Abstract
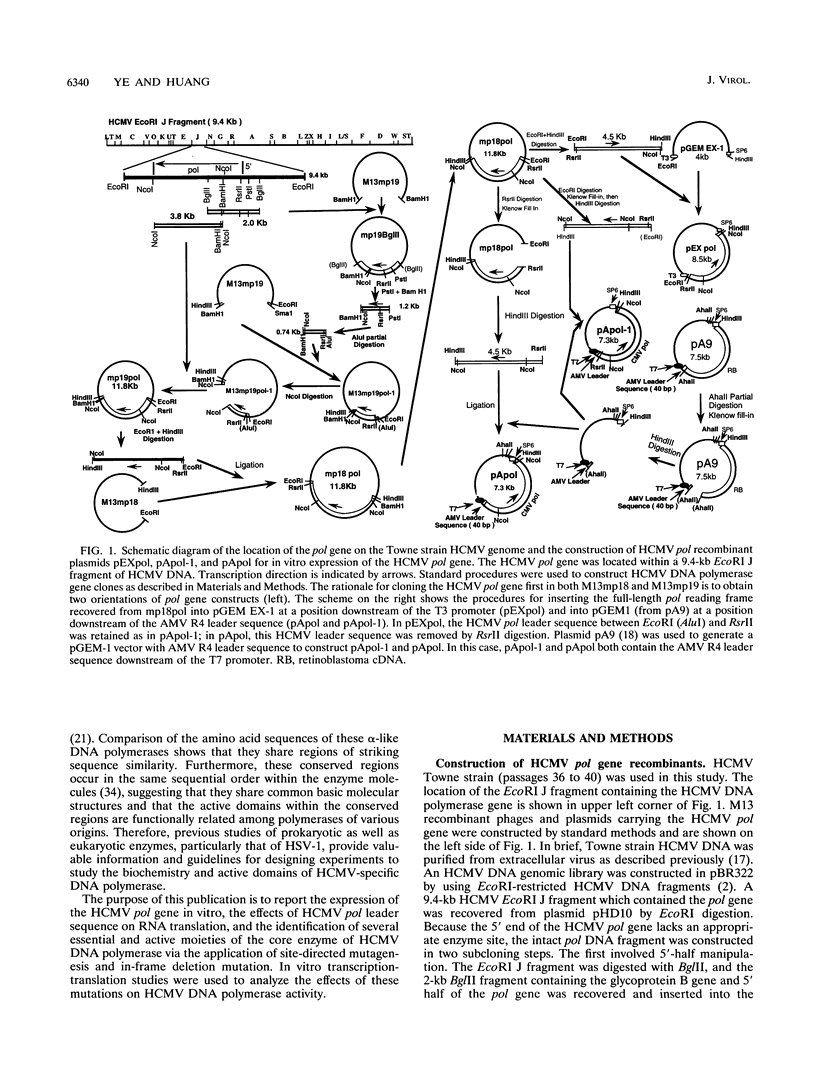
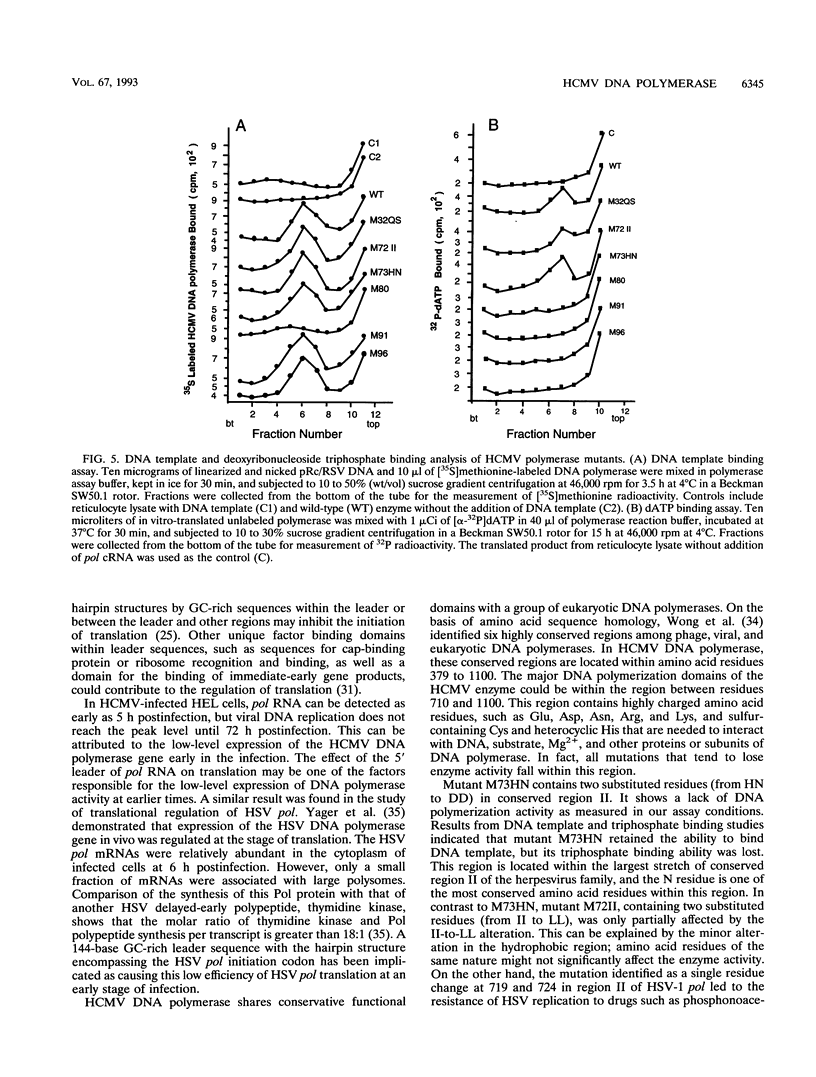
Genomic DNA of the Towne strain human cytomegalovirus polymerase (pol) gene (4.4-kb RsrII-NcoI segment of the EcoRI J fragment) was cloned into plasmids containing either the T3 or the T7 promoter for in vitro transcription-translation studies. The translation efficiency of unmodified pol cRNA was poor in this system and could not be improved by capping. However, the efficiency could be enhanced by replacing the leader sequence with a 40-bp AT-rich sequence derived from an alfalfa mosaic virus, R4. pol cRNA directed the synthesis of a 140-kDa polypeptide in a rabbit reticulocyte translation system. The in vitro-translated wild-type enzyme possessed significant polymerization activity which could be stimulated by salt as could that of the authentic enzyme purified from virus-infected cells. To study the critical domains of this enzyme, nine mutations were introduced into the pol gene around the conserved domains of eukaryotic polymerase by oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Two constructs with mutations at amino acid residues 323 to 325 (M32QS) and 725 to 726 (M72II) remained active, with partial loss of enzyme activity, while the enzyme activities of other mutants with alterations at four domains located around amino acid residues 729 to 730 (M73HN), 804 to 807 (M80 and DE80), 910 to 913 (M91 and DE91), and 962 to 964 (M96 and DE96) were abolished. DNA template and triphosphate binding assays indicated that the mutation at 804 to 807 (conserved region III) lost the ability to bind DNA template, and four mutants, M73HN (within conserved region II), M80 (in region III), M91 (in region I), and M96 (around region V [962 to 964; amino acid sequence KKR]), failed to bind deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate. These data suggest that conserved region III is essential for DNA template binding, while residues between conserved region II and V (725 to 964) are involved in triphosphate binding.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernad A., Blanco L., Lázaro J. M., Martín G., Salas M. A conserved 3'----5' exonuclease active site in prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA polymerases. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90883-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. G., Kenney S. C., Kamine J., Pagano J. S., Huang E. S. Immediate-early gene region of human cytomegalovirus trans-activates the promoter of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8642–8646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delarue M., Poch O., Tordo N., Moras D., Argos P. An attempt to unify the structure of polymerases. Protein Eng. 1990 May;3(6):461–467. doi: 10.1093/protein/3.6.461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derbyshire V., Freemont P. S., Sanderson M. R., Beese L., Friedman J. M., Joyce C. M., Steitz T. A. Genetic and crystallographic studies of the 3',5'-exonucleolytic site of DNA polymerase I. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):199–201. doi: 10.1126/science.2832946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S. Expression of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase gene by in vitro translation and effects of gene deletions on activity. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3224–3232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3224-3232.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S. Site-specific mutagenesis of a highly conserved region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase gene. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1394–1397. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1394-1397.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertl P. F., Powell K. L. Physical and functional interaction of human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase and its accessory protein (ICP36) expressed in insect cells. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4126–4133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4126-4133.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ertl P. F., Thomas M. S., Powell K. L. High level expression of DNA polymerases from herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1991 Jul;72(Pt 7):1729–1734. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-7-1729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes J. E., Huang E. S. Stimulation of cellular thymidine kinases by human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):13–21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.13-21.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo M. L., Dorsky D. I., Crumpacker C. S., Parris D. S. The essential 65-kilodalton DNA-binding protein of herpes simplex virus stimulates the virus-encoded DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5023–5029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5023-5029.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Chiou H. C., Bastow K. F., Cheng Y. C., Coen D. M. Identification of amino acids in herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase involved in substrate and drug recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6672–6676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Chiou H. C., Hall J. D., Mount D. W., Retondo M. J., Weller S. K., Coen D. M. Sequence and mapping analyses of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene predict a C-terminal substrate binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7969–7973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. Cytomegalovirus infections following renal transplantation. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1151–1178. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb J., Marcy A. I., Coen D. M., Challberg M. D. The herpes simplex virus type 1 UL42 gene product: a subunit of DNA polymerase that functions to increase processivity. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5976–5987. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5976-5987.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez T. R., Lehman I. R. Functional interaction between the herpes simplex-1 DNA polymerase and UL42 protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11227–11232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S., Chen S. T., Pagano J. S. Human cytomegalovirus. I. Purification and characterization of viral DNA. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1473–1481. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1473-1481.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus. III. Virus-induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1975 Aug;16(2):298–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.2.298-310.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Wang N. P., Tseng B. Y., Lee W. H., Lee E. H. Two distinct and frequently mutated regions of retinoblastoma protein are required for binding to SV40 T antigen. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1815–1822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobling S. A., Gehrke L. Enhanced translation of chimaeric messenger RNAs containing a plant viral untranslated leader sequence. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):622–625. doi: 10.1038/325622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joung I., Horwitz M. S., Engler J. A. Mutagenesis of conserved region I in the DNA polymerase from human adenovirus serotype 2. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90840-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf C. W. The herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA polymerase gene: site of phosphonoacetic acid resistance mutation in strain Angelotti is highly conserved. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1429–1433. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Bankier A. T., Satchwell S. C., Weston K., Tomlinson P., Barrell B. G. Sequence and transcription analysis of the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase gene. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.125-133.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler E., Stuart A. D., Chee M. S. Human cytomegalovirus UL97 open reading frame encodes a protein that phosphorylates the antiviral nucleoside analogue ganciclovir. Nature. 1992 Jul 9;358(6382):160–162. doi: 10.1038/358160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lurain N. S., Thompson K. D., Holmes E. W., Read G. S. Point mutations in the DNA polymerase gene of human cytomegalovirus that result in resistance to antiviral agents. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7146–7152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7146-7152.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mar E. C., Chiou J. F., Cheng Y. C., Huang E. S. Human cytomegalovirus-induced DNA polymerase and its interaction with the triphosphates of 1-(2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-methyluracil, -5-iodocytosine, and -5-methylcytosine. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):846–851. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.846-851.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcy A. I., Hwang C. B., Ruffner K. L., Coen D. M. Engineered herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase point mutants: the most highly conserved region shared among alpha-like DNA polymerases is involved in substrate recognition. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5883–5890. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5883-5890.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenberg R. M., Fortney J., Barlow S. W., Magrane B. P., Nelson J. A., Ghazal P. Promoter-specific trans activation and repression by human cytomegalovirus immediate-early proteins involves common and unique protein domains. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1556–1565. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1556-1565.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan V., Biron K. K., Talarico C., Stanat S. C., Davis M., Pozzi L. M., Coen D. M. A point mutation in the human cytomegalovirus DNA polymerase gene confers resistance to ganciclovir and phosphonylmethoxyalkyl derivatives. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jan;37(1):19–25. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughan P. J., Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. DNA-binding protein associated with herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):501–508. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.501-508.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. W., Wahl A. F., Yuan P. M., Arai N., Pearson B. E., Arai K., Korn D., Hunkapiller M. W., Wang T. S. Human DNA polymerase alpha gene expression is cell proliferation dependent and its primary structure is similar to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic replicative DNA polymerases. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):37–47. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager D. R., Marcy A. I., Coen D. M. Translational regulation of herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2217–2225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2217-2225.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]