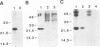Abstract
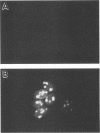
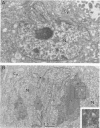
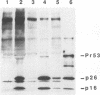
One of the six putative accessory genes of bovine immunodeficiency virus (BIV) is similar to those identified as rev in the human immunodeficiency virus and visna virus genomes. To further analyze the BIV rev gene locus, protein, and function, rev cDNAs were cloned and characterized. BIV rev mRNA is derived from the full-length transcript by multiple splicing events and consists of three exons, including the untranslated leader sequence and two coding exons. BIV rev cDNA was expressed in bacteria and in a mammalian in vitro translation expression system. A 23-kDa Rev protein (p23rev) was immunologically detected in lysates from both systems by using an antiserum made to a synthetic Rev peptide. Recombinant p23rev made in bacteria was purified and used to make a polyvalent antiserum. Antisera to Rev peptide and recombinant p23rev immunoprecipitated p23rev from BIV-infected mammalian cells but not from virions. A mammalian expression vector using the BIV rev cDNA was constructed; p23rev was immunoprecipitated with anti-Rev serum from 32P-labeled lysates of monkey cells transfected with this plasmid, demonstrating that BIV Rev is phosphorylated. Immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy with anti-BIV Rev antisera localized Rev in the nucleus and, particularly, in the nucleoli of BIV-infected cells. In functional studies, the expression of BIV Rev was shown to positively regulate the appearance both of Gag protein, which is translated from the unspliced primary viral transcript, and of singly spliced env mRNA but not that of the multiply spliced tat mRNA. These results demonstrate that BIV Rev activity correlates with the known function of lentivirus Rev proteins.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S., Rosenblatt J. D., Chen I. S. Analysis of rev gene function on human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication in lymphoid cells by using a quantitative polymerase chain reaction method. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4875–4881. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4875-4881.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S., Zack J. A., Chen I. S. Characterization and expression of novel singly spliced RNA species of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4585–4588. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4585-4588.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battles J. K., Hu M. Y., Rasmussen L., Tobin G. J., Gonda M. A. Immunological characterization of the gag gene products of bovine immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):6868–6877. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.6868-6877.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Aepinus C., Dobrovnik M., Fleckenstein B., Hauber J., Böhnlein E. Mutational analysis of functional domains in the HIV-1 Rev trans-regulatory protein. Virology. 1991 Aug;183(2):630–635. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90992-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer R. A., Lehner C. F., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M. J., Lahn S., Boyd A. L., Kost T. A., Nagashima K., Gonda M. A. Molecular cloning of biologically active proviruses of bovine immunodeficiency-like virus. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):515–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. M., Blume M., Lee S. G., Hung P. P., Hirsch V. M., Johnson P. R. Coexpression of biologically active simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) Rev and Env in an SV40 system: the SIV rev gene regulates env expression. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):816–819. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90556-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland T. D., Tsai W. P., Kim Y. D., Oroszlan S. Envelope proteins of human T cell leukemia virus type I: characterization by antisera to synthetic peptides and identification of a natural epitope. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2945–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Regulation of HIV-1 gene expression. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2361–2368. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.1712325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dear S., Staden R. A sequence assembly and editing program for efficient management of large projects. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3907–3911. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Vazeux R., Peden K. The rev gene product of the human immunodeficiency virus affects envelope-specific RNA localization. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1155–1165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fankhauser C., Izaurralde E., Adachi Y., Wingfield P., Laemmli U. K. Specific complex of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 rev and nucleolar B23 proteins: dissociation by the Rev response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2567–2575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Jarrett R. F., Aldovini A., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. HTLV-III expression and production involve complex regulation at the levels of splicing and translation of viral RNA. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):807–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felber B. K., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., Cladaras C., Copeland T., Pavlakis G. N. rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 affects the stability and transport of the viral mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1495–1499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey K. J., Oberste M. S., Elser J. E., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of biologically active proviruses of the bovine immunodeficiency-like virus. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):391–409. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90424-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson T., Hillier L. A trace display and editing program for data from fluorescence based sequencing machines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6481–6483. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda M. A. Bovine immunodeficiency virus. AIDS. 1992 Aug;6(8):759–776. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199208000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda M. A., Braun M. J., Carter S. G., Kost T. A., Bess J. W., Jr, Arthur L. O., Van der Maaten M. J. Characterization and molecular cloning of a bovine lentivirus related to human immunodeficiency virus. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):388–391. doi: 10.1038/330388a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M. Rapid and quantitative preparation of cytoplasmic RNA from small numbers of cells. Anal Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;173(1):93–95. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarskjöld M. L., Heimer J., Hammarskjöld B., Sangwan I., Albert L., Rekosh D. Regulation of human immunodeficiency virus env expression by the rev gene product. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1959–1966. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1959-1966.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A. Molecular biology of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. FASEB J. 1991 Jul;5(10):2349–2360. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.10.1829694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Bouvier M., Malim M. H., Cullen B. R. Phosphorylation of the rev gene product of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4801–4804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4801-4804.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., McGill C., Hughes S. H. Expression of soluble, enzymatically active, human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli and analysis of mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1218–1222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis N., Williams J., Rekosh D., Hammarskjöld M. L. Identification of a cis-acting element in human immunodeficiency virus type 2 (HIV-2) that is responsive to the HIV-1 rev and human T-cell leukemia virus types I and II rex proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1690–1697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1690-1697.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. Q., Sheridan D., Wood C. Identification and characterization of the bovine immunodeficiency-like virus tat gene. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5137–5140. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5137-5140.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malim M. H., Böhnlein S., Hauber J., Cullen B. R. Functional dissection of the HIV-1 Rev trans-activator--derivation of a trans-dominant repressor of Rev function. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90416-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazarin V., Gourdou I., Querat G., Sauze N., Audoly G., Vitu C., Russo P., Rousselot C., Filippi P., Vigne R. Subcellular localization of rev-gene product in visna virus-infected cells. Virology. 1990 Sep;178(1):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90410-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazarin V., Gourdou I., Quérat G., Sauze N., Vigne R. Genetic structure and function of an early transcript of visna virus. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4813–4818. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4813-4818.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald D., Hope T. J., Parslow T. G. Posttranscriptional regulation by the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Rev and human T-cell leukemia virus type I Rex proteins through a heterologous RNA binding site. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7232–7238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7232-7238.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberste M. S., Gonda M. A. Conservation of amino-acid sequence motifs in lentivirus Vif proteins. Virus Genes. 1992 Jan;6(1):95–102. doi: 10.1007/BF01703760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberste M. S., Greenwood J. D., Gonda M. A. Analysis of the transcription pattern and mapping of the putative rev and env splice junctions of bovine immunodeficiency-like virus. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3932–3937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3932-3937.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins A., Cochrane A. W., Ruben S. M., Rosen C. A. Structural and functional characterization of the human immunodeficiency virus rev protein. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1989;2(3):256–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifat D. Y., Ennis W. H., Ward J. M., Oberste M. S., Gonda M. A. Persistent infection of rabbits with bovine immunodeficiency-like virus. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4518–4524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4518-4524.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L., Battles J. K., Ennis W. H., Nagashima K., Gonda M. A. Characterization of virus-like particles produced by a recombinant baculovirus containing the gag gene of the bovine immunodeficiency-like virus. Virology. 1990 Oct;178(2):435–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90341-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L., Greenwood J. D., Gonda M. A. Expression of bovine immunodeficiency-like virus envelope glycoproteins by a recombinant baculovirus in insect cells. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):551–561. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90021-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Benko D. M., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Cloning and functional analysis of multiply spliced mRNA species of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2519–2529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2519-2529.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Env and Vpu proteins of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 are produced from multiple bicistronic mRNAs. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5448–5456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5448-5456.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Dayton A., Terwilliger E., Haseltine W. A second post-transcriptional trans-activator gene required for HTLV-III replication. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):412–417. doi: 10.1038/321412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. M., Derse D., Rice N. R. Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding equine infectious anemia virus tat and putative Rev proteins. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3716–3725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3716-3725.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tager H. S. Coupling of peptides to albumin with difluorodinitrobenzene. Anal Biochem. 1976 Apr;71(2):367–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiley L. S., Brown P. H., Le S. Y., Maizel J. V., Clements J. E., Cullen B. R. Visna virus encodes a post-transcriptional regulator of viral structural gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7497–7501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetstone C. A., VanDerMaaten M. J., Black J. W. Humoral immune response to the bovine immunodeficiency-like virus in experimentally and naturally infected cattle. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3557–3561. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3557-3561.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetstone C. A., VanDerMaaten M. J., Miller J. M. A western blot assay for the detection of antibodies to bovine immunodeficiency-like virus in experimentally inoculated cattle, sheep, and goats. Arch Virol. 1991;116(1-4):119–131. doi: 10.1007/BF01319236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]