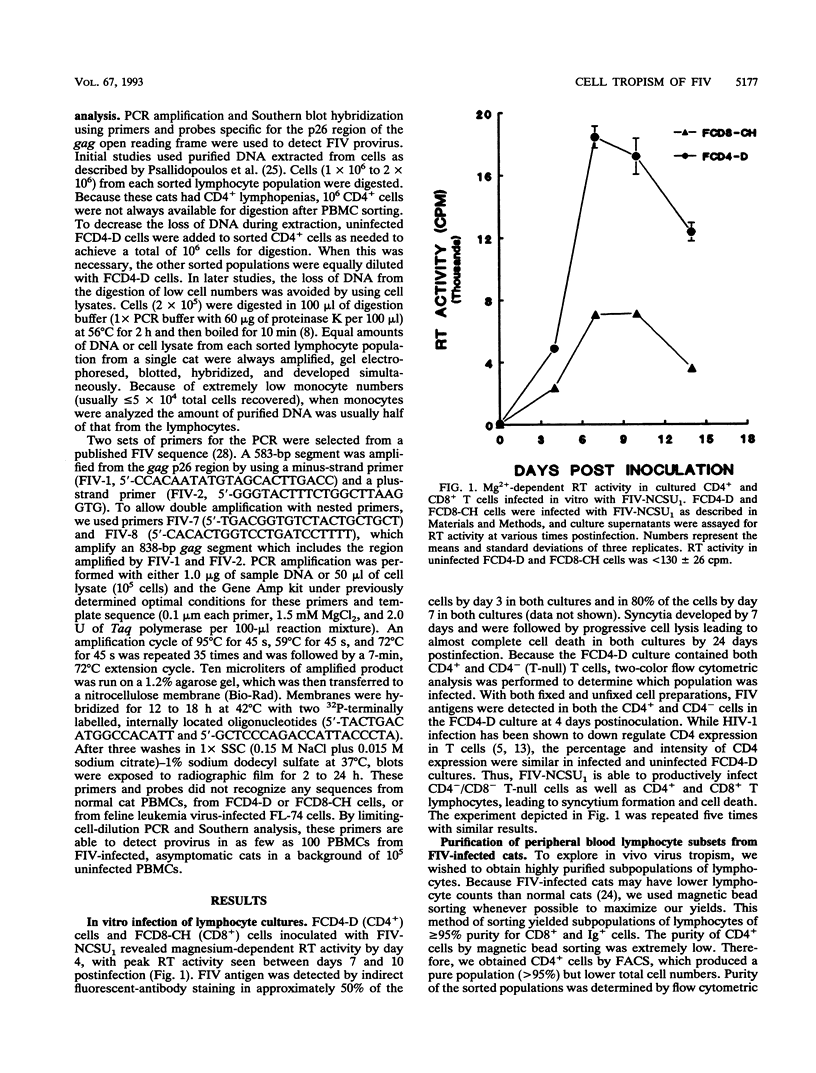
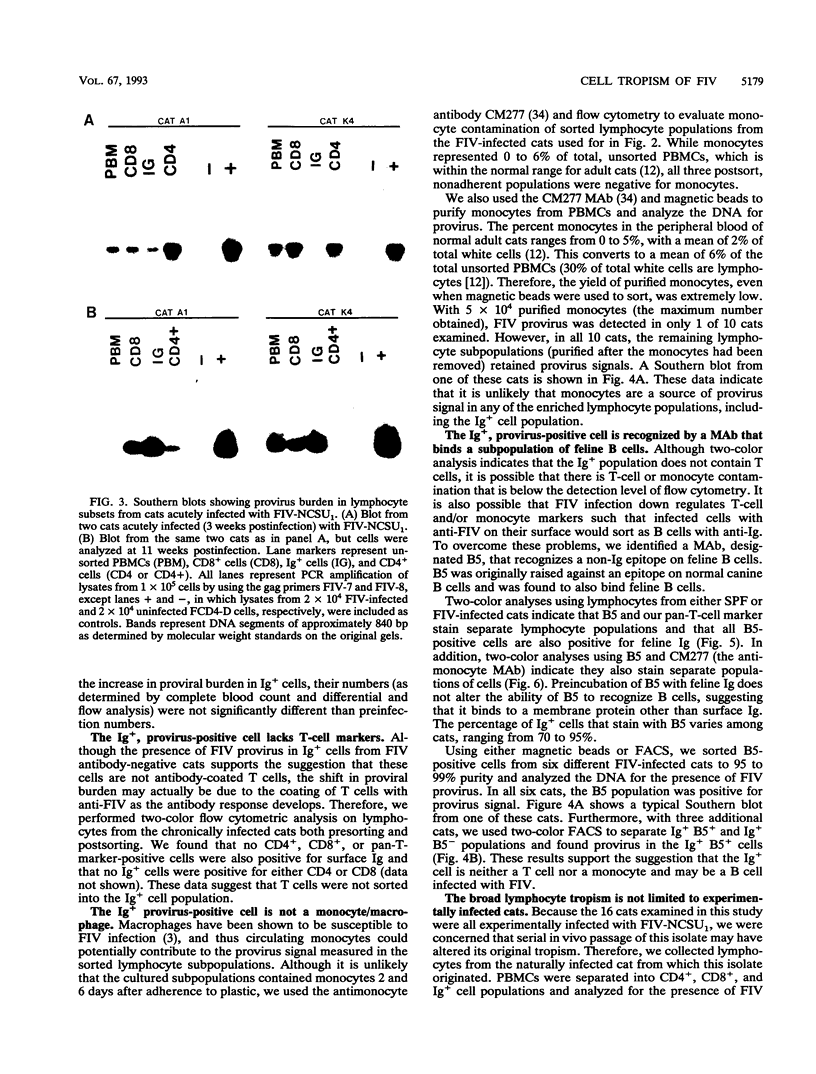
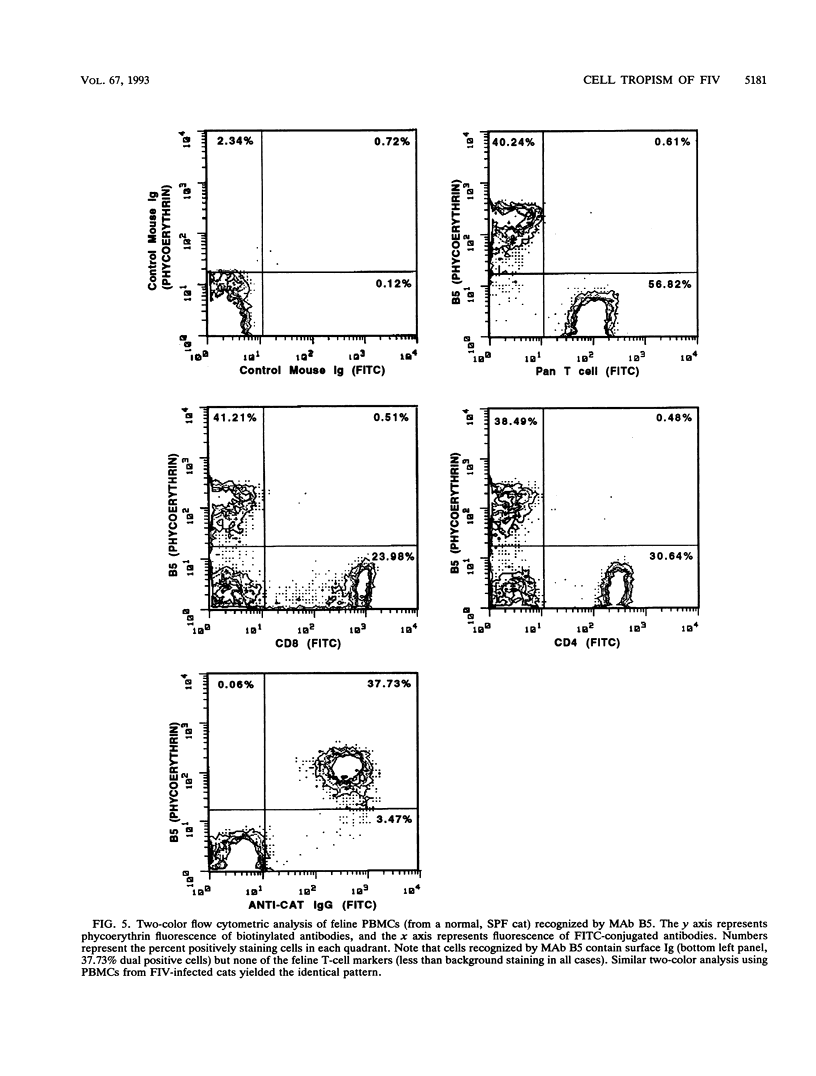
Feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV) infection in the cat is similar to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection in causing a selective reduction in CD4+ cell numbers, leading to inversion of the CD4+/CD8+ ratio. To determine whether FIV, similar to human immunodeficiency virus type 1, has a tropism for CD4+ cells, we examined the in vitro and in vivo susceptibilities of feline lymphocyte subpopulations to FIV infection. Infection of interleukin-2-dependent CD4+ or CD8+ lymphocyte cultures with the NCSU1 isolate of FIV (FIV-NCSU1) resulted in syncytium formation, cell death, and Mg(2+)-dependent reverse transcriptase (RT) activity in both cases. Monoclonal antibodies to feline lymphocyte subsets were used to sort peripheral blood mononuclear cells from FIV-infected cats into highly (> 95%) purified CD4+ cell, CD8+ cell, immunoglobulin-positive (Ig+) cell, and monocyte subpopulations. The mononuclear cell subpopulations were analyzed for FIV provirus by polymerase chain reaction and Southern blot analysis and for virus expression by RT activity. All 16 cats infected with FIV-NCSU1 demonstrated FIV provirus in CD4+ cell-, CD8+ cell-, and Ig+ cell-enriched lymphocyte populations. Southern blot detection of amplified gag gene sequences and limiting-cell-dilution polymerase chain reaction analysis indicated that Ig+ cells carried a higher FIV provirus burden in chronically (> or = 1-year) infected cats than either CD4+ or CD8+ cells. In contrast, CD4+ cells carried the greatest provirus burden in acutely (2- to 4-week) infected cats. FIV provirus was detected in monocytes from only 1 of 10 cats with asymptomatic infection. Addition of culture supernatants from enriched CD4+, CD8+, and Ig+ cells from FIV-infected cats to an FIV-susceptible CD4+ lymphocyte culture resulted in syncytium formation, cell death, and RT activity. Infection of Ig+ cells is not unique to FIV-NCSU1, as lymphocyte subpopulations from other cats with natural infections and cats infected with the Petaluma or Mount Airy isolate of FIV demonstrated a similar distribution of FIV provirus and RT activity. These data suggest that FIV possesses a broad tropism for peripheral blood mononuclear cells and that an Ig+ cell may serve as a major reservoir for the virus in chronically infected cats.
Full text
PDF



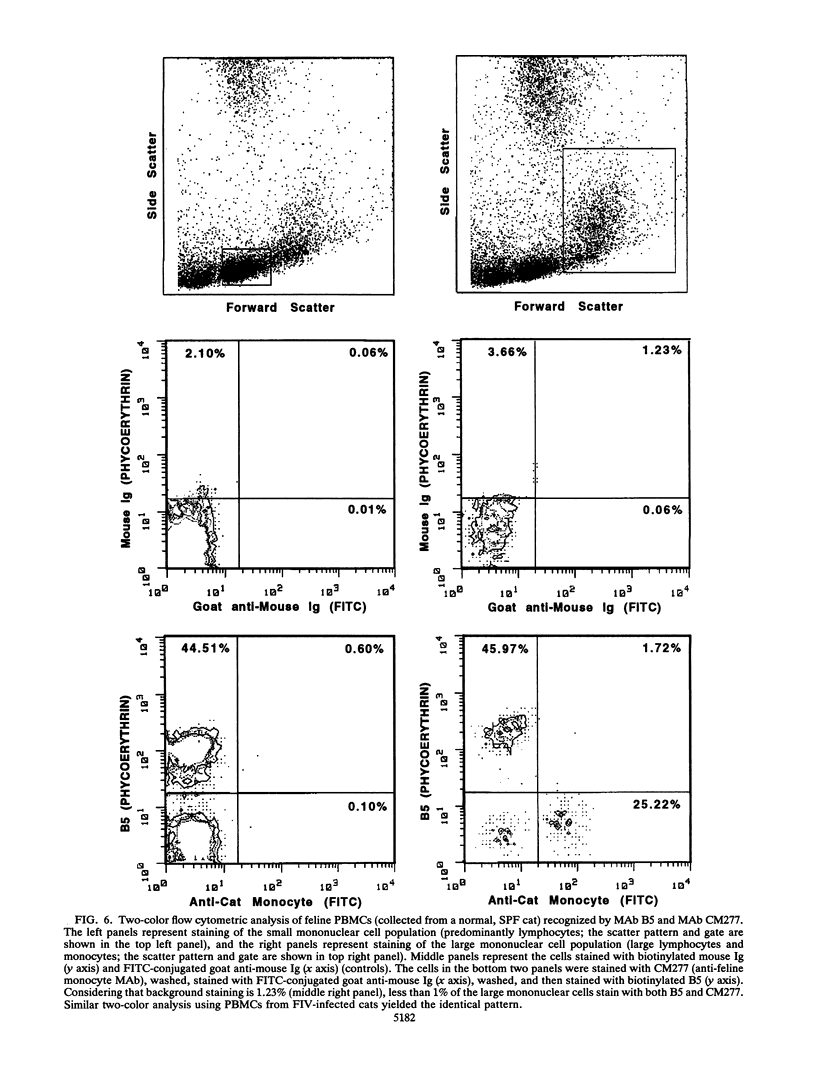

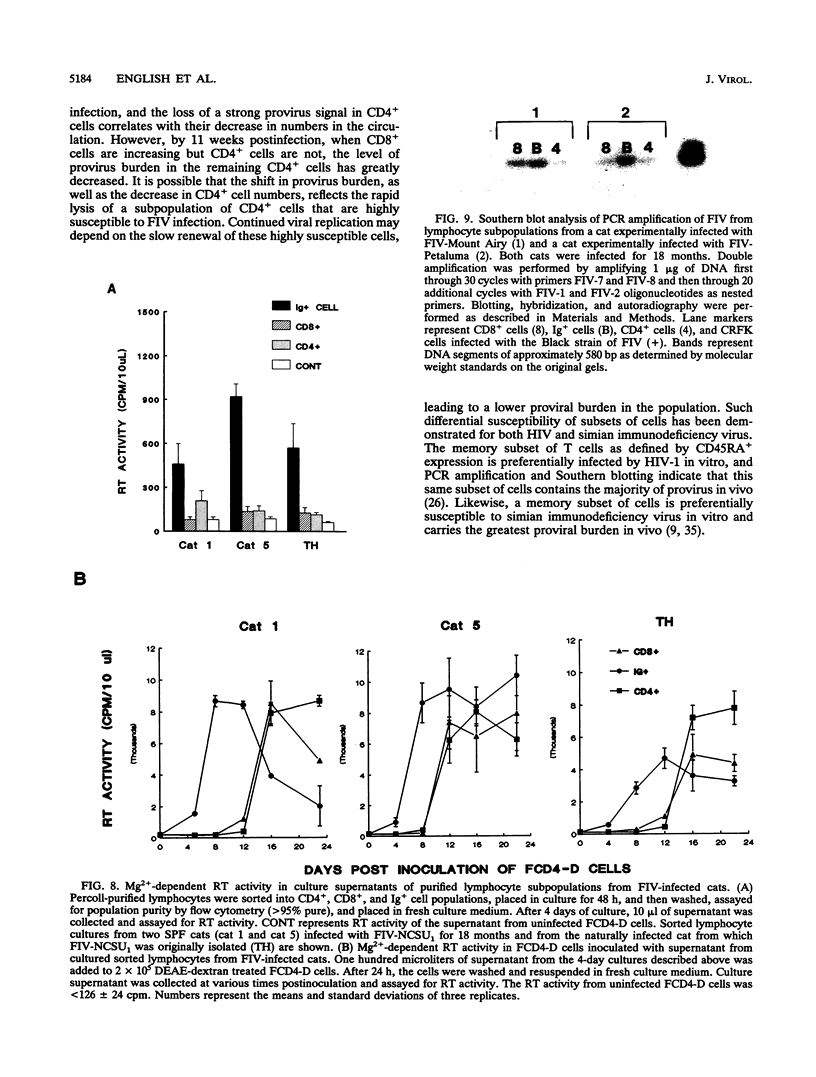


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackley C. D., Yamamoto J. K., Levy N., Pedersen N. C., Cooper M. D. Immunologic abnormalities in pathogen-free cats experimentally infected with feline immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5652–5655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5652-5655.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. C., Bissey L., Logan K. S., Pedersen N. C., Elder J. H., Collisson E. W. Feline immunodeficiency virus infects both CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3359–3364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3359-3364.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner D., Pedersen N. C. Infection of peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo with feline immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5483–5488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5483-5488.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehimi J., Bandyopadhyay S., Prakash K., Perussia B., Hassan N. F., Kawashima H., Campbell D., Kornbluth J., Starr S. E. In vitro infection of natural killer cells with different human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1812–1822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1812-1822.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish A. G., Beverley P. C., Clapham P. R., Crawford D. H., Greaves M. F., Weiss R. A. The CD4 (T4) antigen is an essential component of the receptor for the AIDS retrovirus. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):763–767. doi: 10.1038/312763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dow S. W., Dreitz M. J., Hoover E. A. Feline immunodeficiency virus neurotropism: evidence that astrocytes and microglia are the primary target cells. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1992 Dec;35(1-2):23–35. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(92)90118-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dow S. W., Poss M. L., Hoover E. A. Feline immunodeficiency virus: a neurotropic lentivirus. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(7):658–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallatin W. M., Gale M. J., Jr, Hoffman P. A., Willerford D. M., Draves K. E., Benveniste R. E., Morton W. R., Clark E. A. Selective replication of simian immunodeficiency virus in a subset of CD4+ lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3301–3305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Luciw P. A. Animal models of AIDS. FASEB J. 1989 Dec;3(14):2593–2606. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.14.2556312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatzmann D., Barré-Sinoussi F., Nugeyre M. T., Danquet C., Vilmer E., Griscelli C., Brun-Veziret F., Rouzioux C., Gluckman J. C., Chermann J. C. Selective tropism of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) for helper-inducer T lymphocytes. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):59–63. doi: 10.1126/science.6328660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A., Shimabukuro J., McHugh T., Casavant C., Stites D., Oshiro L. AIDS-associated retroviruses (ARV) can productively infect other cells besides human T helper cells. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90146-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D. S., Bowman D. D., Jacobson R. H., Barr M. C., Fevereiro M., Williams J. R., Noronha F. M., Scott F. W., Avery R. J. Suppression of lymphocyte blastogenesis to mitogens in cats experimentally infected with feline immunodeficiency virus. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1990 Oct;26(2):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(90)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massari F. E., Poli G., Schnittman S. M., Psallidopoulos M. C., Davey V., Fauci A. S. In vivo T lymphocyte origin of macrophage-tropic strains of HIV. Role of monocytes during in vitro isolation and in vivo infection. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4628–4632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McChesney M. B., Oldstone M. B. Virus-induced immunosuppression: infections with measles virus and human immunodeficiency virus. Adv Immunol. 1989;45:335–380. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monroe J. E., Calender A., Mulder C. Epstein-Barr virus-positive and -negative B-cell lines can be infected with human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3497–3500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3497-3500.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montagnier L., Gruest J., Chamaret S., Dauguet C., Axler C., Guétard D., Nugeyre M. T., Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Brunet J. B. Adaptation of lymphadenopathy associated virus (LAV) to replication in EBV-transformed B lymphoblastoid cell lines. Science. 1984 Jul 6;225(4657):63–66. doi: 10.1126/science.6328661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Clements J. E. Biology and pathogenesis of lentiviruses. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jul;70(Pt 7):1617–1639. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-7-1617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotney C., English R. V., Housman J., Davidson M. G., Nasisse M. P., Jeng C. R., Davis W. C., Tompkins M. B. Lymphocyte population changes in cats naturally infected with feline immunodeficiency virus. AIDS. 1990 Dec;4(12):1213–1218. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199012000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor T. P., Jr, Tanguay S., Steinman R., Smith R., Barr M. C., Yamamoto J. K., Pedersen N. C., Andersen P. R., Tonelli Q. J. Development and evaluation of immunoassay for detection of antibodies to the feline T-lymphotropic lentivirus (feline immunodeficiency virus). J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):474–479. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.474-479.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C., Ho E. W., Brown M. L., Yamamoto J. K. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic virus from domestic cats with an immunodeficiency-like syndrome. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):790–793. doi: 10.1126/science.3643650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. C., Yamamoto J. K., Ishida T., Hansen H. Feline immunodeficiency virus infection. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 May;21(1):111–129. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Psallidopoulos M. C., Schnittman S. M., Thompson L. M., 3rd, Baseler M., Fauci A. S., Lane H. C., Salzman N. P. Integrated proviral human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is present in CD4+ peripheral blood lymphocytes in healthy seropositive individuals. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4626–4631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4626-4631.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Lane H. C., Greenhouse J., Justement J. S., Baseler M., Fauci A. S. Preferential infection of CD4+ memory T cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1: evidence for a role in the selective T-cell functional defects observed in infected individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6058–6062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnittman S. M., Psallidopoulos M. C., Lane H. C., Thompson L., Baseler M., Massari F., Fox C. H., Salzman N. P., Fauci A. S. The reservoir for HIV-1 in human peripheral blood is a T cell that maintains expression of CD4. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.2665081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbott R. L., Sparger E. E., Lovelace K. M., Fitch W. M., Pedersen N. C., Luciw P. A., Elder J. H. Nucleotide sequence and genomic organization of feline immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5743–5747. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins M. B., Nelson P. D., English R. V., Novotney C. Early events in the immunopathogenesis of feline retrovirus infections. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1991 Nov 15;199(10):1311–1315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins M. B., Ogilvie G. K., Franklin R. A., Kelley K. W., Tompkins W. A. Induction of IL-2 and lymphokine activated killer cells in the cat. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Sep;16(1-2):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(87)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompkins M. B., Pang V. F., Michaely P. A., Feinmehl R. I., Basgall E. J., Baszler T. V., Zachary J. F., Tompkins W. A. Feline cytotoxic large granular lymphocytes induced by recombinant human IL-2. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):749–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torten M., Franchini M., Barlough J. E., George J. W., Mozes E., Lutz H., Pedersen N. C. Progressive immune dysfunction in cats experimentally infected with feline immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2225–2230. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2225-2230.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehurst C. E., Hill R. J., Day N. K., Gengozian N. Phenotypic markers for the feline monocyte: rosette formation with human erythrocytes and a monoclonal antibody which binds myeloid cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1991 Jul;197(3):317–325. doi: 10.3181/00379727-197-43262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willerford D. M., Gale M. J., Jr, Benveniste R. E., Clark E. A., Gallatin W. M. Simian immunodeficiency virus is restricted to a subset of blood CD4+ lymphocytes that includes memory cells. J Immunol. 1990 May 15;144(10):3779–3783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagury D., Bernard J., Leonard R., Cheynier R., Feldman M., Sarin P. S., Gallo R. C. Long-term cultures of HTLV-III--infected T cells: a model of cytopathology of T-cell depletion in AIDS. Science. 1986 Feb 21;231(4740):850–853. doi: 10.1126/science.2418502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]