Abstract
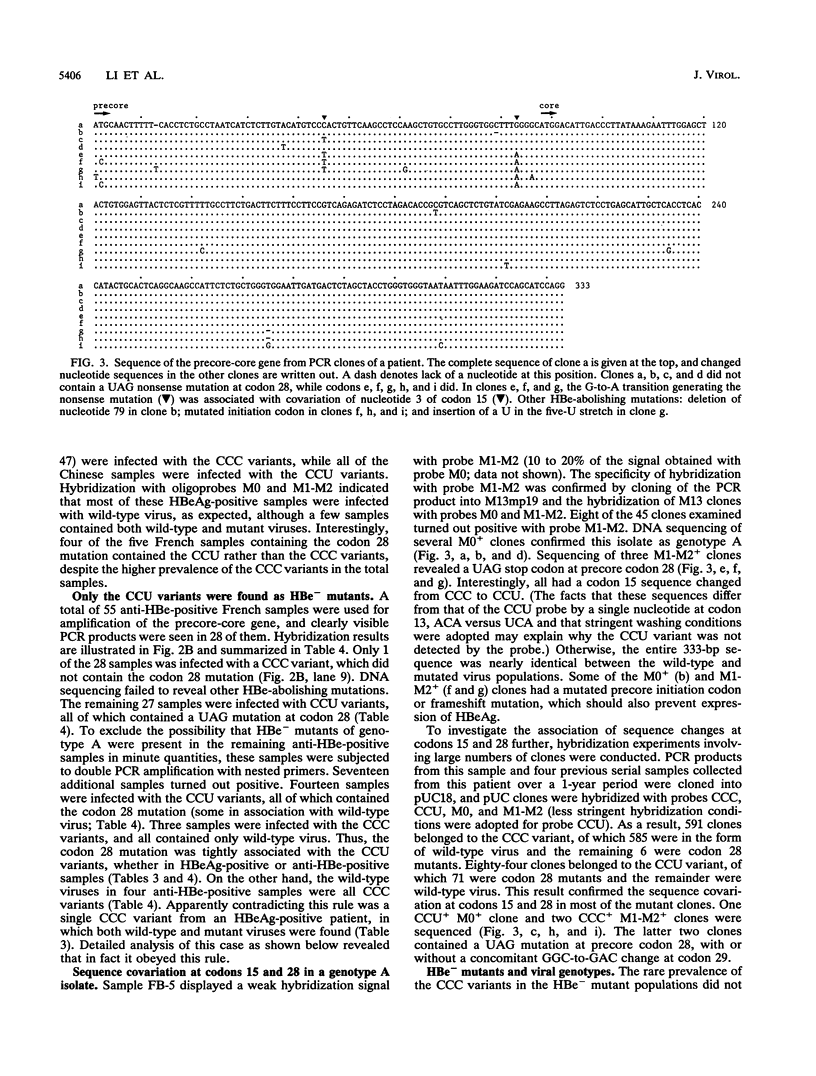
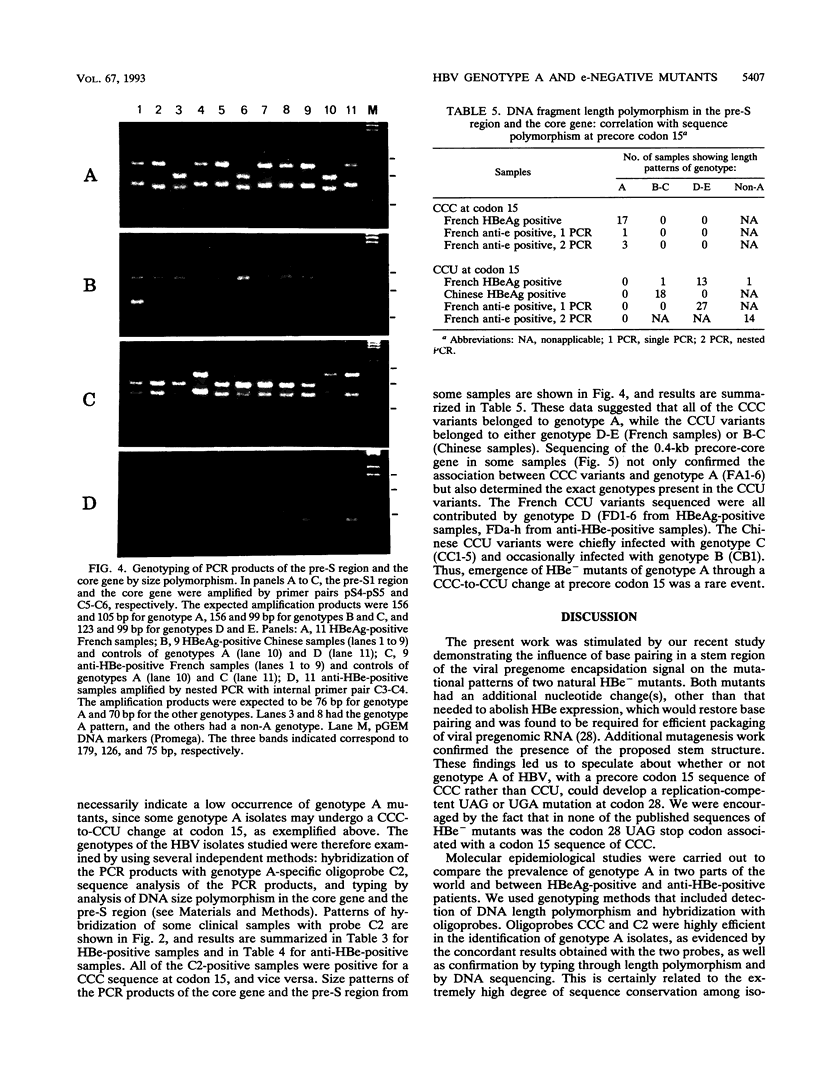
The emergence of HBe-minus hepatitis B virus (HBV) mutants, usually through a UAG nonsense mutation at codon 28 of the precore region, helps the virus to survive the anti-HBe immune response of the host. Host and viral factors that predispose to the emergence of such mutants are not well characterized. The fact that the precore region forms a hairpin structure essential for the packaging of viral pregenomic RNA may explain the extremely high prevalence of the UAG mutation at codon 28. It converts a wobble U-G pair in the packaging signal between nucleotide 3 of codon 15 (CCU) and nucleotide 2 of codon 28 (UGG) into a U-A pair. Since genotype A of HBV has a CCC sequence at codon 15, the UAG mutation would, instead, disrupt a C-G pair present in the wild-type virus. This alteration was shown by transfection experiments to greatly compromise the packaging of pregenomic RNA. The implication of this finding was elucidated by molecular epidemiological studies. Genotype A was found to be the most prevalent genotype in the wild-type virus populations in France but was found in only 1 of the 46 isolates of HBe-minus mutants found there. These mutants were contributed chiefly by genotype D, the second most prevalent genotype in France, which is characterized by a CCU sequence at codon 15. The role of the single nucleotide at codon 15 was confirmed by the finding of the single genotype A isolate in which both wild-type and mutant viruses were present. Interestingly, nearly all of the mutants had a codon 15 sequence of CCU instead of the CCC present in the wild-type viruses. Our results suggest that genotype A of HBV rarely circulates as HBe-minus mutants, probably because of a requirement for a simultaneous sequence change at codon 15. These data, together with the virtual absence of genotype A in the Chinese samples examined, may provide some insights into the uneven prevalence of HBe-minus mutants in the world.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blum H. E., Liang T. J., Galun E., Wands J. R. Persistence of hepatitis B viral DNA after serological recovery from hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology. 1991 Jul;14(1):56–63. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840140110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonino F., Brunetto M. R., Rizzetto M., Will H. Hepatitis B virus unable to secrete e antigen. Gastroenterology. 1991 Apr;100(4):1138–1141. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90296-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L., Carman W. F., Thomas H. C. The clinical significance of molecular variation within the hepatitis B virus genome. Hepatology. 1992 Jan;15(1):144–148. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunetto M. R., Giarin M. M., Oliveri F., Chiaberge E., Baldi M., Alfarano A., Serra A., Saracco G., Verme G., Will H. Wild-type and e antigen-minus hepatitis B viruses and course of chronic hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4186–4190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carman W. F., Ferrao M., Lok A. S., Ma O. C., Lai C. L., Thomas H. C. Precore sequence variation in Chinese isolates of hepatitis B virus. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):127–133. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Enders G., Sprengel R., Peters N., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Expression of the precore region of an avian hepatitis B virus is not required for viral replication. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3322–3325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3322-3325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. S., Kew M. C., Hornbuckle W. E., Tennant B. C., Cote P. J., Gerin J. L., Purcell R. H., Miller R. H. The precore gene of the woodchuck hepatitis virus genome is not essential for viral replication in the natural host. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5682–5684. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5682-5684.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couroucé-Pauty A. M., Plançon A., Soulier J. P. Distribution of HBsAg subtypes in the world. Vox Sang. 1983;44(4):197–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1983.tb01885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan R. B., Chu M. J., Shen L. P., Qian S. W., Li Z. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the cloned DNA of hepatitis B virus subtype adr in pADR-1. Sci Sin B. 1987 May;30(5):507–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther S., Meisel H., Reip A., Miska S., Krüger D. H., Will H. Frequent and rapid emergence of mutated pre-C sequences in HBV from e-antigen positive carriers who seroconvert to anti-HBe during interferon treatment. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90315-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker-Niepmann M., Bartenschlager R., Schaller H. A short cis-acting sequence is required for hepatitis B virus pregenome encapsidation and sufficient for packaging of foreign RNA. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3389–3396. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Tong S., Vitvitski L., Zoulim F., Trépo C. Rapid detection and further characterization of infection with hepatitis B virus variants containing a stop codon in the distal pre-C region. J Gen Virol. 1990 Sep;71(Pt 9):1993–1998. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-9-1993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren K., Kidd A. H. Enzymatic amplification and sequence analysis of precore/core DNA in HBsAg-positive patients. J Med Virol. 1991 Jul;34(3):179–183. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890340309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loncarevic I. F., Zentgraf H., Schröder C. H. Sequence of a replication competent hepatitis B virus genome with a preX open reading frame. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4940–4940. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzin A., Menzo S., Bagnarelli P., Varaldo P. E., Bearzi I., Carloni G., Galibert F., Clementi M. Sequence analysis of the hepatitis B virus pre-C region in hepatocellular carcinoma [HCC] and nontumoral liver tissues from HCC patients. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):890–895. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Jones J. E., Hughes J. L., Price J., Raney A. K., McLachlan A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6599–6603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata N., Miller R. H., Ishak K. G., Purcell R. H. The complete nucleotide sequence of a pre-core mutant of hepatitis B virus implicated in fulminant hepatitis and its biological characterization in chimpanzees. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):263–276. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Tsuda F., Sakugawa H., Sastrosoewignjo R. I., Imai M., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. Typing hepatitis B virus by homology in nucleotide sequence: comparison of surface antigen subtypes. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2575–2583. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Onda H., Sasada R., Igarashi K., Sugino Y., Nishioka K. The complete nucleotide sequences of the cloned hepatitis B virus DNA; subtype adr and adw. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1747–1757. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi Z. H., Yan J., Xiong W. J., Yuan J. G., Song S., Xue C. Q., Cai L. W. Determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of HBV adr NC-1 DNA. Sci China B. 1989 Sep;32(9):1082–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rho H. M., Kim K., Hyun S. W., Kim Y. S. The nucleotide sequence and reading frames of a mutant hepatitis B virus subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2124–2124. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Salfeld J., Schaller H. The duck hepatitis B virus pre-C region encodes a signal sequence which is essential for synthesis and secretion of processed core proteins but not for virus formation. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3701–3709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3701-3709.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A. Variants of hepatitis B virus associated with fulminant liver disease. N Engl J Med. 1991 Jun 13;324(24):1737–1739. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106133242411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura F., Ishii T., Fujii N., Uchida T. Complete nucleotide sequence of hepatitis B virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 11;18(15):4587–4587. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.15.4587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. P., Brotman B., Li J. S., Vitvitski L., Pascal D., Prince A. M., Trépo C. In vitro and in vivo replication capacity of the precore region defective hepatitis B virus variants. J Hepatol. 1991;13 (Suppl 4):S68–S73. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90028-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. P., Diot C., Gripon P., Li J., Vitvitski L., Trépo C., Guguen-Guillouzo C. In vitro replication competence of a cloned hepatitis B virus variant with a nonsense mutation in the distal pre-C region. Virology. 1991 Apr;181(2):733–737. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90908-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. P., Li J. S., Vitvitski L., Kay A., Treépo C. Evidence for a base-paired region of hepatitis B virus pregenome encapsidation signal which influences the patterns of precore mutations abolishing HBe protein expression. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5651–5655. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5651-5655.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. P., Li J. S., Vitvitski L., Trépo C. Active hepatitis B virus replication in the presence of anti-HBe is associated with viral variants containing an inactive pre-C region. Virology. 1990 Jun;176(2):596–603. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90030-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. P., Li J. S., Vitvitski L., Trépo C. Replication capacities of natural and artificial precore stop codon mutants of hepatitis B virus: relevance of pregenome encapsidation signal. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90185-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran A., Kremsdorf D., Capel F., Housset C., Dauguet C., Petit M. A., Brechot C. Emergence of and takeover by hepatitis B virus (HBV) with rearrangements in the pre-S/S and pre-C/C genes during chronic HBV infection. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3566–3574. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3566-3574.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tur-Kaspa R., Klein A., Aharonson S. Hepatitis B virus precore mutants are identical in carriers from various ethnic origins and are associated with a range of liver disease severity. Hepatology. 1992 Dec;16(6):1338–1342. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich P. P., Bhat R. A., Kelly I., Brunetto M. R., Bonino F., Vyas G. N. A precore-defective mutant of hepatitis B virus associated with e antigen-negative chronic liver disease. J Med Virol. 1990 Oct;32(2):109–118. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890320208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudin M., Wolstenholme A. J., Tsiquaye K. N., Zuckerman A. J., Harrison T. J. The complete nucleotide sequence of the genome of a hepatitis B virus isolated from a naturally infected chimpanzee. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1383–1389. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]