Abstract
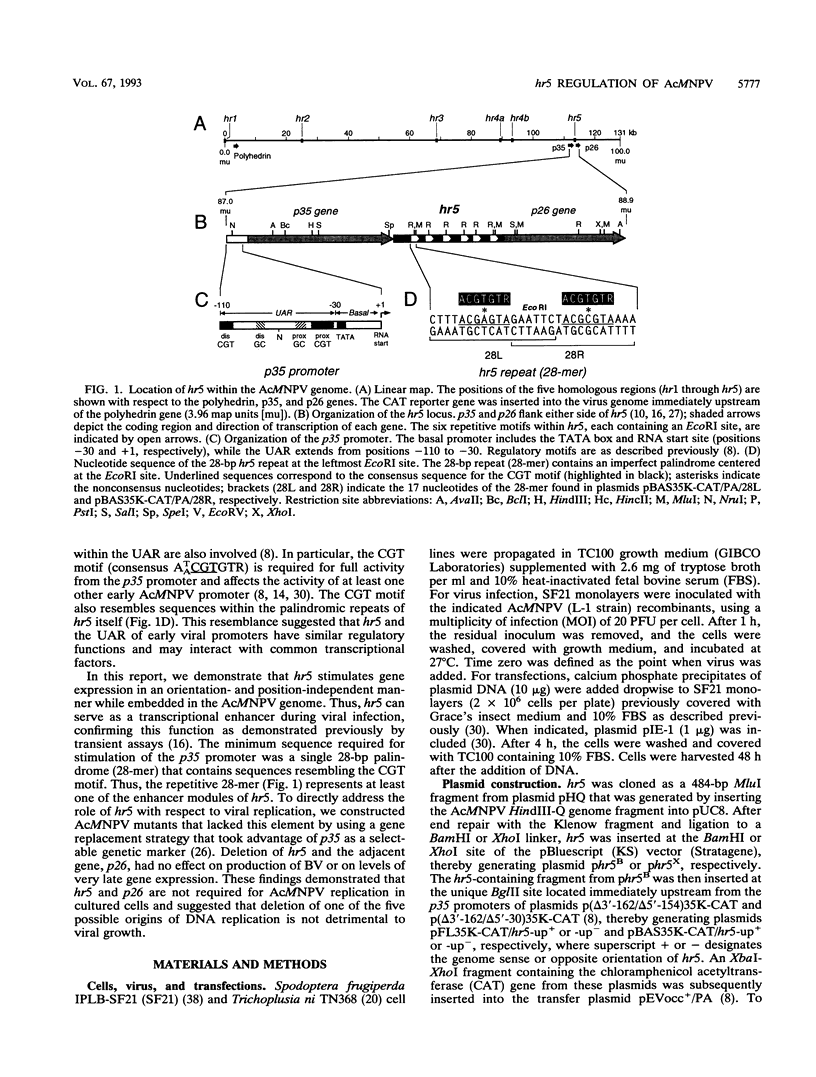
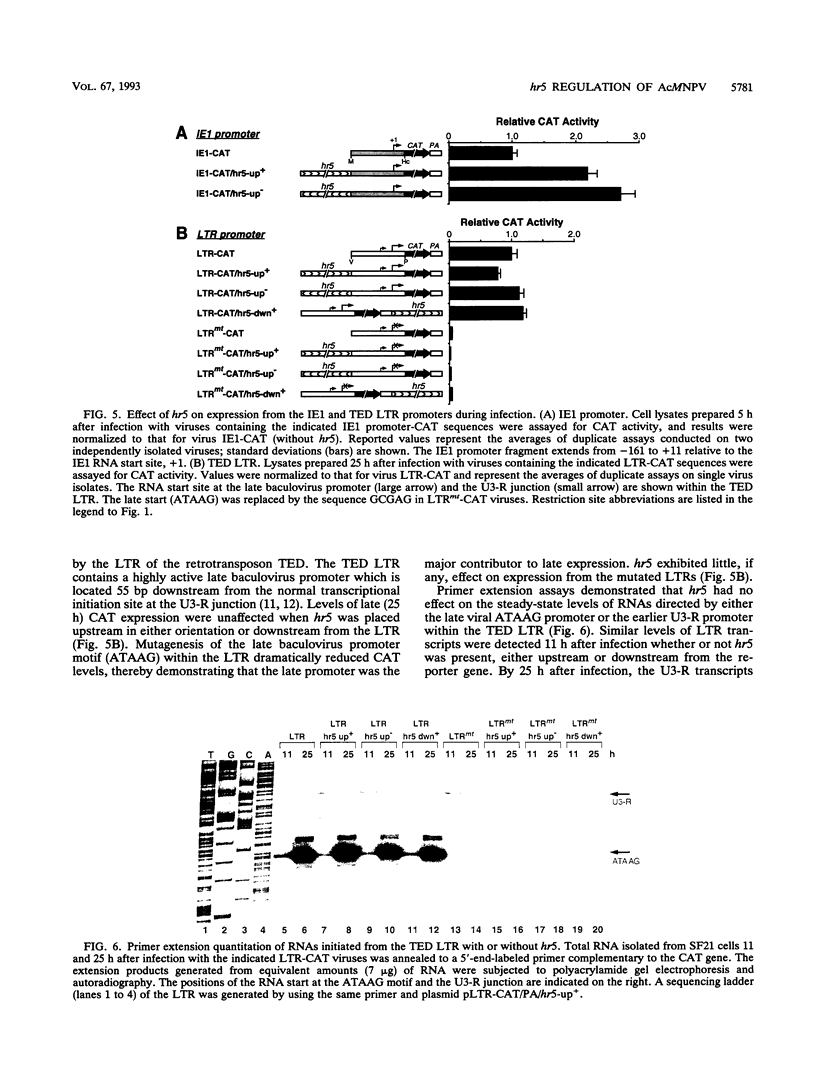
Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV) contains five homologous regions (hr1 through hr5) interspersed throughout its genome. Analysis of plasmid transfections indicates that the hrs function as transcriptional enhancers and possible origins of viral DNA replication. The role of these repetitive elements in regulating expression from the AcMNPV genome was examined by constructing a series of recombinant viruses that tested the effect of hr5 on expression of the adjacent p35 gene (p35). When embedded within the viral genome, hr5 stimulated transcription from the early p35 promoter in a position- and orientation-independent manner. Moreover, hr5 and the upstream activating region of p35 were functionally interchangeable. A 28-bp imperfect palindrome, repeated six times within hr5, was the minimal sequence required for p35 promoter activation. hr5 also stimulated another early AcMNPV promoter but not a late promoter or a host-derived promoter, suggesting that enhancement is promoter specific during infection. To investigate its role during AcMNPV replication, hr5 was deleted from its normal position within the viral genome. The resulting hr5 mutants exhibited no apparent defects in replication, as judged by production of budded virus and levels of very late gene expression, even though steady-state levels of p35 RNA were reduced. These results indicated for the first time that hr5 functions as a transcriptional enhancer within the viral genome. However, the element is not required for AcMNPV replication in cultured cells. Thus, loss of one of five possible origins of DNA replication is not deleterious to viral growth. Since p26 was removed from the hr5 deletion mutants, this gene is also nonessential for viral replication.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blissard G. W., Rohrmann G. F. Baculovirus diversity and molecular biology. Annu Rev Entomol. 1990;35:127–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.35.010190.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. D., Summers M. D., Guarino L. A. Transient expression of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus immediate-early gene, IE-N, is regulated by three viral elements. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):945–951. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.945-951.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm G. E., Henner D. J. Multiple early transcripts and splicing of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus IE-1 gene. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3193–3200. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3193-3200.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clem R. J., Fechheimer M., Miller L. K. Prevention of apoptosis by a baculovirus gene during infection of insect cells. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1388–1390. doi: 10.1126/science.1962198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran M. A., Faulkner P. Location of Homologous DNA Sequences Interspersed at Five Regions in the Baculovirus AcMNPV Genome. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):961–970. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.961-970.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson J. A., Friesen P. D. Identification of upstream promoter elements mediating early transcription from the 35,000-molecular-weight protein gene of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4006–4016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4006-4016.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Divergent transcription of early 35- and 94-kilodalton protein genes encoded by the HindIII K genome fragment of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2264–2272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2264-2272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Nissen M. S. Gene organization and transcription of TED, a lepidopteran retrotransposon integrated within the baculovirus genome. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):3067–3077. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.3067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Rice W. C., Miller D. W., Miller L. K. Bidirectional transcription from a solo long terminal repeat of the retrotransposon TED: symmetrical RNA start sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1599–1607. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Gonzalez M. A., Summers M. D. Complete Sequence and Enhancer Function of the Homologous DNA Regions of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):224–229. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.224-229.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Smith M. Regulation of delayed-early gene transcription by dual TATA boxes. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3733–3739. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3733-3739.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of a trans-activating gene required for expression of a baculovirus delayed-early gene. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.563-571.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Interspersed Homologous DNA of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Enhances Delayed-Early Gene Expression. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):215–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.215-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Nucleotide sequence and temporal expression of a baculovirus regulatory gene. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2091–2099. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2091-2099.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershberger P. A., Dickson J. A., Friesen P. D. Site-specific mutagenesis of the 35-kilodalton protein gene encoded by Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus: cell line-specific effects on virus replication. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5525–5533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5525-5533.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hink W. F. Established insect cell line from the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni. Nature. 1970 May 2;226(5244):466–467. doi: 10.1038/226466b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huh N. E., Weaver R. F. Identifying the RNA polymerases that synthesize specific transcripts of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):195–201. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Fawl R., Roller R. J., Roizman B. Construction and properties of a recombinant herpes simplex virus 1 lacking both S-component origins of DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2123–2132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2123-2132.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kool M., van den Berg P. M., Tramper J., Goldbach R. W., Vlak J. M. Location of two putative origins of DNA replication of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):94–101. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. Y., Krell P. J. Generation and analysis of defective genomes of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4339–4347. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4339-4347.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch R. A., Friesen P. D. The 35-kilodalton protein gene (p35) of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus and the neomycin resistance gene provide dominant selection of recombinant baculoviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1753–1760. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A., Qin J. C., Rankin C., Hardin S. E., Weaver R. F. Nucleotide sequence of a portion of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome containing the EcoRI site-rich region (hr5) and an open reading frame just 5' of the p10 gene. J Gen Virol. 1986 Nov;67(Pt 11):2565–2570. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-11-2565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Roizman B. Generation of an inverting herpes simplex virus 1 mutant lacking the L-S junction a sequences, an origin of DNA synthesis, and several genes including those specifying glycoprotein E and the alpha 47 gene. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.583-591.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malitschek B., Schartl M. Rapid identification of recombinant baculoviruses using PCR. Biotechniques. 1991 Aug;11(2):177–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen M. S., Friesen P. D. Molecular analysis of the transcriptional regulatory region of an early baculovirus gene. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):493–503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.493-503.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson M., Bjornson R., Pearson G., Rohrmann G. The Autographa californica baculovirus genome: evidence for multiple replication origins. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1382–1384. doi: 10.1126/science.1529337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polvino-Bodnar M., Orberg P. K., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 oriL is not required for virus replication or for the establishment and reactivation of latent infection in mice. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3528–3535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3528-3535.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin C., Ooi B. G., Miller L. K. Eight base pairs encompassing the transcriptional start point are the major determinant for baculovirus polyhedrin gene expression. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theilmann D. A., Stewart S. Identification and characterization of the IE-1 gene of Orgyia pseudotsugata multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):492–508. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90063-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. L., Goodwin R. H., Tompkins G. J., McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro. 1977 Apr;13(4):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02615077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlak J. M., Klinkenberg F. A., Zaal K. J., Usmany M., Klinge-Roode E. C., Geervliet J. B., Roosien J., van Lent J. W. Functional studies on the p10 gene of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus using a recombinant expressing a p10-beta-galactosidase fusion gene. J Gen Virol. 1988 Apr;69(Pt 4):765–776. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-4-765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]