Abstract
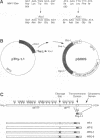
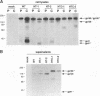
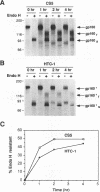
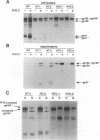
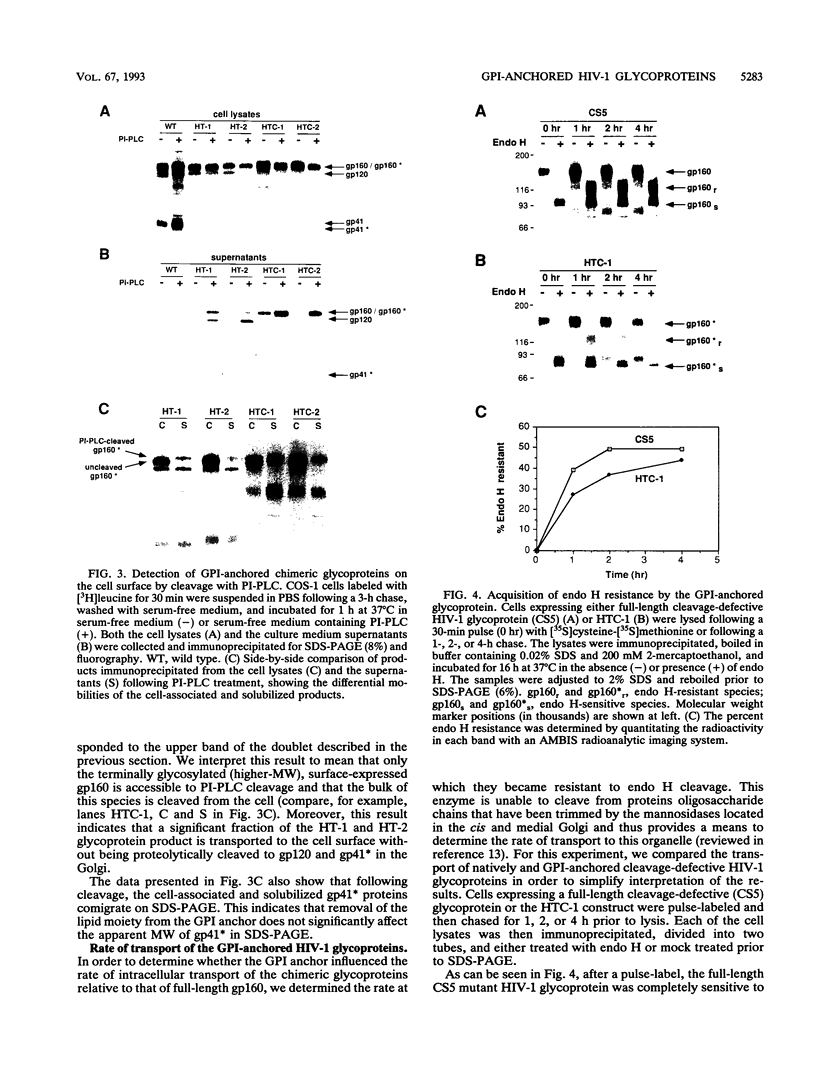
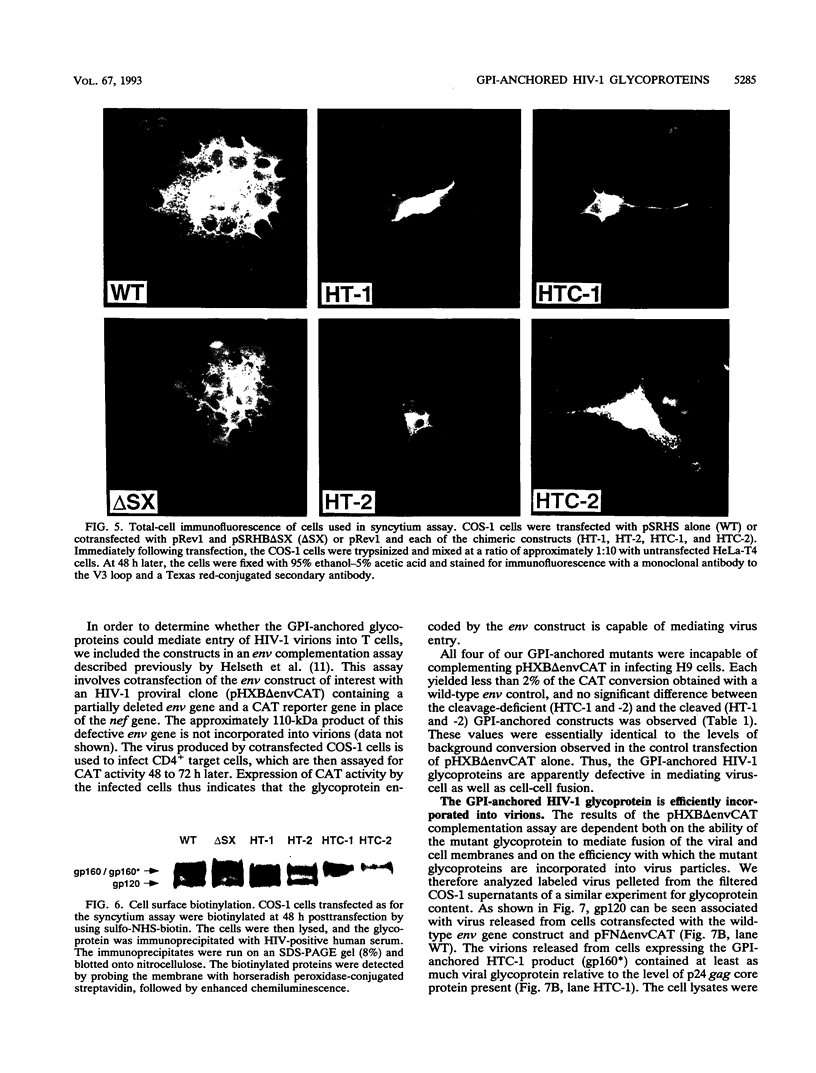
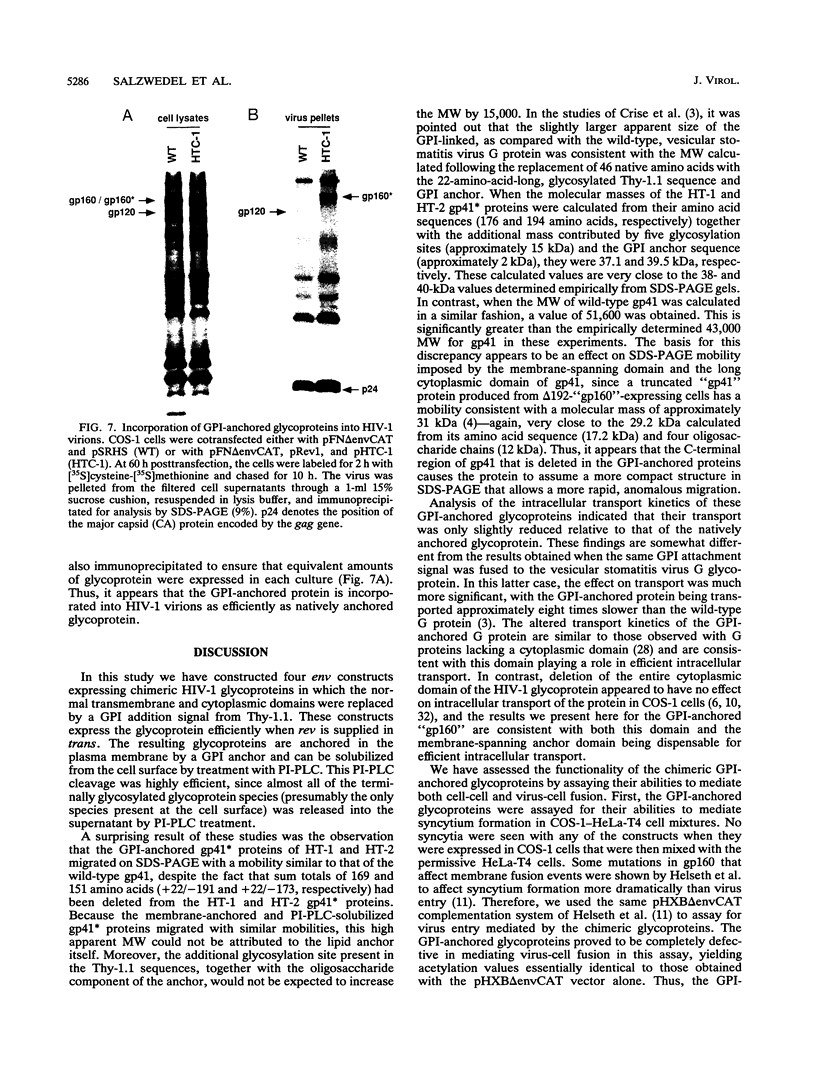
Four chimeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) env genes were constructed which encoded the extracellular domain of either the wild-type or a cleavage-defective HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (gp160) fused at one of two different positions in env to a C-terminal glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) attachment signal from the mouse Thy-1.1 glycoprotein. All four of the constructs encoded glycoproteins that were efficiently expressed when Rev was supplied in trans, and the two cleavable forms were processed normally to gp120 and a chimeric "gp41." The chimeric glycoproteins, in contrast to the wild-type glycoprotein, could be cleaved from the surface of transfected cells by treatment with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, indicating that they were anchored in the plasma membrane by a GPI moiety. These GPI-anchored glycoproteins were transported intracellularly at a rate only slightly lower than that of the full-length HIV-1 glycoprotein and were present on the cell surface in equivalent amounts. Nevertheless, all four glycoproteins were defective in mediating both cell-cell and virus-cell fusion as determined by syncytium formation in COS-1-HeLa-T4 cell mixtures and trans complementation of an env-defective HIV-1 genome.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman P. W., Nunes W. M., Haffar O. K. Expression of membrane-associated and secreted variants of gp160 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vitro and in continuous cell lines. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3135–3142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3135-3142.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crise B., Ruusala A., Zagouras P., Shaw A., Rose J. K. Oligomerization of glycolipid-anchored and soluble forms of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5328–5333. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5328-5333.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubay J. W., Roberts S. J., Brody B., Hunter E. Mutations in the leucine zipper of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein affect fusion and infectivity. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4748–4756. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4748-4756.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubay J. W., Roberts S. J., Hahn B. H., Hunter E. Truncation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein cytoplasmic domain blocks virus infectivity. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6616–6625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6616-6625.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Williams A. F. Cell-surface anchoring of proteins via glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol structures. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:285–320. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D. H., Lever A., Terwilliger E., Sodroski J. Effects of deletions in the cytoplasmic domain on biological functions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoproteins. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3306–3315. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3306-3315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabuzda D., Olshevsky U., Bertani P., Haseltine W. A., Sodroski J. Identification of membrane anchorage domains of the HIV-1 gp160 envelope glycoprotein precursor. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(1):34–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helseth E., Kowalski M., Gabuzda D., Olshevsky U., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Rapid complementation assays measuring replicative potential of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein mutants. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2416–2420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2416-2420.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helseth E., Olshevsky U., Gabuzda D., Ardman B., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Changes in the transmembrane region of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 envelope glycoprotein affect membrane fusion. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6314–6318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6314-6318.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter E., Swanstrom R. Retrovirus envelope glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;157:187–253. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75218-6_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski M., Potz J., Basiripour L., Dorfman T., Goh W. C., Terwilliger E., Dayton A., Rosen C., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Functional regions of the envelope glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Science. 1987 Sep 11;237(4820):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.3629244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis N., Williams J., Rekosh D., Hammarskjöld M. L. Identification of a cis-acting element in human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) that is responsive to the HIV-1 rev and human T-cell leukemia virus types I and II rex proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1690–1697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1690-1697.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Caras I. W., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Fusion proteins containing a minimal GPI-attachment signal are apically expressed in transfected MDCK cells. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jul;99(Pt 3):637–640. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.3.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Sargiacomo M., Graeve L., Saltiel A. R., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Polarized apical distribution of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins in a renal epithelial cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9557–9561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Kincade P. W. Phosphatidylinositol is the membrane-anchoring domain of the Thy-1 glycoprotein. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):62–64. doi: 10.1038/318062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G. The glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol anchor of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Dec 6;988(3):427–454. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran P., Caras I. W. A nonfunctional sequence converted to a signal for glycophosphatidylinositol membrane anchor attachment. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):329–336. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran P., Caras I. W. Fusion of sequence elements from non-anchored proteins to generate a fully functional signal for glycophosphatidylinositol membrane anchor attachment. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1595–1600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Fisher A., Jagodzinski L. L., Mitsuya H., Liou R. S., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. Complete nucleotide sequences of functional clones of the AIDS virus. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1987 Spring;3(1):57–69. doi: 10.1089/aid.1987.3.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Bergmann J. E. Altered cytoplasmic domains affect intracellular transport of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):513–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90384-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Dayton A., Terwilliger E., Haseltine W. A second post-transcriptional trans-activator gene required for HTLV-III replication. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):412–417. doi: 10.1038/321412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse A. G., Barclay A. N., Watts A., Williams A. F. A glycophospholipid tail at the carboxyl terminus of the Thy-1 glycoprotein of neurons and thymocytes. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1003–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.2865810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilk T., Pfeiffer T., Bosch V. Retained in vitro infectivity and cytopathogenicity of HIV-1 despite truncation of the C-terminal tail of the env gene product. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):167–177. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90692-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]