Abstract
The ADV-G strain of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (ADV) is nonpathogenic for mink but replicates permissively in cell culture, whereas the ADV-Utah 1 strain is highly pathogenic for mink but replicates poorly in cell culture. In order to relate these phenotypic differences to primary genomic features, we constructed a series of chimeric plasmids between a full-length replication-competent molecular clone of ADV-G and subgenomic clones of ADV-Utah 1 representing map units (MU) 15 to 88. After transfection of the plasmids into cell culture and serial passage of cell lysates, we determined that substitution of several segments of the ADV-Utah 1 genome (MU 15 to 54 and 65 to 73) within an infectious ADV-G plasmid did not impair the ability of these constructs to yield infectious virus in vitro. Like ADV-G, the viruses derived from these replication-competent clones caused neither detectable viremia 10 days after inoculation nor any evidence of Aleutian disease in adult mink. On the other hand, other chimeric plasmids were incapable of yielding infectious virus and were therefore replication defective in vitro. The MU 54 to 65 EcoRI-EcoRV fragment of ADV-Utah 1 was the minimal segment capable of rendering ADV-G replication defective. Substitution of the ADV-G EcoRI-EcoRV fragment into a replication-defective clone restored replication competence, indicating that this 0.53-kb portion of the genome, wholly located within shared coding sequences for the capsid proteins VP1 and VP2, contained a determinant that governs replication in cell culture. When cultures of cells were studied 5 days after transfection with replication-defective clones, rescue of dimeric replicative form DNA and single-stranded progeny DNA could not be demonstrated. This defect could not be complemented by cotransfection with a replication-competent construction.
Full text
PDF



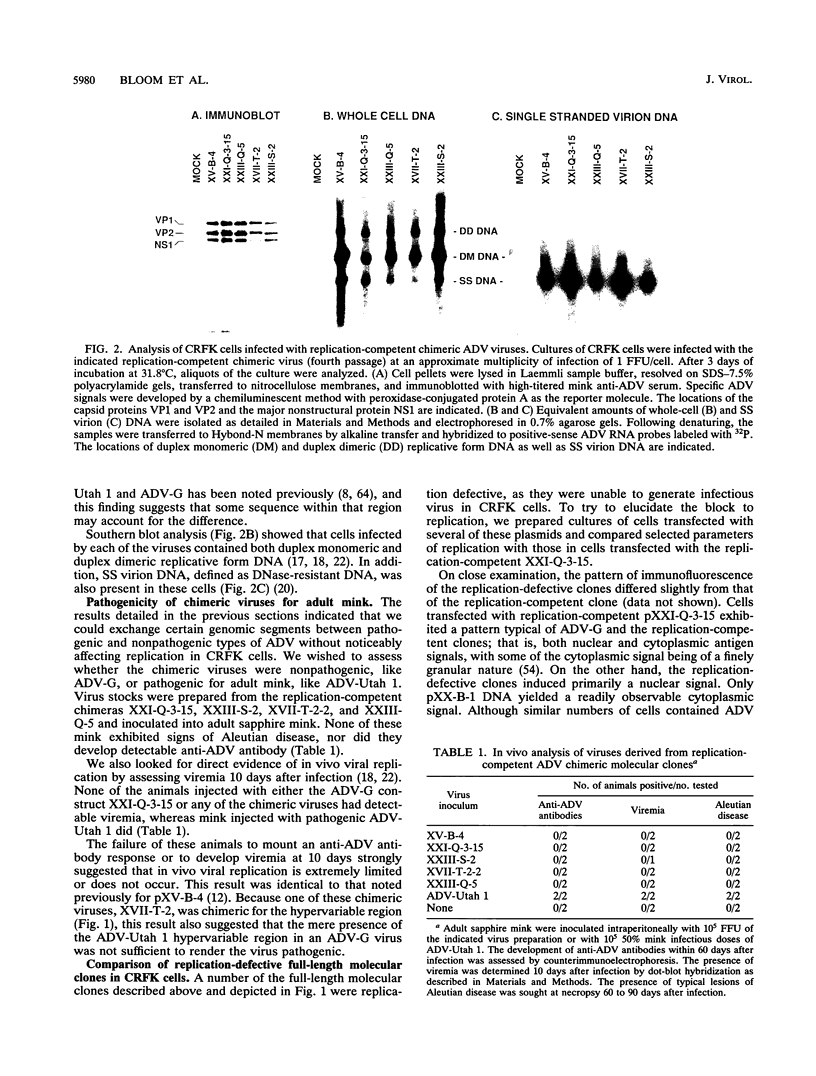








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasted B., Race R. E., Bloom M. E. Aleutian disease virus, a parvovirus, is proteolytically degraded during in vivo infection in mink. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):7–13. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.7-13.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Perryman S. Detailed transcription map of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3684–3694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3684-3694.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E. Studies on the sequential development of acute interstitial pneumonia caused by Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.81-86.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Wolfinbarger J. Evidence of restricted viral replication in adult mink infected with Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1495–1507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1495-1507.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Wolfinbarger J., Race R. E. In situ molecular hybridization for detection of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus DNA by using strand-specific probes: identification of target cells for viral replication in cell cultures and in mink kits with virus-induced interstitial pneumonia. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2407–2419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2407-2419.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S. Pathogenesis of disease caused by Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. APMIS Suppl. 1990;14:1–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Uttenthal-Jensen A., Aasted B. Demonstration of non-degraded Aleutian disease virus (ADV) proteins in lung tissue from experimentally infected mink kits. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1986;87(1-2):127–133. doi: 10.1007/BF01310549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball-Goodrich L. J., Moir R. D., Tattersall P. Parvoviral target cell specificity: acquisition of fibrotropism by a mutant of the lymphotropic strain of minute virus of mice involves multiple amino acid substitutions within the capsid. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):175–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90834-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball-Goodrich L. J., Tattersall P. Two amino acid substitutions within the capsid are coordinately required for acquisition of fibrotropism by the lymphotropic strain of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3415–3423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3415-3423.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbis D. P., Chang S. F., Parrish C. R. Mutations adjacent to the dimple of the canine parvovirus capsid structure affect sialic acid binding. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90192-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Alexandersen S., Garon C. F., Mori S., Wei W., Perryman S., Wolfinbarger J. B. Nucleotide sequence of the 5'-terminal palindrome of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus and construction of an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3551–3556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3551-3556.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Alexandersen S., Mori S., Wolfinbarger J. B. Analysis of parvovirus infections using strand-specific hybridization probes. Virus Res. 1989 Sep;14(1):1–25. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(89)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Alexandersen S., Perryman S., Lechner D., Wolfinbarger J. B. Nucleotide sequence and genomic organization of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (ADV): sequence comparisons between a nonpathogenic and a pathogenic strain of ADV. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2903–2915. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2903-2915.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Kaaden O. R., Huggans E., Cohn A., Wolfinbarger J. B. Molecular comparisons of in vivo- and in vitro-derived strains of Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):132–138. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.132-138.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Lechner D., Wiedbrauk D. L., Wolfinbarger J. B. Analysis of molecularly cloned DNA reveals minor differences among three virus strains of Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1987;92(1-2):175–181. doi: 10.1007/BF01310071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Mayer L. W., Garon C. F. Characterization of the Aleutian disease virus genome and its intracellular forms. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):977–984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.977-984.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Aasted B., Wolfinbarger J. B. Analysis of Aleutian disease virus infection in vitro and in vivo: demonstration of Aleutian disease virus DNA in tissues of infected mink. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):696–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.696-703.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Hadlow W. J., Chesebro B. Aleutian disease of mink: the antibody response of sapphire and pastel mink to Aleutian disease virus. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1034–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Analysis of Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus infection using strand-specific hybridization probes. Intervirology. 1987;27(2):102–111. doi: 10.1159/000149727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Characterization of Aleutian disease virus as a parvovirus. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):836–843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.836-843.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Identification of a nonvirion protein of Aleutian disease virus: mink with Aleutian disease have antibody to both virion and nonvirion proteins. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):608–616. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.608-616.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissy R., Astell C. R. An Escherichia coli recBCsbcBrecF host permits the deletion-resistant propagation of plasmid clones containing the 5'-terminal palindrome of minute virus of mice. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownstein D. G., Smith A. L., Johnson E. A., Pintel D. J., Naeger L. K., Tattersall P. The pathogenesis of infection with minute virus of mice depends on expression of the small nonstructural protein NS2 and on the genotype of the allotropic determinants VP1 and VP2. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3118–3124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3118-3124.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. F., Sgro J. Y., Parrish C. R. Multiple amino acids in the capsid structure of canine parvovirus coordinately determine the canine host range and specific antigenic and hemagglutination properties. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):6858–6867. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.6858-6867.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Bloom M., Hadlow W., Race R. Purification and ultrastructure of Aleutian disease virus of mink. Nature. 1975 Apr 3;254(5499):456–457. doi: 10.1038/254456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Bloom M., Wehrly K., Nishio J. Persistence of infectious Friend virus in spleens of mice after spontaneous recovery from virus-induced erythroleukemia. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):832–837. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.832-837.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens D. L., Wolfinbarger J. B., Mori S., Berry B. D., Hayes S. F., Bloom M. E. Expression of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus capsid proteins by a recombinant vaccinia virus: self-assembly of capsid proteins into particles. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3077–3085. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3077-3085.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Sturzenbecker L. J., Tattersall P. The autonomous parvovirus MVM encodes two nonstructural proteins in addition to its capsid polypeptides. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):333–343. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The autonomously replicating parvoviruses of vertebrates. Adv Virus Res. 1987;33:91–174. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60317-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crandell R. A., Fabricant C. G., Nelson-Rees W. A. Development, characterization, and viral susceptibility of a feline (Felis catus) renal cell line (CRFK). In Vitro. 1973 Nov-Dec;9(3):176–185. doi: 10.1007/BF02618435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerig C., Hirt B., Beard P., Antonietti J. P. Minute virus of mice non-structural protein NS-1 is necessary and sufficient for trans-activation of the viral P39 promoter. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2563–2573. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubensky T. W., Campbell B. A., Villarreal L. P. Direct transfection of viral and plasmid DNA into the liver or spleen of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7529–7533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eklund C. M., Hadlow W. J., Kennedy R. C., Boyle C. C., Jackson T. A. Aleutian disease of mink: properties of the etiologic agent and the host responses. J Infect Dis. 1968 Dec;118(5):510–526. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.5.510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner E. M., Tattersall P. Evidence that developmentally regulated control of gene expression by a parvoviral allotropic determinant is particle mediated. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1713–1722. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1713-1722.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner E. M., Tattersall P. Mapping of the fibrotropic and lymphotropic host range determinants of the parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2605–2613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2605-2613.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalck E., Alexandersen S., Cohn A., Poulsen L. A., Bloom M. E., Aasted B. Nucleotide sequence analysis of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus shows that multiple virus types are present in infected mink. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4378–4386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4378-4386.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadlow W. J., Race R. E., Kennedy R. C. Comparative pathogenicity of four strains of Aleutian disease virus for pastel and sapphire mink. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1016–1023. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1016-1023.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn E. C., Ramos L., Kenyon A. J. Expression of Aleutian mink disease antigen in cell culture. Infect Immun. 1977 Jan;15(1):204–211. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.1.204-211.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson N. D., Rhode S. L., 3rd Parvovirus NS1 stimulates P4 expression by interaction with the terminal repeats and through DNA amplification. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4325–4333. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4325-4333.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno H., Wolfinbarger J. B., Bloom M. E. Aleutian mink disease parvovirus infection of mink peritoneal macrophages and human macrophage cell lines. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2075–2082. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2075-2082.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanno H., Wolfinbarger J. B., Bloom M. E. Identification of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus transcripts in macrophages of infected adult mink. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5305–5312. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5305-5312.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy I. M., Haddow J. K., Clements J. B. Analysis of human papillomavirus type 16 late mRNA 3' processing signals in vitro and in vivo. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1825–1829. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1825-1829.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legendre D., Rommelaere J. Terminal regions of the NS-1 protein of the parvovirus minute virus of mice are involved in cytotoxicity and promoter trans inhibition. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5705–5713. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5705-5713.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Rhode S. L., 3rd Nonstructural protein NS2 of parvovirus H-1 is required for efficient viral protein synthesis and virus production in rat cells in vivo and in vitro. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):117–130. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90828-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Rhode S. L., 3rd The parvovirus H-1 NS2 protein affects viral gene expression through sequences in the 3' untranslated region. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):10–19. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. M., Green S. W., Shimada T., Young N. S. A block in full-length transcript maturation in cells nonpermissive for B19 parvovirus. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4686–4692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4686-4692.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 6;950(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. W., Aasted B., Garon C. F., Bloom M. E. Molecular cloning of the Aleutian disease virus genome: expression of Aleutian disease virus antigens by a recombinant plasmid. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):573–579. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.573-579.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Wolfinbarger J. B., Dowling N., Wei W., Bloom M. E. Simultaneous identification of viral proteins and nucleic acids in cells infected with Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. Microb Pathog. 1990 Oct;9(4):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90013-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naeger L. K., Cater J., Pintel D. J. The small nonstructural protein (NS2) of the parvovirus minute virus of mice is required for efficient DNA replication and infectious virus production in a cell-type-specific manner. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6166–6175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6166-6175.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish C. R., Aquadro C. F., Carmichael L. E. Canine host range and a specific epitope map along with variant sequences in the capsid protein gene of canine parvovirus and related feline, mink, and raccoon parvoviruses. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):293–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90500-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish C. R., Carmichael L. E., Antczak D. F. Antigenic relationships between canine parvovirus type 2, feline panleukopenia virus and mink enteritis virus using conventional antisera and monoclonal antibodies. Arch Virol. 1982;72(4):267–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01315223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish C. R., Leathers C. W., Pearson R., Gorham J. R. Comparisons of feline panleukopenia virus, canine parvovirus, raccoon parvovirus, and mink enteritis virus and their pathogenicity for mink and ferrets. Am J Vet Res. 1987 Oct;48(10):1429–1435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D. Aleutian disease: a persistent parvovirus infection of mink with a maximal but ineffective host humoral immune response. Prog Med Virol. 1986;33:42–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E. Aleutian disease of mink. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):32–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Cox N. A., Porter H. G., Suffin S. C. Isolation of Aleutian disease virus of mink in cell culture. Intervirology. 1977;8(3):129–144. doi: 10.1159/000148888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Larsen A. E., Porter H. G. The pathogenesis of Aleutian disease of mink. I. In vivo viral replication and the host antibody response to viral antigen. J Exp Med. 1969 Sep 1;130(3):575–593. doi: 10.1084/jem.130.3.575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race R. E., Chesebro B., Bloom M. E., Aasted B., Wolfinbarger J. Monoclonal antibodies against Aleutian disease virus distinguish virus strains and differentiate sites of virus replication from sites of viral antigen sequestration. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):285–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.285-293.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed A. P., Jones E. V., Miller T. J. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of canine parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):266–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.266-276.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Both excision and replication of cloned autonomous parvovirus DNA require the NS1 (rep) protein. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4249–4256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4249-4256.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Replication process of the parvovirus H-1 V. Isolation and characterization of temperature-sensitive H-1 mutants. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):659–667. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.659-667.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd trans-Activation of parvovirus P38 promoter by the 76K noncapsid protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):886–889. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.886-889.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich I. N., Vogt C., Pentz S. Erythropoietin gene expression in vitro and in vivo detected by in situ hybridization. Blood Cells. 1988;14(2-3):505–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ron D., Tal J. Coevolution of cells and virus as a mechanism for the persistence of lymphotropic minute virus of mice in L-cells. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):424–430. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.424-430.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The cloned genome of ground squirrel hepatitis virus is infectious in the animal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5849–5852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Tattersall P. Interaction of minute virus of mice with differentiated cells: strain-dependent target cell specificity is mediated by intracellular factors. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):937–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.937-943.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Bratton J. Reciprocal productive and restrictive virus-cell interactions of immunosuppressive and prototype strains of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):944–955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.944-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracy S. Improved rapid methodology for the isolation of nucleic acids from agarose gels. Prep Biochem. 1981;11(3):251–268. doi: 10.1080/00327488108061767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Miller I. L., Carter B. J. Genetic analysis of adeno-associated virus: properties of deletion mutants constructed in vitro and evidence for an adeno-associated virus replication function. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.611-619.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Miller I. L., Carter B. J. Genetic analysis of adeno-associated virus: properties of deletion mutants constructed in vitro and evidence for an adeno-associated virus replication function. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.611-619.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao J., Chapman M. S., Agbandje M., Keller W., Smith K., Wu H., Luo M., Smith T. J., Rossmann M. G., Compans R. W. The three-dimensional structure of canine parvovirus and its functional implications. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1456–1464. doi: 10.1126/science.2006420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis G. E., Burger L. R., Pintel D. J. The trypsin-sensitive RVER domain in the capsid proteins of minute virus of mice is required for efficient cell binding and viral infection but not for proteolytic processing in vivo. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):846–857. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90260-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevacharya J., Compans R. W. The NS and capsid genes determine the host range of porcine parvovirus. Virology. 1992 Apr;187(2):515–524. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90454-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Portetelle D., Kerkhofs P., Chen G., Burny A., Mammerickx M., Kettmann R. In vivo transfection of bovine leukemia provirus into sheep. Virology. 1992 Aug;189(2):775–777. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90604-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson-Gunn S. I., Kilpatrick J. E., Imperiale M. J. Regulated adenovirus mRNA 3'-end formation in a coupled in vitro transcription-processing system. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5418–5424. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5418-5424.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Q., Kadam A., Trempe J. P. Mutational analysis of the adeno-associated virus rep gene. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6058–6069. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6058-6069.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]