Abstract
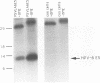
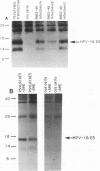
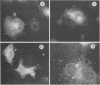
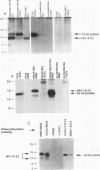
The human papillomavirus (HPV) E5 proteins are predicted from DNA sequence analysis to be small hydrophobic molecules, and the HPV type 6 (HPV-6) and HPV-11 E5 proteins share several structural similarities with the bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV-1) E5 protein. Also similar to the BPV-1 E5 protein, the HPV-6 and HPV-16 E5 proteins exhibit transforming activity when assayed on NIH 3T3 and C127 cells. In this study, we expressed epitope-tagged E5 proteins from both the "low-risk" HPV-6 and the "high-risk" HPV-16 in order to permit their immunologic identification and biochemical characterization. While the HPV-6 and HPV-16 E5 proteins fail to form disulfide-linked dimers and oligomers, they did resemble the BPV-1 E5 protein in their intracellular localization to the Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, and nuclear membranes. In addition, the HPV E5 proteins also bound to the 16-kDa pore-forming protein component of the vacuolar ATPase, a known characteristic of the BPV-1 E5 protein. These studies reveal a common intramembrane localization and potential cellular protein target for both the BPV and HPV E5 proteins.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Laimins L. A. The E6-E7 region of human papillomavirus type 18 is sufficient for transformation of NIH 3T3 and rat-1 cells. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3635–3640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3635-3640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A., DiMaio D., Schlegel R. Genetic and biochemical definition of the bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2381–2385. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02515.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. L., Mounts P. Transforming activity of E5a protein of human papillomavirus type 6 in NIH 3T3 and C127 cells. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3226–3233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3226-3233.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosson P., Lankford S. P., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Membrane protein association by potential intramembrane charge pairs. Nature. 1991 May 30;351(6325):414–416. doi: 10.1038/351414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiMaio D., Guralski D., Schiller J. T. Translation of open reading frame E5 of bovine papillomavirus is required for its transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1797–1801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Dzarlieva-Petrusevska R. T., Boukamp P., Fusenig N. E., Gissmann L. Molecular and cytogenetic analysis of immortalized human primary keratinocytes obtained after transfection with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. Oncogene. 1987;1(3):251–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., zur Hausen H. A papillomavirus DNA from a cervical carcinoma and its prevalence in cancer biopsy samples from different geographic regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3812–3815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbow M. E., Pitts J. D., Goldstein D. J., Schlegel R., Findlay J. B. The E5 oncoprotein target: a 16-kDa channel-forming protein with diverse functions. Mol Carcinog. 1991;4(6):441–444. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940040605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Andresson T., Sparkowski J. J., Schlegel R. The BPV-1 E5 protein, the 16 kDa membrane pore-forming protein and the PDGF receptor exist in a complex that is dependent on hydrophobic transmembrane interactions. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4851–4859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Finbow M. E., Andresson T., McLean P., Smith K., Bubb V., Schlegel R. Bovine papillomavirus E5 oncoprotein binds to the 16K component of vacuolar H(+)-ATPases. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):347–349. doi: 10.1038/352347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Kulke R., Dimaio D., Schlegel R. A glutamine residue in the membrane-associating domain of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 E5 oncoprotein mediates its binding to a transmembrane component of the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):405–413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.405-413.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Schlegel R. The E5 oncoprotein of bovine papillomavirus binds to a 16 kd cellular protein. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):137–145. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08089.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. H., Burkhardt A. L., Schlegel R., DiMaio D. 44-amino-acid E5 transforming protein of bovine papillomavirus requires a hydrophobic core and specific carboxyl-terminal amino acids. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4071–4078. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B. H., Weinstat D. L., DiMaio D. Transforming activity of a 16-amino-acid segment of the bovine papillomavirus E5 protein linked to random sequences of hydrophobic amino acids. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4515–4519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4515-4519.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito Y., Fukuyama K., Yabe K., Epstein W. L. Purification and properties of aminoendopeptidase from rat epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Oct;83(4):265–269. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12340333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaur P., McDougall J. K. Characterization of primary human keratinocytes transformed by human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):1917–1924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.1917-1924.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. At least six nucleotides preceding the AUG initiator codon enhance translation in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leechanachai P., Banks L., Moreau F., Matlashewski G. The E5 gene from human papillomavirus type 16 is an oncogene which enhances growth factor-mediated signal transduction to the nucleus. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):19–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim P. S., Jenson A. B., Cowsert L., Nakai Y., Lim L. Y., Jin X. W., Sundberg J. P. Distribution and specific identification of papillomavirus major capsid protein epitopes by immunocytochemistry and epitope scanning of synthetic peptides. J Infect Dis. 1990 Dec;162(6):1263–1269. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.6.1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Vass W. C., Schiller J. T., Lowy D. R., Velu T. J. The bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein can stimulate the transforming activity of EGF and CSF-1 receptors. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90866-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mincheva A., Gissmann L., zur Hausen H. Chromosomal integration sites of human papillomavirus DNA in three cervical cancer cell lines mapped by in situ hybridization. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1987;176(5):245–256. doi: 10.1007/BF00190531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson H., Nelson N. Disruption of genes encoding subunits of yeast vacuolar H(+)-ATPase causes conditional lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3503–3507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Taiz L. The evolution of H+-ATPases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., DiMaio D. Stable association between the bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein and activated platelet-derived growth factor receptor in transformed mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6736–6740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petti L., Nilson L. A., DiMaio D. Activation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor by the bovine papillomavirus E5 transforming protein. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):845–855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pim D., Collins M., Banks L. Human papillomavirus type 16 E5 gene stimulates the transforming activity of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirisi L., Yasumoto S., Feller M., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Transformation of human fibroblasts and keratinocytes with human papillomavirus type 16 DNA. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1061–1066. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1061-1066.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller J. T., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Identification of a second transforming region in bovine papillomavirus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7880–7884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Phelps W. C., Zhang Y. L., Barbosa M. Quantitative keratinocyte assay detects two biological activities of human papillomavirus DNA and identifies viral types associated with cervical carcinoma. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3181–3187. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedman S. A., Barbosa M. S., Vass W. C., Hubbert N. L., Haas J. A., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. The full-length E6 protein of human papillomavirus type 16 has transforming and trans-activating activities and cooperates with E7 to immortalize keratinocytes in culture. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4860–4866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4860-4866.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Settleman J., DiMaio D. Efficient transactivation and morphologic transformation by bovine papillomavirus genes expressed from a bovine papillomavirus/simian virus 40 recombinant virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9007–9011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straight S. W., Hinkle P. M., Jewers R. J., McCance D. J. The E5 oncoprotein of human papillomavirus type 16 transforms fibroblasts and effects the downregulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor in keratinocytes. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4521–4532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4521-4532.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts S. L., Phelps W. C., Ostrow R. S., Zachow K. R., Faras A. J. Cellular transformation by human papillomavirus DNA in vitro. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):634–636. doi: 10.1126/science.6330900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Okayama H., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus contains multiple transforming genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1030–1034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto S., Burkhardt A. L., Doniger J., DiPaolo J. A. Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA-induced malignant transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):572–577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.572-577.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zur Hausen H. Papillomaviruses in human cancers. Mol Carcinog. 1988;1(3):147–150. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Brule A. J., Claas E. C., du Maine M., Melchers W. J., Helmerhorst T., Quint W. G., Lindeman J., Meijer C. J., Walboomers J. M. Use of anticontamination primers in the polymerase chain reaction for the detection of human papilloma virus genotypes in cervical scrapes and biopsies. J Med Virol. 1989 Sep;29(1):20–27. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890290105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]