Abstract
The human cytomegalovirus (CMV) virion glycoprotein gpUL4 (gp48) gene expresses a transcript that contains three AUG codons upstream from the one used to initiate synthesis of the gp48 protein. Previously we reported that the second of these AUG codons, AUG2, was necessary but insufficient for inhibition of downstream translation (M. Schleiss, C. R. Degnin, and A. P. Geballe, J. Virol. 65:6782-6789, 1991). We now demonstrate that the coding information of the upstream open reading frame initiated by AUG2 (uORF2) is critical for the inhibitory signal. Several missense mutations, particularly those involving the carboxy-terminal codons of uORF2, inactivate the inhibitory signal, while mutations that preserve the coding content of uORF2 uniformly retain the inhibitory signal. The uORF2 termination codon is essential for inhibition, but leader sequences further downstream are not critical. Conservation of uORF2 among clinical strains of CMV suggests that uORF2 provides an important function in the CMV infectious cycle. Although these results indicate that the peptide product of uORF2 mediates the inhibitory effect, we demonstrate that the uORF2 signal acts only in cis, and we propose a model of inhibition by the gp48 uORF2 signal.
Full text
PDF
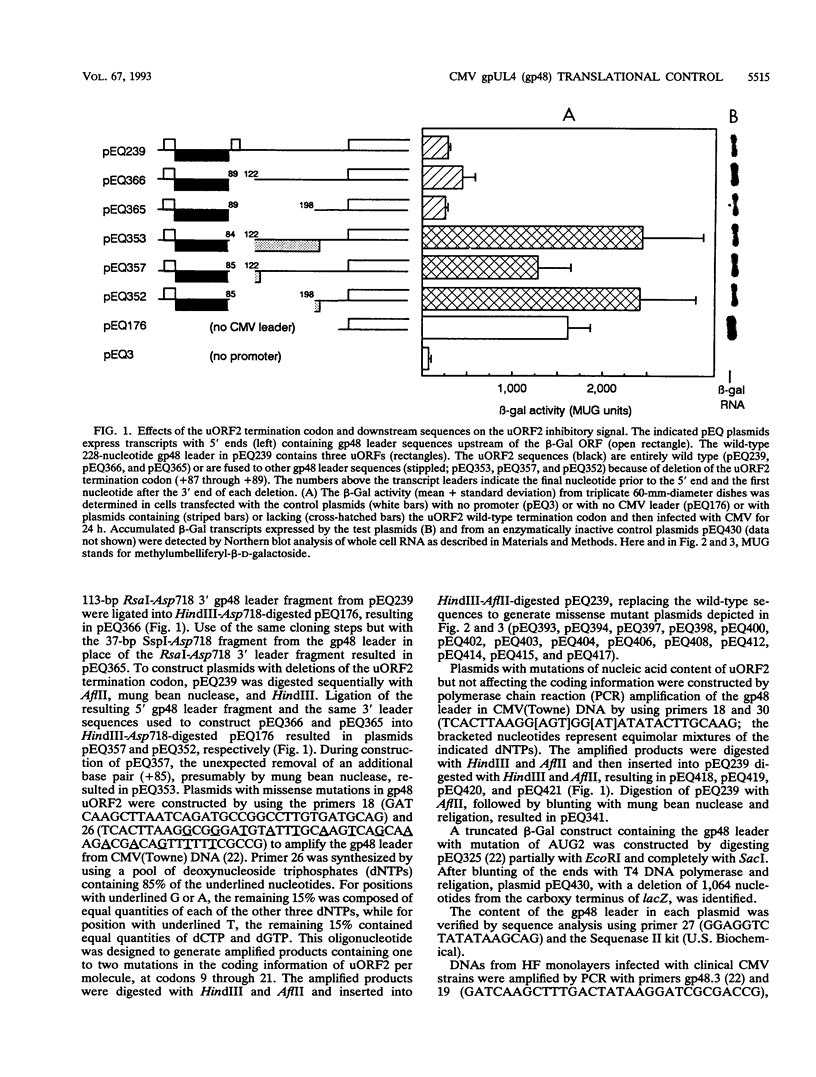

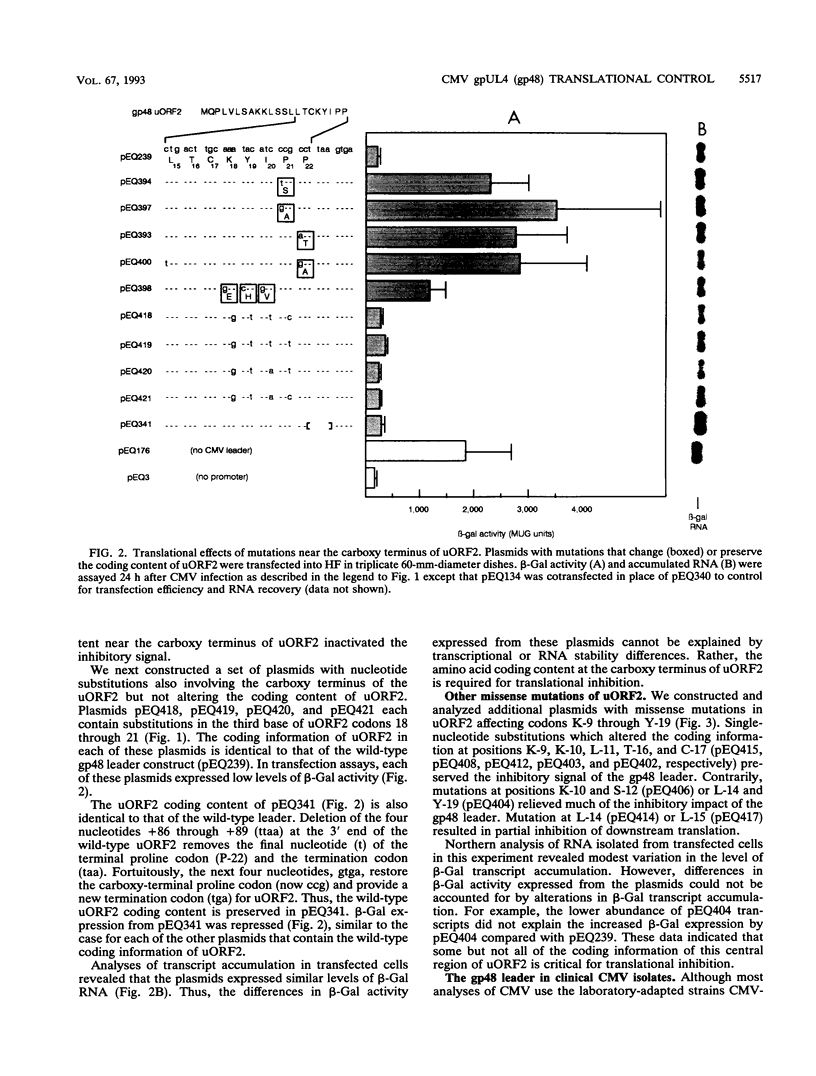
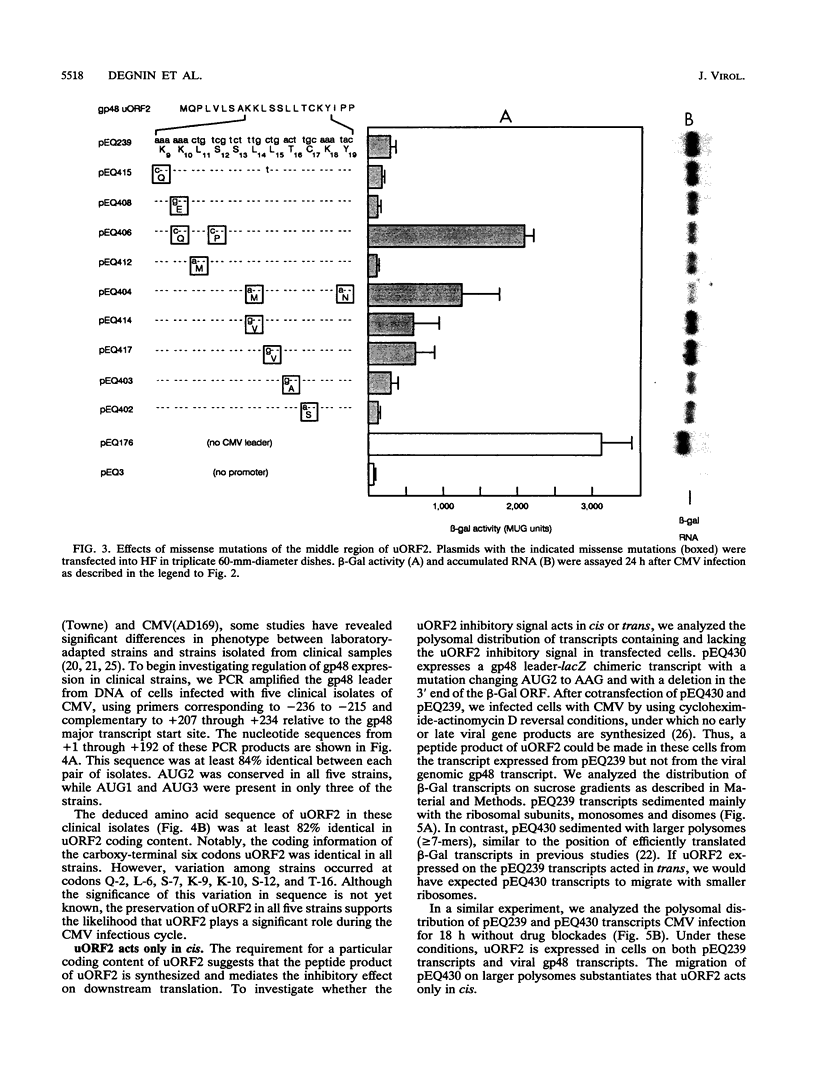
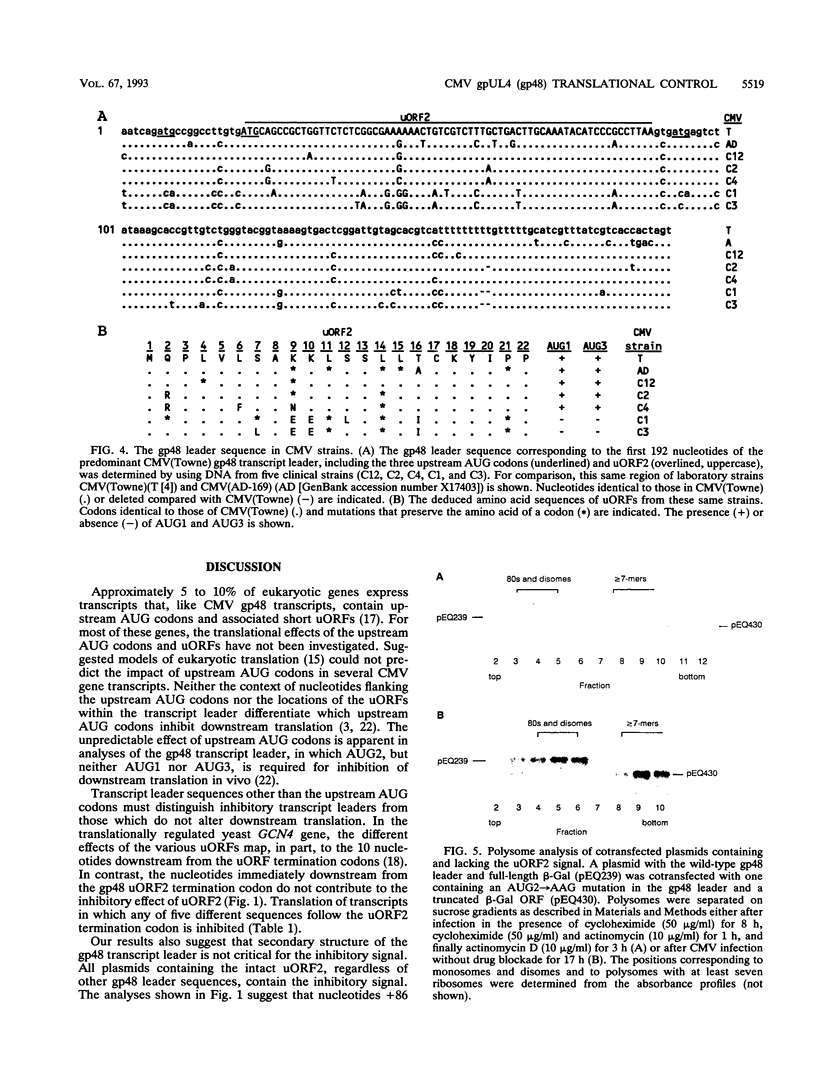


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barkan A., Mertz J. E. The number of ribosomes on simian virus 40 late 16S mRNA is determined in part by the nucleotide sequence of its leader. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):813–816. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein H. D., Poritz M. A., Strub K., Hoben P. J., Brenner S., Walter P. Model for signal sequence recognition from amino-acid sequence of 54K subunit of signal recognition particle. Nature. 1989 Aug 10;340(6233):482–486. doi: 10.1038/340482a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biegalke B. J., Geballe A. P. Translational inhibition by cytomegalovirus transcript leaders. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):657–667. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90531-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. P., Vesole D. H., Nelson J., Oldstone M. B., Stinski M. F. Identification and expression of a human cytomegalovirus early glycoprotein. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3330–3337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3330-3337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chee M. S., Bankier A. T., Beck S., Bohni R., Brown C. M., Cerny R., Horsnell T., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Kouzarides T., Martignetti J. A. Analysis of the protein-coding content of the sequence of human cytomegalovirus strain AD169. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:125–169. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doohan J. P., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides: ribosome pausing during the translation of reovirus S1 mRNA. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):409–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90006-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo J. E., Shatkin A. J. Translation of bicistronic viral mRNA in transfected cells: regulation at the level of elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):328–332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavini N., Pulakat L. Role of ribosome release in the basal level of expression of the Escherichia coli gene pheA. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Mar;137(3):679–684. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-3-679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Leach F. S., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus late gene expression: gamma genes are controlled by posttranscriptional events. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):864–874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.864-874.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Mocarski E. S. Translational control of cytomegalovirus gene expression is mediated by upstream AUG codons. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3334–3340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3334-3340.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geballe A. P., Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. A cis-acting element within the 5' leader of a cytomegalovirus beta transcript determines kinetic class. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):865–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goins W. F., Stinski M. F. Expression of a human cytomegalovirus late gene is posttranscriptionally regulated by a 3'-end-processing event occurring exclusively late after infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4202–4213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. R., Morris D. R. Cell-specific translational regulation of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase mRNA. Dependence on translation and coding capacity of the cis-acting upstream open reading frame. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):726–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. A short leader sequence impairs the fidelity of initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Gene Expr. 1991 May;1(2):111–115. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of vertebrate mRNA sequences: intimations of translational control. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):887–903. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Sequences that surround the stop codons of upstream open reading frames in GCN4 mRNA determine their distinct functions in translational control. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1217–1225. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Bonyhadi M., Salimi S., McCune J. M., Kaneshima H. Human cytomegalovirus in a SCID-hu mouse: thymic epithelial cells are prominent targets of viral replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):104–108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin S. A., Starr S. E., Friedman H. M., Brayman K., Harris S., Jackson S., Tustin N. B., Grossman R., Dafoe D., Barker C. Effect of Towne live virus vaccine on cytomegalovirus disease after renal transplant. A controlled trial. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Apr 1;114(7):525–531. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-114-7-525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleiss M. R., Degnin C. R., Geballe A. P. Translational control of human cytomegalovirus gp48 expression. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6782–6789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6782-6789.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedman S. A., Gelembiuk G. W., Mertz J. E. Translation initiation at a downstream AUG occurs with increased efficiency when the upstream AUG is located very close to the 5' cap. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):453–457. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.453-457.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedman S. A., Good P. J., Mertz J. E. Leader-encoded open reading frames modulate both the absolute and relative rates of synthesis of the virion proteins of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3884–3893. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3884-3893.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons P., Kaushansky K., Torok-Storb B. Mechanisms of cytomegalovirus-mediated myelosuppression: perturbation of stromal cell function versus direct infection of myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1386–1390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Mocarski E. S. Regulation of cytomegalovirus gene expression: alpha and beta promoters are trans activated by viral functions in permissive human fibroblasts. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.135-143.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaete R. R., Thayer R. M., Probert W. S., Masiarz F. R., Chamberlain S. H., Rasmussen L., Merigan T. C., Pachl C. Human cytomegalovirus strain Towne glycoprotein B is processed by proteolytic cleavage. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):207–225. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamminger T., Puchtler E., Fleckenstein B. Discordant expression of the immediate-early 1 and 2 gene regions of human cytomegalovirus at early times after infection involves posttranscriptional processing events. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2273–2282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2273-2282.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Depto A. S., Fortney J., Nelson J. A. Regulated expression of early and late RNAs and proteins from the human cytomegalovirus immediate-early gene region. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2699–2708. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2699-2708.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M., Feller A., Messenguy F., Piérard A. The leader peptide of yeast gene CPA1 is essential for the translational repression of its expression. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90618-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolin S. L., Walter P. Ribosome pausing and stacking during translation of a eukaryotic mRNA. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3559–3569. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. A., Spector D. H. Posttranscriptional regulation of a class of human cytomegalovirus phosphoproteins encoded by an early transcription unit. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3117–3127. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3117-3127.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]