Abstract
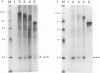
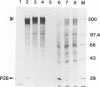
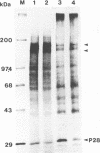
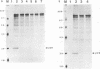
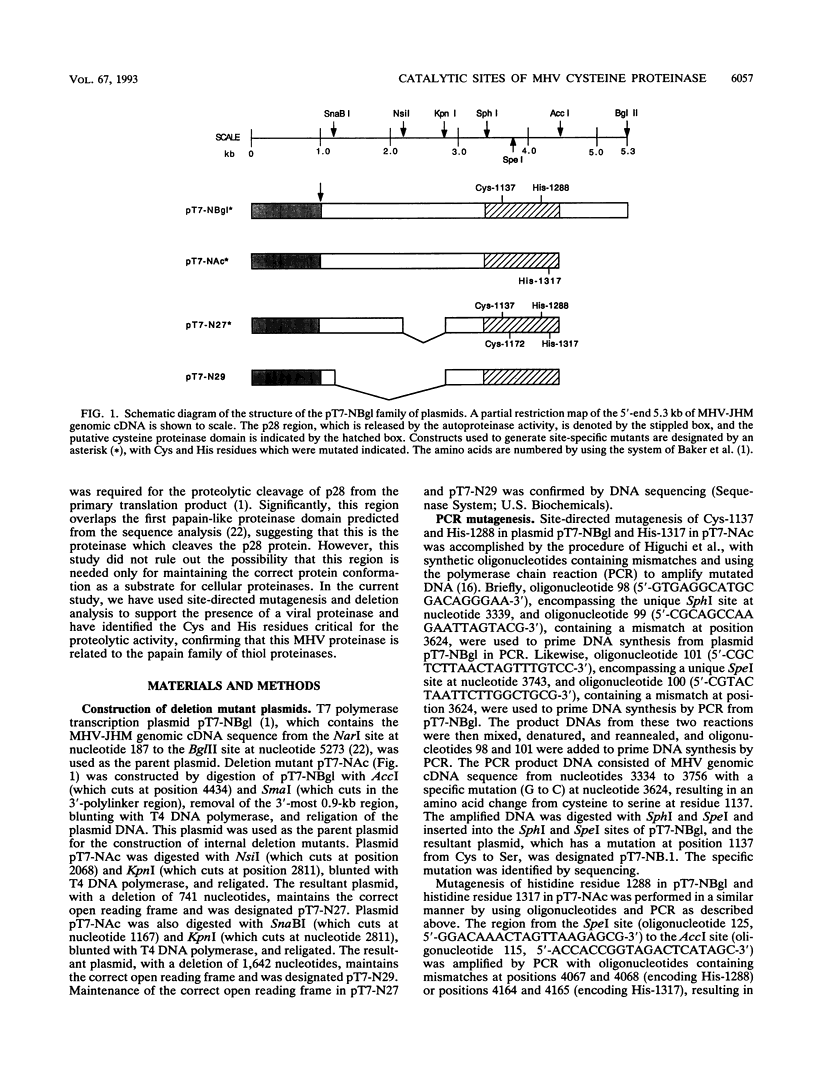
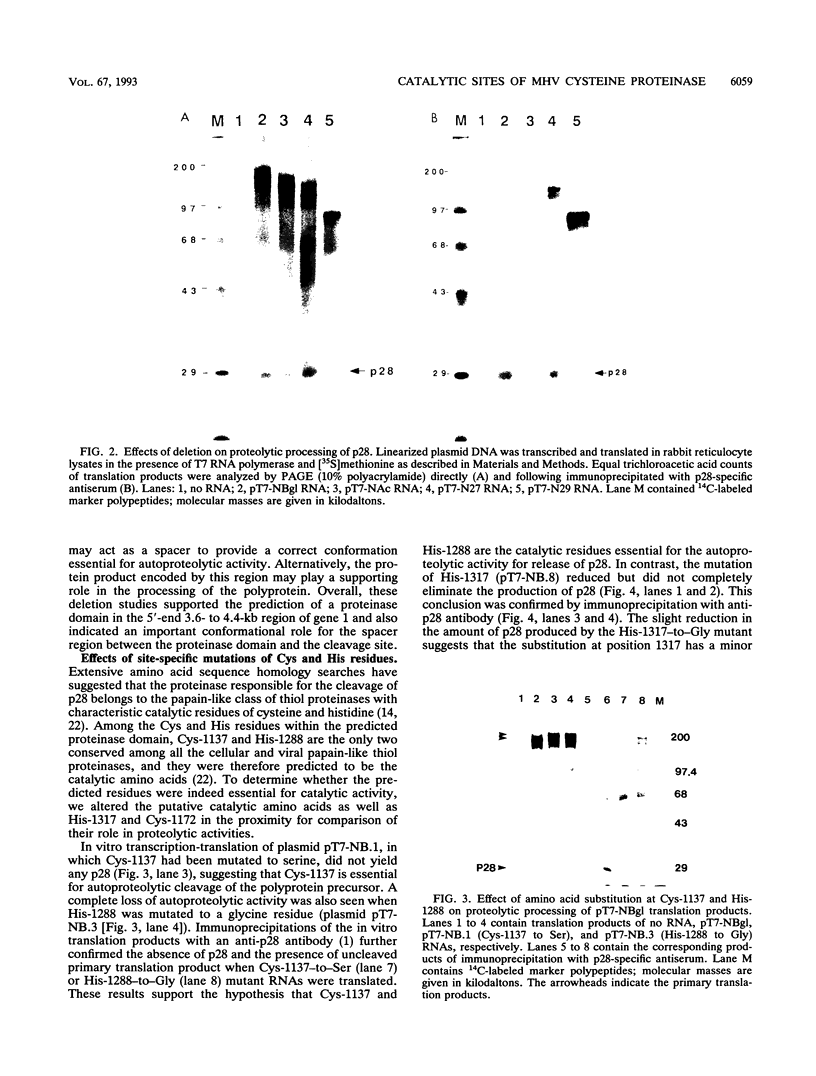
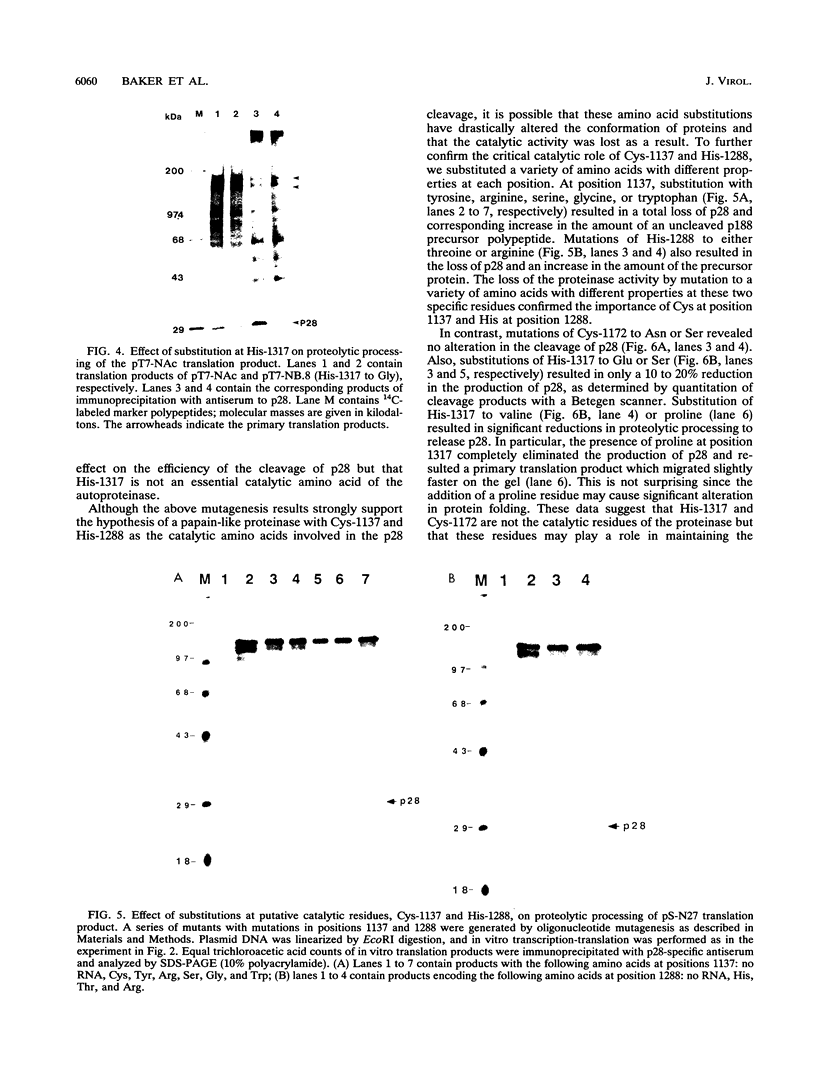
The murine coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus gene 1 is expressed as a polyprotein, which is cleaved into multiple proteins posttranslationally. One of the proteins is p28, which represents the amino-terminal portion of the polyprotein and is presumably generated by the activity of an autoproteinase domain of the polyprotein (S. C. Baker, C. K. Shieh, L. H. Soe, M.-F. Chang, D. M. Vannier, and M. M. C. Lai, J. Virol. 63:3693-3699, 1989). In this study, the boundaries and the critical amino acid residues of this putative proteinase domain were characterized by deletion analysis and site-directed mutagenesis. Proteinase activity was monitored by examining the generation of p28 during in vitro translation in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Deletion analysis defined the proteinase domain to be within the sequences encoded from the 3.6- to 4.4-kb region from the 5' end of the genome. A 0.7-kb region between the substrate (p28) and proteinase domain could be deleted without affecting the proteolytic cleavage. However, a larger deletion (1.6 kb) resulted in the loss of proteinase activity, suggesting the importance of spacing sequences between proteinase and substrate. Computer-assisted analysis of the amino acid sequence of the proteinase domain identified potential catalytic cysteine and histidine residues in a stretch of sequence distantly related to papain-like cysteine proteinases. The role of these putative catalytic residues in the proteinase activity was studied by site-specific mutagenesis. Mutations of Cys-1137 or His-1288 led to a complete loss of proteinase activity, implicating these residues as essential for the catalytic activity. In contrast, most mutations of His-1317 or Cys-1172 had no or only minor effects on proteinase activity. This study establishes that mouse hepatitis virus gene 1 encodes a proteinase domain, in the region from 3.6 to 4.4 kb from the 5' end of the genome, which resembles members of the papain family of cysteine proteinases and that this proteinase domain is responsible for the cleavage of the N-terminal peptide.
Full text
PDF

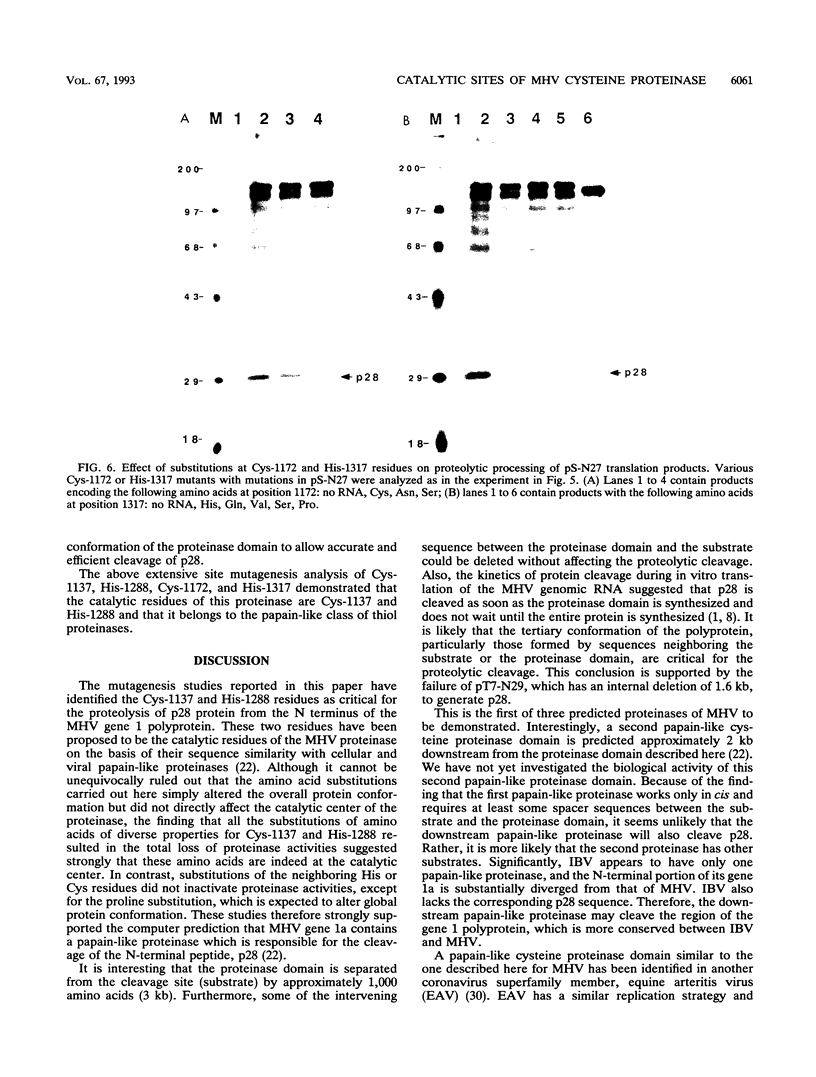


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker S. C., Shieh C. K., Soe L. H., Chang M. F., Vannier D. M., Lai M. M. Identification of a domain required for autoproteolytic cleavage of murine coronavirus gene A polyprotein. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3693–3699. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3693-3699.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baric R. S., Fu K., Schaad M. C., Stohlman S. A. Establishing a genetic recombination map for murine coronavirus strain A59 complementation groups. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):646–656. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90530-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Characterization of replicative intermediate RNA of mouse hepatitis virus: presence of leader RNA sequences on nascent chains. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):633–640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.633-640.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredenbeek P. J., Pachuk C. J., Noten A. F., Charité J., Luytjes W., Weiss S. R., Spaan W. J. The primary structure and expression of the second open reading frame of the polymerase gene of the coronavirus MHV-A59; a highly conserved polymerase is expressed by an efficient ribosomal frameshifting mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1825–1832. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Boursnell M. E., Binns M. M., Bilimoria B., Blok V. C., Brown T. D., Inglis S. C. An efficient ribosomal frame-shifting signal in the polymerase-encoding region of the coronavirus IBV. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3779–3785. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02713.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brierley I., Digard P., Inglis S. C. Characterization of an efficient coronavirus ribosomal frameshifting signal: requirement for an RNA pseudoknot. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. R., Perlman S. Translation and processing of mouse hepatitis virus virion RNA in a cell-free system. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.12-18.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. R., Zoltick P. W., Hughes S. A., Giangreco B., Olson A. L., Perlman S., Leibowitz J. L., Weiss S. R. Intracellular processing of the N-terminal ORF 1a proteins of the coronavirus MHV-A59 requires multiple proteolytic events. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):274–284. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90703-R. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. R., Zoltick P. W., Leibowitz J. L., Pachuk C. J., Weiss S. R. Identification of polypeptides encoded in open reading frame 1b of the putative polymerase gene of the murine coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus A59. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3076–3082. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3076-3082.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M., Perlman S. Identification of putative polymerase gene product in cells infected with murine coronavirus A59. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):565–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90303-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M. Coronavirus genome: prediction of putative functional domains in the non-structural polyprotein by comparative amino acid sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4847–4861. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Lai M. M. Putative papain-related thiol proteases of positive-strand RNA viruses. Identification of rubi- and aphthovirus proteases and delineation of a novel conserved domain associated with proteases of rubi-, alpha- and coronaviruses. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81034-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy W. R., Strauss J. H. Processing the nonstructural polyproteins of sindbis virus: nonstructural proteinase is in the C-terminal half of nsP2 and functions both in cis and in trans. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4653–4664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4653-4664.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Phillips S., Edgell M. H., Gillam S., Jahnke P., Smith M. Mutagenesis at a specific position in a DNA sequence. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6551–6560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonin E. V., Gorbalenya A. E., Purdy M. A., Rozanov M. N., Reyes G. R., Bradley D. W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8259–8263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M. Coronavirus: organization, replication and expression of genome. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:303–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A. Presence of leader sequences in the mRNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1027-1033.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. J., Shieh C. K., Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., La Monica N., Tuler J., Bagdzhadzhyan A., Lai M. M. The complete sequence (22 kilobases) of murine coronavirus gene 1 encoding the putative proteases and RNA polymerase. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):567–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90071-I. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., Weiss S. R., Paavola E., Bond C. W. Cell-free translation of murine coronavirus RNA. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):905–913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.905-913.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. K., Thompson D. V. Efficient site directed in vitro mutagenesis using ampicillin selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 25;18(12):3439–3443. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.12.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh C. S., Carrington J. C. Identification of essential residues in potyvirus proteinase HC-Pro by site-directed mutagenesis. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):692–699. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90582-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachuk C. J., Bredenbeek P. J., Zoltick P. W., Spaan W. J., Weiss S. R. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the putative polymerase of mouse hepatitis coronavirus, strain A59. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90520-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaad M. C., Stohlman S. A., Egbert J., Lum K., Fu K., Wei T., Jr, Baric R. S. Genetics of mouse hepatitis virus transcription: identification of cistrons which may function in positive and negative strand RNA synthesis. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):634–645. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90529-Z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. Coronavirus JHM: coding assignments of subgenomic mRNAs. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):113–125. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snijder E. J., Wassenaar A. L., Spaan W. J. The 5' end of the equine arteritis virus replicase gene encodes a papainlike cysteine protease. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7040–7048. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7040-7048.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soe L. H., Shieh C. K., Baker S. C., Chang M. F., Lai M. M. Sequence and translation of the murine coronavirus 5'-end genomic RNA reveals the N-terminal structure of the putative RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3968–3976. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3968-3976.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Delius H., Skinner M., Armstrong J., Rottier P., Smeekens S., van der Zeijst B. A., Siddell S. G. Coronavirus mRNA synthesis involves fusion of non-contiguous sequences. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1839–1844. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., De Groot R. J., Levinson R., Strauss J. H. Identification of the active site residues in the nsP2 proteinase of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):932–940. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90268-T. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., Hardy W. R., Shirako Y., Strauss J. H. Cleavage-site preferences of Sindbis virus polyproteins containing the non-structural proteinase. Evidence for temporal regulation of polyprotein processing in vivo. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2631–2638. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Boon J. A., Snijder E. J., Chirnside E. D., de Vries A. A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Equine arteritis virus is not a togavirus but belongs to the coronaviruslike superfamily. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2910–2920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2910-2920.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]