Abstract
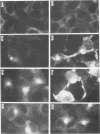
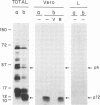
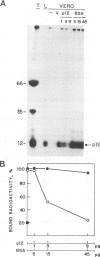
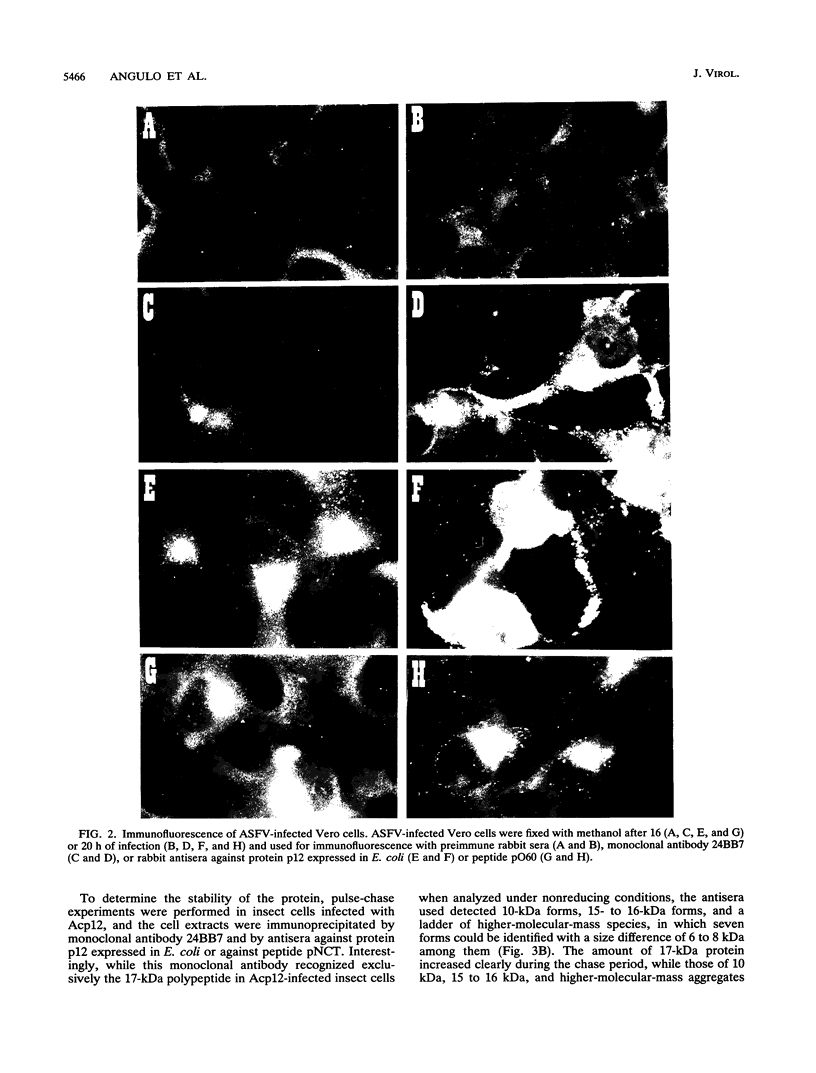
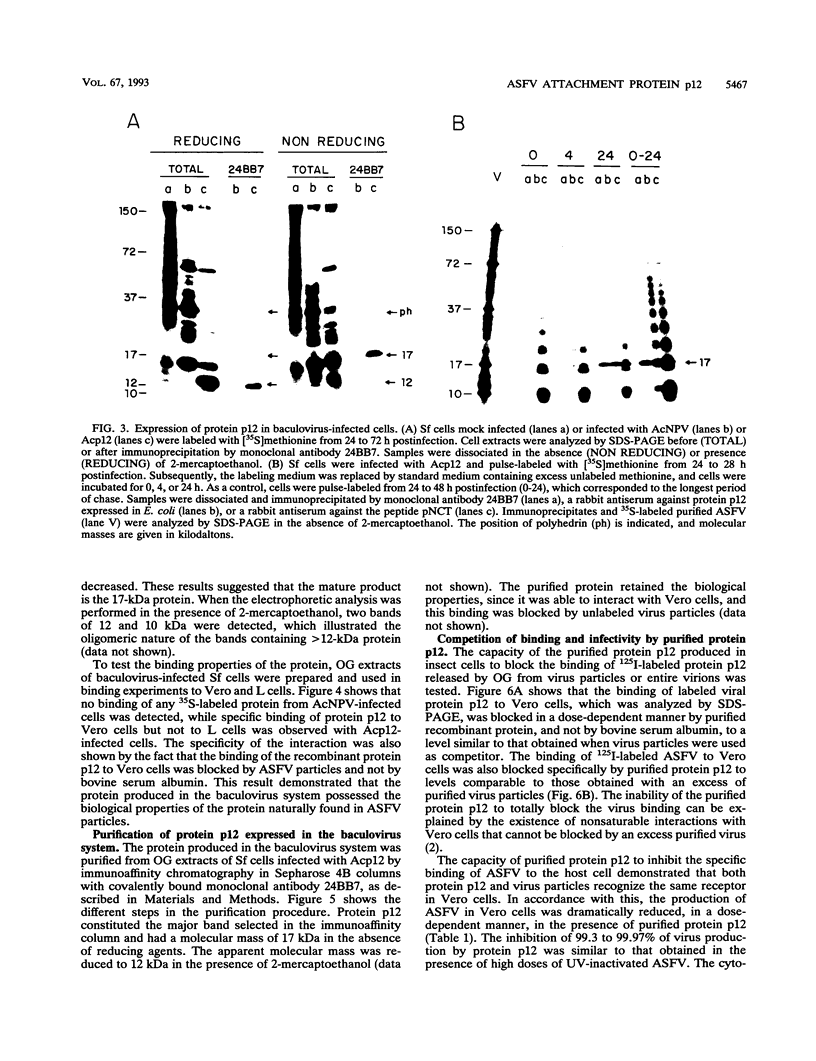
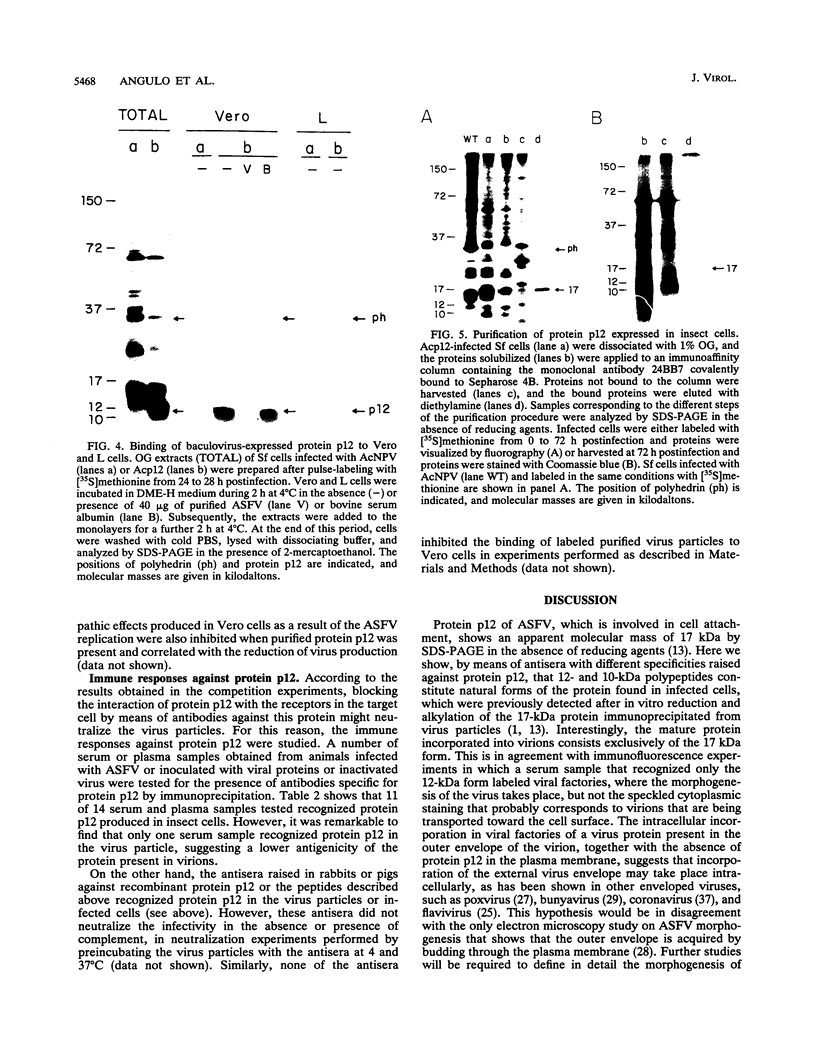
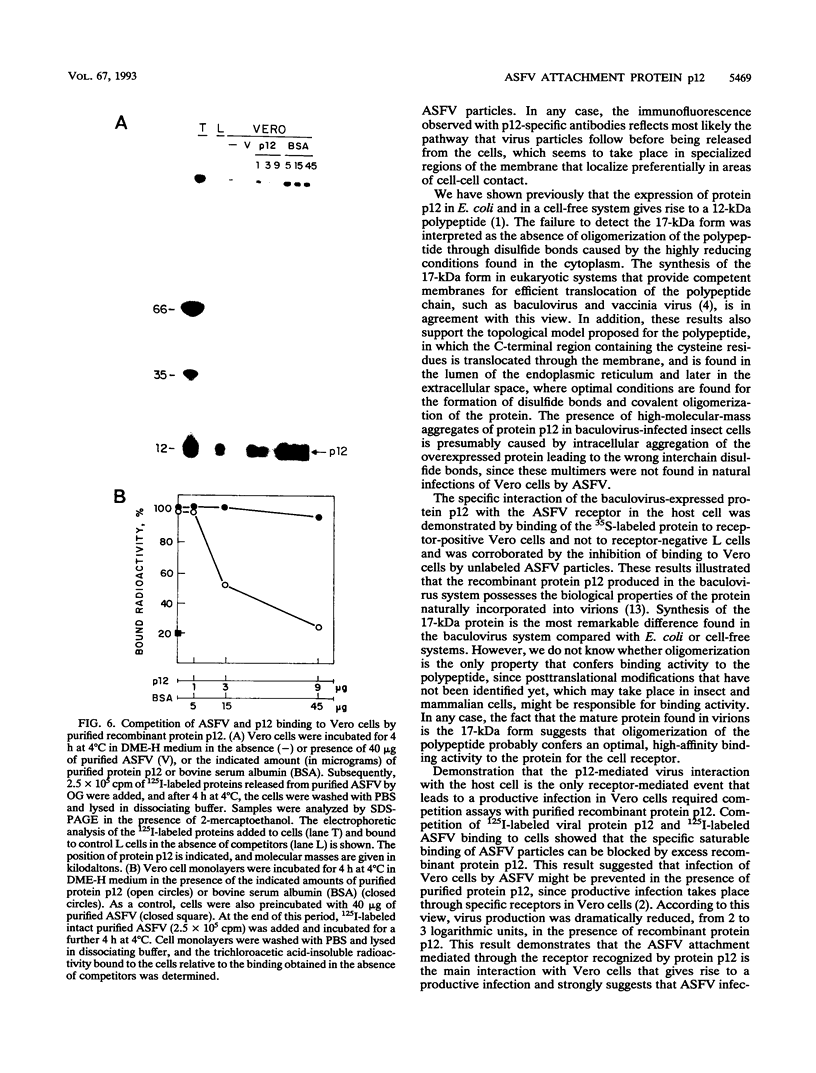
The African swine fever virus protein p12, involved in virus attachment to the host cell, has an apparent molecular mass of 17 kDa in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under nonreducing conditions. We have also identified 12- and 10-kDa forms of the p12 protein in infected Vero cells and found that the mature 17-kDa protein is the only form present in virus particles. The p12 protein has been produced in large amounts in Spodoptera frugiperda insect cells infected with a recombinant baculovirus. A 17-kDa protein that possessed the biological properties of the viral protein was produced, since it bound to susceptible Vero cells and not to receptor-negative L cells, which do not support virus replication. The binding of the baculovirus-expressed protein p12 to Vero cells was specifically blocked by virus particles. In addition, the recombinant protein purified by immunoaffinity chromatography blocked the specific binding of virus particles to susceptible cells and prevented infection, demonstrating that the p12 protein mediates the attachment of virions to specific receptors and indicating that blocking the p12-mediated interaction between African swine fever virus and receptors in Vero cells can inhibit infection. However, although antibodies specific for protein p12 are induced in natural infections and in animals inoculated with inactivated virus or recombinant protein p12, these antisera did not inhibit virus binding to the host cell or neutralize virus infectivity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcamí A., Angulo A., López-Otín C., Muñoz M., Freije J. M., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Amino acid sequence and structural properties of protein p12, an African swine fever virus attachment protein. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3860–3868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3860-3868.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcamí A., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Interaction of African swine fever virus with macrophages. Virus Res. 1990 Oct;17(2):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90071-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcamí A., Carrascosa A. L., Viñuela E. Saturable binding sites mediate the entry of African swine fever virus into Vero cells. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):393–398. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angulo A., Viñuela E., Alcamí A. Comparison of the sequence of the gene encoding African swine fever virus attachment protein p12 from field virus isolates and viruses passaged in tissue culture. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3869–3872. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3869-3872.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buller R. M., Palumbo G. J. Poxvirus pathogenesis. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):80–122. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.80-122.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campadelli-Fiume G., Stirpe D., Boscaro A., Avitabile E., Foá-Tomasi L., Barker D., Roizman B. Glycoprotein C-dependent attachment of herpes simplex virus to susceptible cells leading to productive infection. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90396-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa A. L., Saastre I., González P., Viñuela E. Localization of the African swine fever virus attachment protein P12 in the virus particle by immunoelectron microscopy. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):460–465. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa A. L., Sastre I., Viñuela E. African swine fever virus attachment protein. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2283–2289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2283-2289.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrascosa A. L., del Val M., Santarén J. F., Viñuela E. Purification and properties of African swine fever virus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.337-344.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Boer C. J. Studies to determine neutralizing antibody in sera from animals recovered from African swine fever and laboratory animals inoculated with African virus with adjuvants. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;20(2):164–179. doi: 10.1007/BF01241270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Barreno B., Sanz A., Nogal M. L., Viñuela E., Enjuanes L. Monoclonal antibodies of African swine fever virus: antigenic differences among field virus isolates and viruses passaged in cell culture. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):385–392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.385-392.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herold B. C., WuDunn D., Soltys N., Spear P. G. Glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus type 1 plays a principal role in the adsorption of virus to cells and in infectivity. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1090–1098. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1090-1098.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leary K., Blair C. D. Sequential events in the morphogenesis of japanese Encephalitis virus. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 Aug;72(2):123–129. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Possee R. D., Overton H. A., Bishop D. H. Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1233–1250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Harrison A. K., Whitfield S. G. Bunyaviridae: morphologic and morphogenetic similarities of Bunyamwera serologic supergroup viruses and several other arthropod-borne viruses. Intervirology. 1973;1(4):297–316. doi: 10.1159/000148858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes J. F., Vigário J. D., Terrinha A. M. Ultrastructural study of African swine fever virus replication in cultures of swine bone marrow cells. Arch Virol. 1975;49(1):59–66. doi: 10.1007/BF02175596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G. The canyon hypothesis. Hiding the host cell receptor attachment site on a viral surface from immune surveillance. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14587–14590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs D. H., Leight G., Cone J., Schwarz S., Stuart L., Rosenberg S. Transplantation in miniature swine. I. Fixation of the major histocompatibility complex. Transplantation. 1976 Dec;22(6):559–567. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197612000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz A., García-Barreno B., Nogal M. L., Viñuela E., Enjuanes L. Monoclonal antibodies specific for African swine fever virus proteins. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):199–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.199-206.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears A. E., McGwire B. S., Roizman B. Infection of polarized MDCK cells with herpes simplex virus 1: two asymmetrically distributed cell receptors interact with different viral proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 15;88(12):5087–5091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.12.5087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis W., Brown J. H., Cusack S., Paulson J. C., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature. 1988 Jun 2;333(6172):426–431. doi: 10.1038/333426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Val M., Viñuela E. Glycosylated components induced in African swine fever (ASF) virus-infected Vero cells. Virus Res. 1987 Jun;7(4):297–308. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]