Abstract
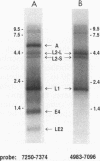
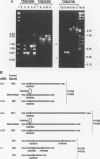
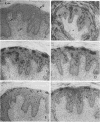
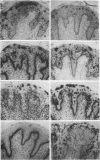
The papillomavirus life cycle is tightly linked with keratinocyte differentiation in squamous epithelia. Vegetative viral DNA replication begins in the spinous layer, while synthesis of capsid proteins and virus maturation is restricted to the most differentiated or granular layer of the epithelium. In this study, in situ hybridization of bovine fibropapillomas was used to demonstrate that the activity of two promoters of bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV-1) is regulated in a differentiation-specific manner. In situ hybridization with a late promoter (PL)-specific oligonucleotide probe suggested that PL is dramatically upregulated in the granular layer of the fibropapilloma. Northern (RNA) blot analysis of RNA from BPV-1-infected fibropapillomas indicated that the three major BPV-1 late-region mRNAs were transcribed from PL. These RNAs include the previously described L1 (major capsid) mRNA as well as two larger mRNAs. The two larger mRNAs were characterized and shown to contain the L2 (minor capsid protein) open reading frame as well as the L1 open reading frame. In contrast to PL, the P2443 promoter was maximally active in basal keratinocytes and the fibroma. The major mRNA transcribed from P2443 is the putative E5 oncoprotein mRNA which is spliced between nucleotides 2505 and 3225. No signal was detected above the basal layer with use of a probe specific for this mRNA. The E5 oncoprotein has previously been localized by immunoperoxidase staining to the granular cell layer as well as the basal cell layer of the fibropapilloma (S. Burnett, N. Jareborg, and D. DiMaio, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:5665-5669, 1992). These data suggest that E5 proteins in the basal cell and granular cell layers are not translated from the same mRNA.
Full text
PDF




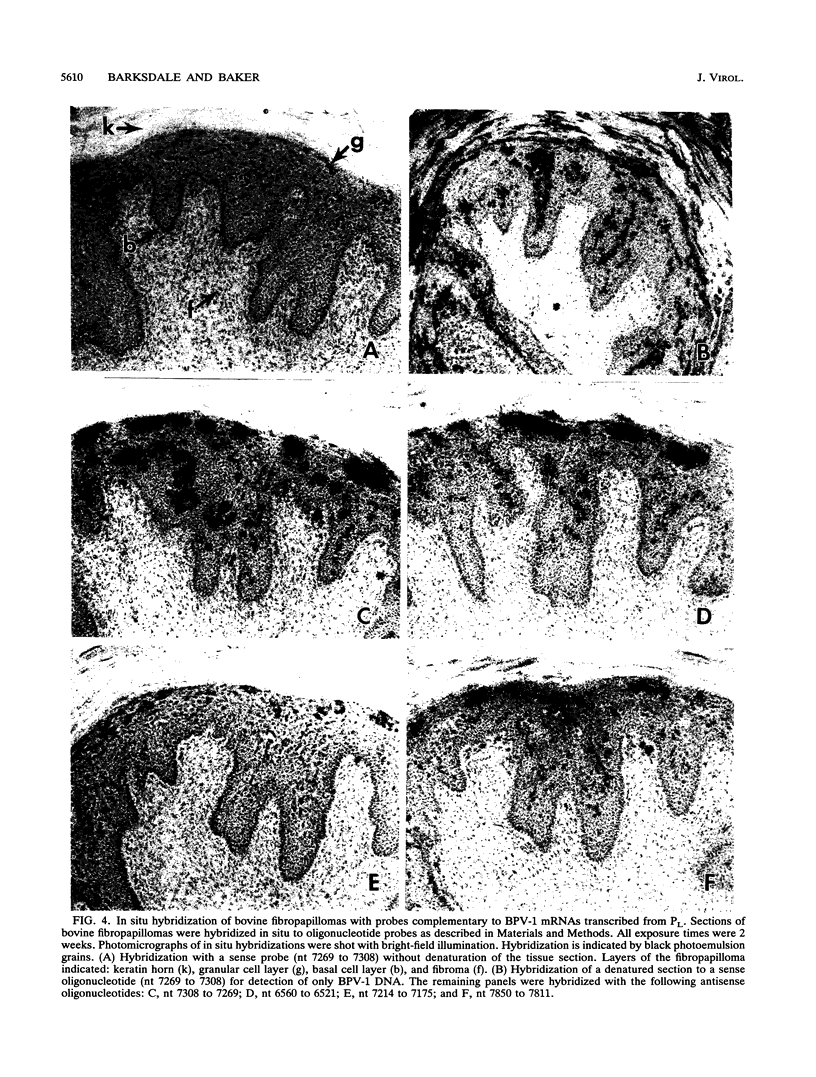

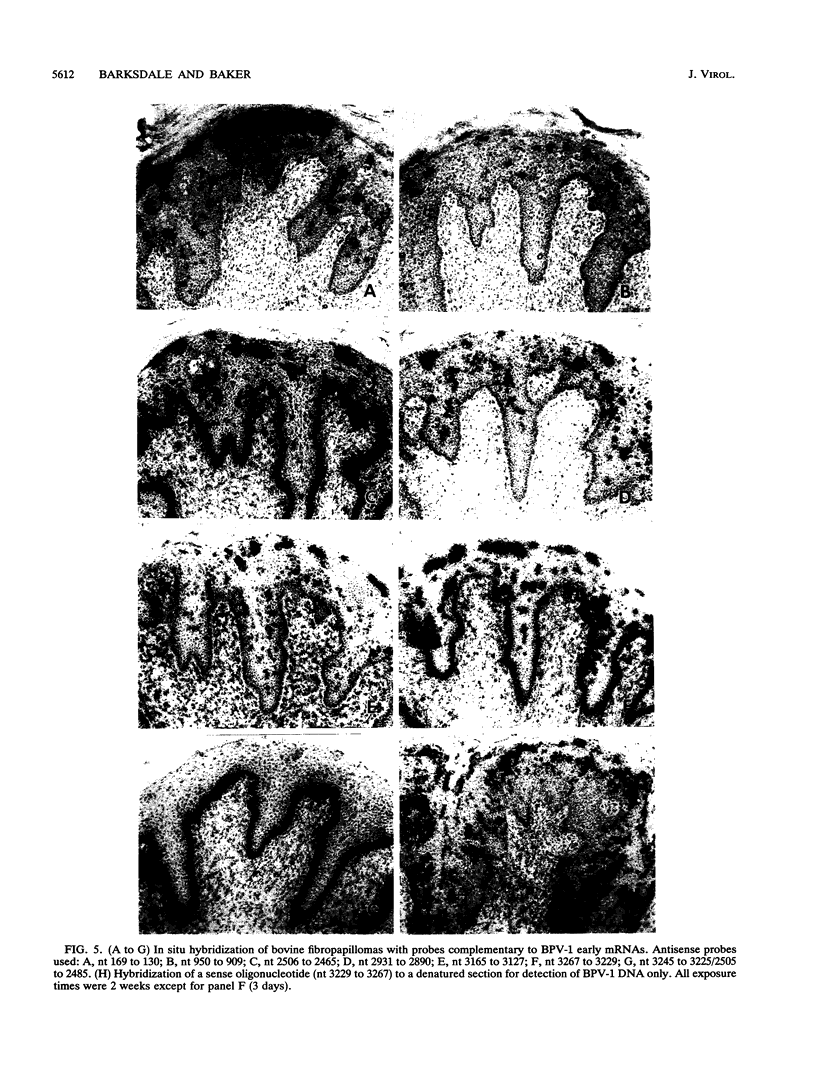




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahola H., Stenlund A., Moreno-López J., Pettersson U. Promoters and processing sites within the transforming region of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2240–2244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2240-2244.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allan G. M., Todd D., Smyth J. A., Mackie D. P., Burns J., McNulty M. S. In situ hybridization: an optimised detection protocol for a biotinylated DNA probe renders it more sensitive than a comparable 35S-labelled probe. J Virol Methods. 1989 Apr-May;24(1-2):181–190. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(89)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Howley P. M. Differential promoter utilization by the bovine papillomavirus in transformed cells and productively infected wart tissues. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1027–1035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Noe J. S. Transcriptional termination between bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV-1) early and late polyadenylation sites blocks late transcription in BPV-1-transformed cells. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3529–3534. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3529-3534.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Hudson J. B., Golub T. R., Turyk M. E., Hosken M., Wilbanks G. D., Laimins L. A. Amplification of human papillomavirus genomes in vitro is dependent on epithelial differentiation. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2254–2260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2254-2260.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett S., Jareborg N., DiMaio D. Localization of bovine papillomavirus type 1 E5 protein to transformed basal keratinocytes and permissive differentiated cells in fibropapilloma tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett S., Kiessling U., Pettersson U. Loss of bovine papillomavirus DNA replication control in growth-arrested transformed cells. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2215–2225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2215-2225.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett S., Ström A. C., Jareborg N., Alderborn A., Dillner J., Moreno-Lopez J., Pettersson U., Kiessling U. Induction of bovine papillomavirus E2 gene expression and early region transcription by cell growth arrest: correlation with viral DNA amplification and evidence for differential promoter induction. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5529–5541. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5529-5541.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Howley P. M., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H. The primary structure and genetic organization of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 genome. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):529–534. doi: 10.1038/299529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choe J., Vaillancourt P., Stenlund A., Botchan M. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 encodes two forms of a transcriptional repressor: structural and functional analysis of new viral cDNAs. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1743–1755. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1743-1755.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowsert L. M., Pilacinski W. P., Jenson A. B. Identification of the bovine papillomavirus L1 gene product using monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1988 Aug;165(2):613–615. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90608-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crum C. P., Nuovo G., Friedman D., Silverstein S. J. Accumulation of RNA homologous to human papillomavirus type 16 open reading frames in genital precancers. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):84–90. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.84-90.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollard S. C., Wilson J. L., Demeter L. M., Bonnez W., Reichman R. C., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Production of human papillomavirus and modulation of the infectious program in epithelial raft cultures. OFF. Genes Dev. 1992 Jul;6(7):1131–1142. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.7.1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. A quantitative in vitro focus assay for bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel L. W., Heilman C. A., Howley P. M. Transcriptional organization of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):516–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.516-528.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen T. H., Cripe T. P., Ginder G. D., Karin M., Turek L. P. Trans-activation of an upstream early gene promoter of bovine papilloma virus-1 by a product of the viral E2 gene. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):145–152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04732.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Howley P. M. Mutational analysis of the 3' open reading frames and the splice junction at nucleotide 3225 of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3889–3895. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3889-3895.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Spalholz B. A., Howley P. M. The bovine papillomavirus P2443 promoter is E2 trans-responsive: evidence for E2 autoregulation. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2815–2822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houff S. A., Katz D., Kufta C. V., Major E. O. A rapid method for in situ hybridization for viral DNA in brain biopsies from patients with AIDS. AIDS. 1989 Dec;3(12):843–845. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198912000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbert N. L., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Androphy E. J. Bovine papilloma virus-transformed cells contain multiple E2 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5864–5868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iftner T., Oft M., Böhm S., Wilczynski S. P., Pfister H. Transcription of the E6 and E7 genes of human papillomavirus type 6 in anogenital condylomata is restricted to undifferentiated cell layers of the epithelium. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4639–4646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4639-4646.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin X. W., Cowsert L. M., Pilacinski W. P., Jenson A. B. Identification of L2 open reading frame gene products of bovine papillomavirus type 1 using monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1989 May;70(Pt 5):1133–1140. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-5-1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Effects of intercistronic length on the efficiency of reinitiation by eucaryotic ribosomes. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3438–3445. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Structural features in eukaryotic mRNAs that modulate the initiation of translation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):19867–19870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroczek R. A., Siebert E. Optimization of northern analysis by vacuum-blotting, RNA-transfer visualization, and ultraviolet fixation. Anal Biochem. 1990 Jan;184(1):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Hubbert N. L., Howley P. M., Schiller J. T. Genetic assignment of multiple E2 gene products in bovine papillomavirus-transformed cells. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3151–3154. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3151-3154.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Monk B. C., Howley P. M. Phenotypic analysis of bovine papillomavirus type 1 E2 repressor mutants. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):950–956. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.950-956.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Spalholz B. A., Howley P. M. A transcriptional repressor encoded by BPV-1 shares a common carboxy-terminal domain with the E2 transactivator. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancaster W. D., Olson C. Animal papillomaviruses. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Jun;46(2):191–207. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.2.191-207.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J. D., Jackson S. P., Tjian R., Botchan M. R. Direct interaction between Sp1 and the BPV enhancer E2 protein mediates synergistic activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90467-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linz U., Baker C. C. Promoters of bovine papillomavirus type 1: in vitro activity and utilization. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2537–2543. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2537-2543.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neary K., DiMaio D. Open reading frames E6 and E7 of bovine papillomavirus type 1 are both required for full transformation of mouse C127 cells. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):259–266. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.259-266.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash S. S., Horwitz B. H., Zibello T., Settleman J., DiMaio D. Bovine papillomavirus E2 gene regulates expression of the viral E5 transforming gene. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3608–3613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3608-3613.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson B. L., Cote G. J., Berget S. M. Exon definition may facilitate splice site selection in RNAs with multiple exons. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):84–94. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Identification of a second transforming region in bovine papillomavirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7880–7884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senapathy P., Shapiro M. B., Harris N. L. Splice junctions, branch point sites, and exons: sequence statistics, identification, and applications to genome project. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:252–278. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83018-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Lambert P. F., Yee C. L., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus transcriptional regulation: localization of the E2-responsive elements of the long control region. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2128–2137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2128-2137.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Transactivation of a bovine papilloma virus transcriptional regulatory element by the E2 gene product. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenlund A., Zabielski J., Ahola H., Moreno-Lopez J., Pettersson U. Messenger RNAs from the transforming region of bovine papilloma virus type I. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):541–554. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90240-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler M. H., Wolinsky S. M., Whitbeck A., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Differentiation-linked human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 transcription in genital condylomata revealed by in situ hybridization with message-specific RNA probes. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):331–340. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90135-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymanski P., Stenlund A. Regulation of early gene expression from the bovine papillomavirus genome in transiently transfected C127 cells. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5710–5720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5710-5720.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS M., BOIRON M., TANZER J., LEVY J. P., BERNARD J. IN VITRO TRANSFORMATION OF MICE CELLS BY BOVINE PAPILLOMA VIRUS. Nature. 1964 May 16;202:709–710. doi: 10.1038/202709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talerico M., Berget S. M. Effect of 5' splice site mutations on splicing of the preceding intron. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6299–6305. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav M., Stenlund A. Transient replication of BPV-1 requires two viral polypeptides encoded by the E1 and E2 open reading frames. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):449–457. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaillancourt P., Nottoli T., Choe J., Botchan M. R. The E2 transactivator of bovine papillomavirus type 1 is expressed from multiple promoters. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3927–3937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3927-3937.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Li R., Mohr I. J., Clark R., Botchan M. R. Activation of BPV-1 replication in vitro by the transcription factor E2. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):628–632. doi: 10.1038/353628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Mohr I., Li R., Nottoli T., Sun S., Botchan M. Transcription factor E2 regulates BPV-1 DNA replication in vitro by direct protein-protein interaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1991;56:335–346. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1991.056.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Okayama H., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus contains multiple transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1030–1034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd Simultaneous use of digoxigenin- and radiolabeled oligodeoxyribonucleotide probes for hybridization histochemistry. Neuropeptides. 1989 May-Jun;13(4):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(89)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]