Abstract
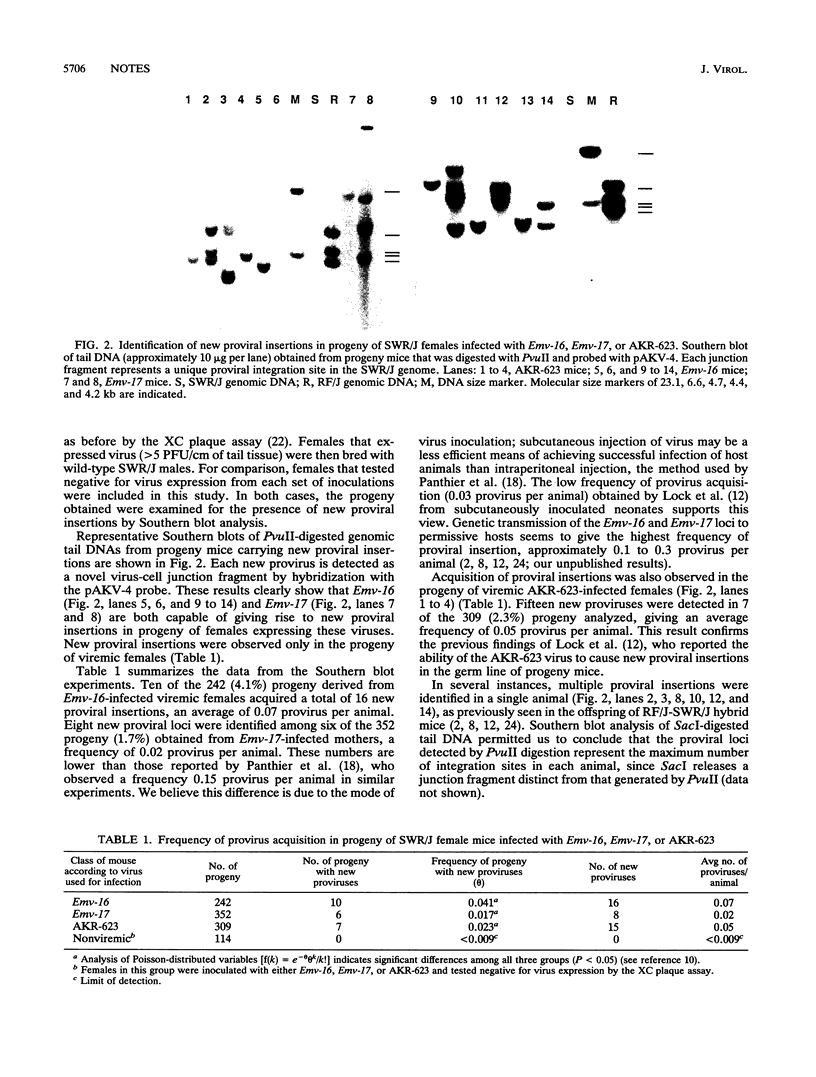
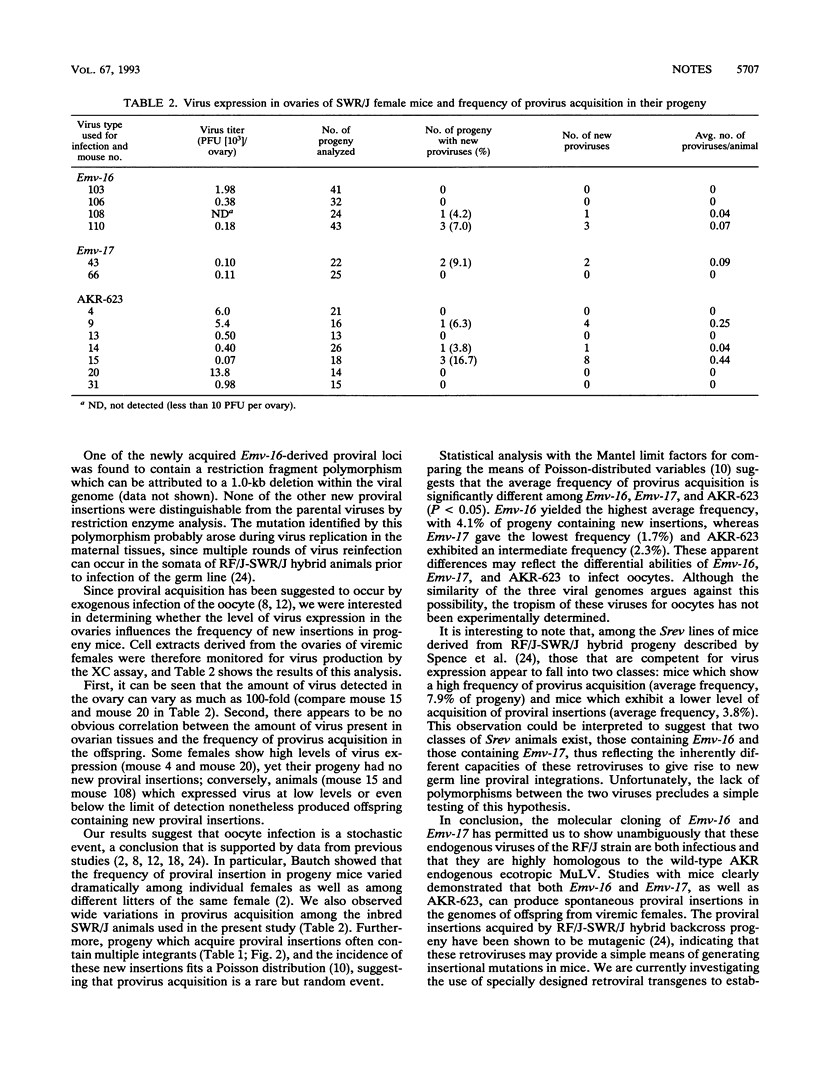
New germ line proviral insertions are acquired at a high frequency by the progeny of SWR/J-RF/J hybrid female mice that carry the endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia proviruses Emv-16 and Emv-17. The tight linkage of these RF/J strain proviral loci has prevented genetic segregation of the retroviral genomes. Hence, it is not known whether both of these proviruses are capable of giving rise to new proviral insertions. We have molecularly cloned Emv-16 and Emv-17 and have characterized them in vitro and in vivo. Restriction enzyme analysis of the recombinant clones revealed that the proviral genomes are very similar to each other and closely resemble the wild-type AKR virus. A comparison of the flanking cellular DNA suggests that the Emv-16 and Emv-17 loci did not arise by simple duplication of a viral insertion site within the RF/J genome but most likely are independent integration events. Both proviruses produce infectious virus when transfected into NIH 3T3 cells, indicating that they are nondefective retroviruses. Exogenous infection of SWR/J mice with either Emv-16 or Emv-17 leads to viremia in the host animals, and in both cases, progeny of viremic females acquire new proviral insertions. The ability of these retroviruses to generate novel retroviral integration sites in the mouse genome provides a simple method for inducing insertional mutations in mice.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bautch V. L. Genetic background affects integration frequency of ecotropic proviral sequences into the mouse germ line. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):693–701. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.693-701.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchberg A. M., Taylor B. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Chromosomal localization of Emv-16 and Emv-17, two closely linked ecotropic proviruses of RF/J mice. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1175–1178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1175-1178.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Structure of endogenous murine leukemia virus DNA in mouse genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Rowe W. P. Close similarity between endogenous ecotropic virus of Mus musculus molossinus and AKR virus. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):499–505. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.499-505.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gilbert W. Somatically acquired recombinant murine leukemia proviruses in thymic leukemias of AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):70–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.70-82.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W. Nucleotide sequence of AKV murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):471–478. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.471-478.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. High frequency germline acquisition of ecotropic MuLV proviruses in SWR/J-RF/J hybrid mice. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):811–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King S. R., Horowitz J. M., Risser R. Nucleotide conservation of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia proviruses in inbred mice: implications for viral origin and dispersal. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):543–547. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90298-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock L. F., Keshet E., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Studies of the mechanism of spontaneous germline ecotropic provirus acquisition in mice. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4169–4177. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03313.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rands E., Chattopadhyay S. K., Garon C. F., Hager G. L. Molecular cloning of infectious integrated murine leukemia virus DNA from infected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer A., Struuck F. D., Duran-Reynals M. L., Lilly F. Maternally transmitted resistance to lymphoma development in mice of reciprocal crosses of the RF/J and AKR/J strains. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):431–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90517-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCubrey J., Horowitz J. M., Risser R. Structure and expression of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia viruses in RF/J mice. J Exp Med. 1982 Nov 1;156(5):1461–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.5.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melamedoff M., Lilly F., Duran-Reynals M. L. Suppression of endogenous murine leukemia virus by maternal resistance factor. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):506–514. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panthier J. J., Condamine H., Jacob F. Inoculation of newborn SWR/J females with an ecotropic murine leukemia virus can produce transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1156–1160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. I. Tissue culture studies of naturally occurring viruses. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1219–1233. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rands E., Lowy D. R., Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. Restriction endonuclease mapping of ecotropic murine leukemia viral DNAs: size and sequence heterogeneity of the long terminal repeat. Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):445–452. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Kozak C. A. Germ-line reinsertions of AKR murine leukemia virus genomes in Akv-1 congenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4871–4874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence S. E., Gilbert D. J., Swing D. A., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Spontaneous germ line virus infection and retroviral insertional mutagenesis in eighteen transgenic Srev lines of mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):177–184. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. L., Bird S., Weinberg R. A. Evidence for the Asiatic origin of endogenous AKR-type murine leukemia proviruses. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):824–835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.824-835.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Rands E., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Verma I. M. Long terminal repeat of murine retroviral DNAs: sequence analysis, host-proviral junctions, and preintegration site. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):542–556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.542-556.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]