Abstract
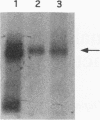
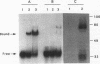
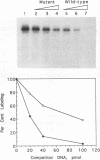
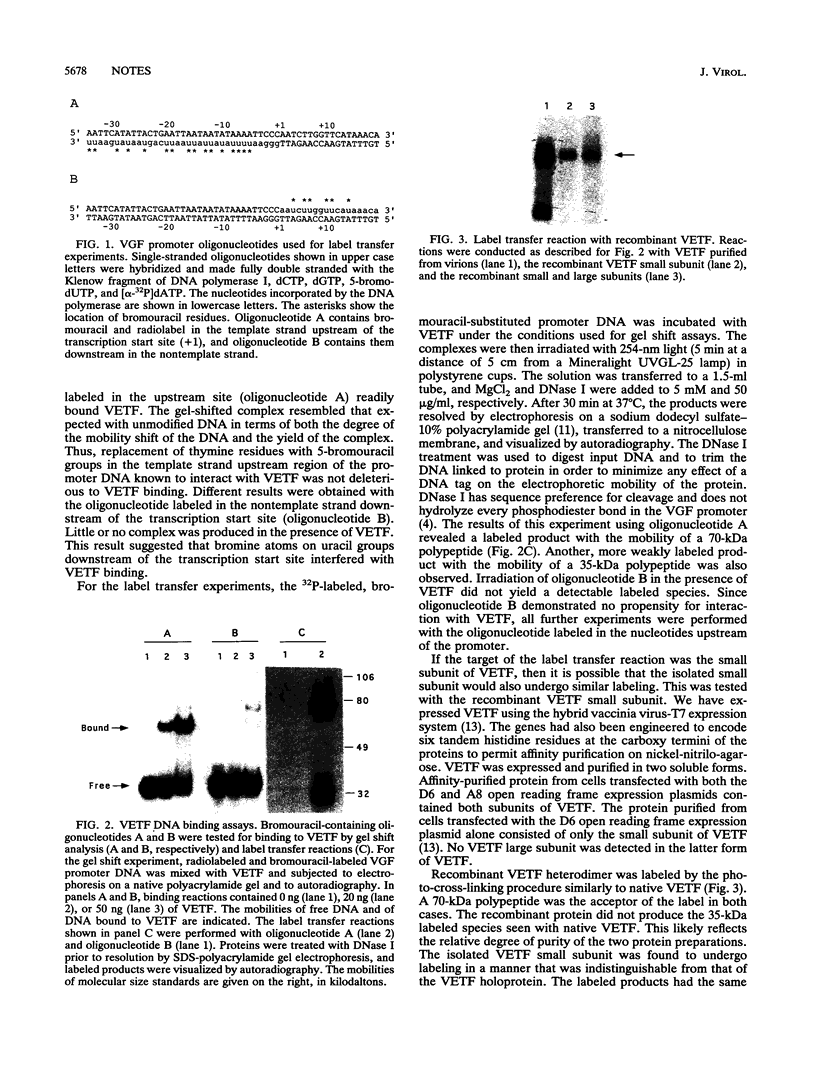
The vaccinia virus early transcription factor (VETF), in addition to the viral RNA polymerase, is required for efficient transcription of early genes in vitro. VETF is a heterodimeric protein that binds specifically to early gene promoters. In order to localize the VETF DNA binding domain, we have used photoreactive oligonucleotide probes with the sequence of the vaccinia virus growth factor promoter. The probes consisted of double-stranded oligonucleotides incorporating radiolabeled dAMP and 5-bromo-dUMP into sequences of the promoter known to contact VETF. Irradiation of a DNA probe having these nucleotides located upstream of the transcription start site in the presence of VETF resulted in the transfer of label to a polypeptide that comigrated with the small subunit of VETF. The label transfer reaction was shown to occur with the recombinant VETF small subunit in the absence of the large subunit. These results indicate that the small subunit comprises at least part of the VETF DNA binding domain and contacts the promoter in the region upstream of the transcription start site.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blatter E. E., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Identification of an amino acid-base contact in the GCN4-DNA complex by bromouracil-mediated photocrosslinking. Nature. 1992 Oct 15;359(6396):650–652. doi: 10.1038/359650a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S. A role for ATP hydrolysis in vaccinia virus early gene transcription. Dissociation of the early transcription factor-promoter complex. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15545–15548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Fesler B. S. Vaccinia virus gene encoding a component of the viral early transcription factor. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1523–1529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1523-1529.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Moss B. DNA-dependent ATPase activity associated with vaccinia virus early transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10761–10765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Yuen L., Shuman S., Moss B. Purification of a factor required for transcription of vaccinia virus early genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10754–10760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Moss B. Structure of vaccinia virus early promoters. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 20;210(4):749–769. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon P. D., Moss B. Early transcription factor subunits are encoded by vaccinia virus late genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4401–4405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel S. J., Johnson G. P., Perkus M. E., Davis S. W., Winslow J. P., Paoletti E. The complete DNA sequence of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1990 Nov;179(1):247-66, 517-63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90294-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler J., Shuman S. Structural analysis of ternary complexes of vaccinia RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10099–10103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Broyles S. S. Recruitment of vaccinia virus RNA polymerase to an early gene promoter by the viral early transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2773–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Ahn B. Y., Amegadzie B., Gershon P. D., Keck J. G. Cytoplasmic transcription system encoded by vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1355–1358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Regulation of vaccinia virus transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:661–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R., Gilbert W. Contacts between the lac repressor and the thymines in the lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4973–4976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebeille F., Gans P., Chagvardieff P., Pean M., Tapie P., Thibault P. Mass spectrometric determination of the inorganic carbon species assimilated by photoautotrophic cells of Euphorbia characias L. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12373–12377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. R., Linder P. D-E-A-D protein family of putative RNA helicases. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos J. C., Sasker M., Stunnenberg H. G. Promoter melting by a stage-specific vaccinia virus transcription factor is independent of the presence of RNA polymerase. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90412-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick K. L., Matthews K. S. Interactions between lac repressor protein and site-specific bromodeoxyuridine-substituted operator DNA. Ultraviolet footprinting and protein-DNA cross-link formation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6106–6112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. F., Moss B. Identification of factors specific for transcription of the late class of vaccinia virus genes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4224–4233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4224-4233.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]