Abstract
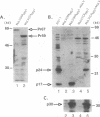
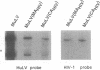
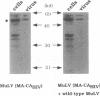
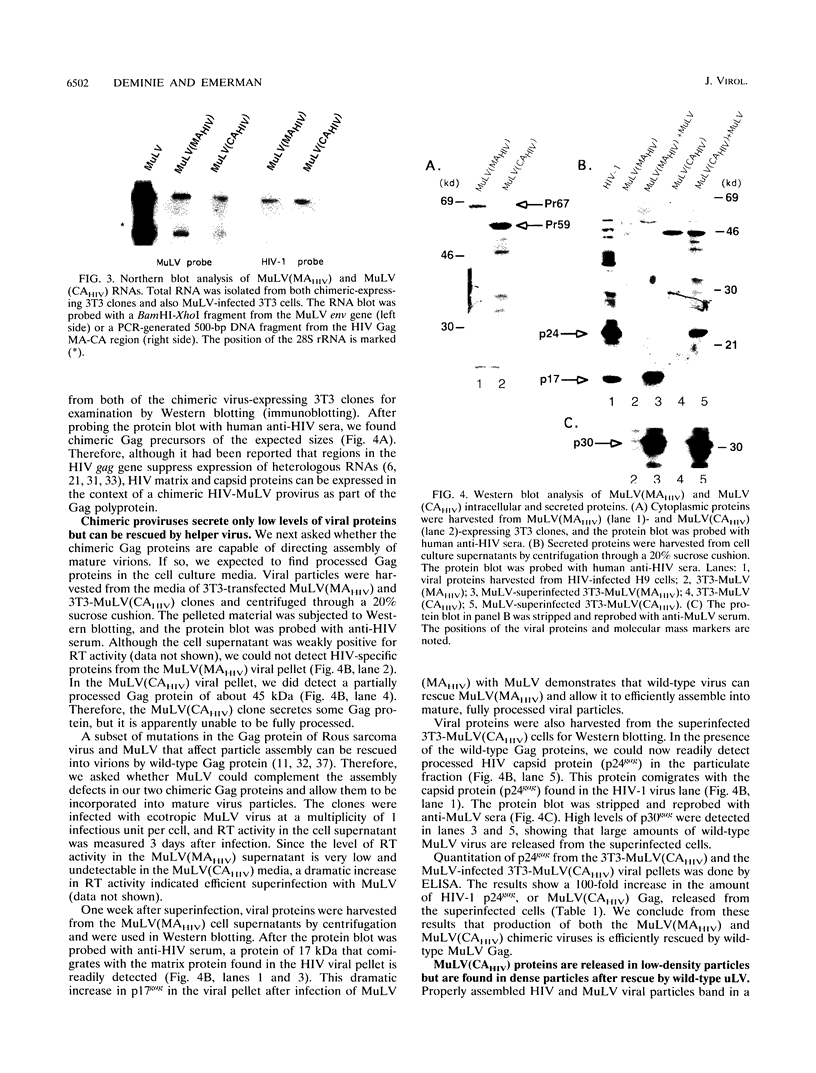
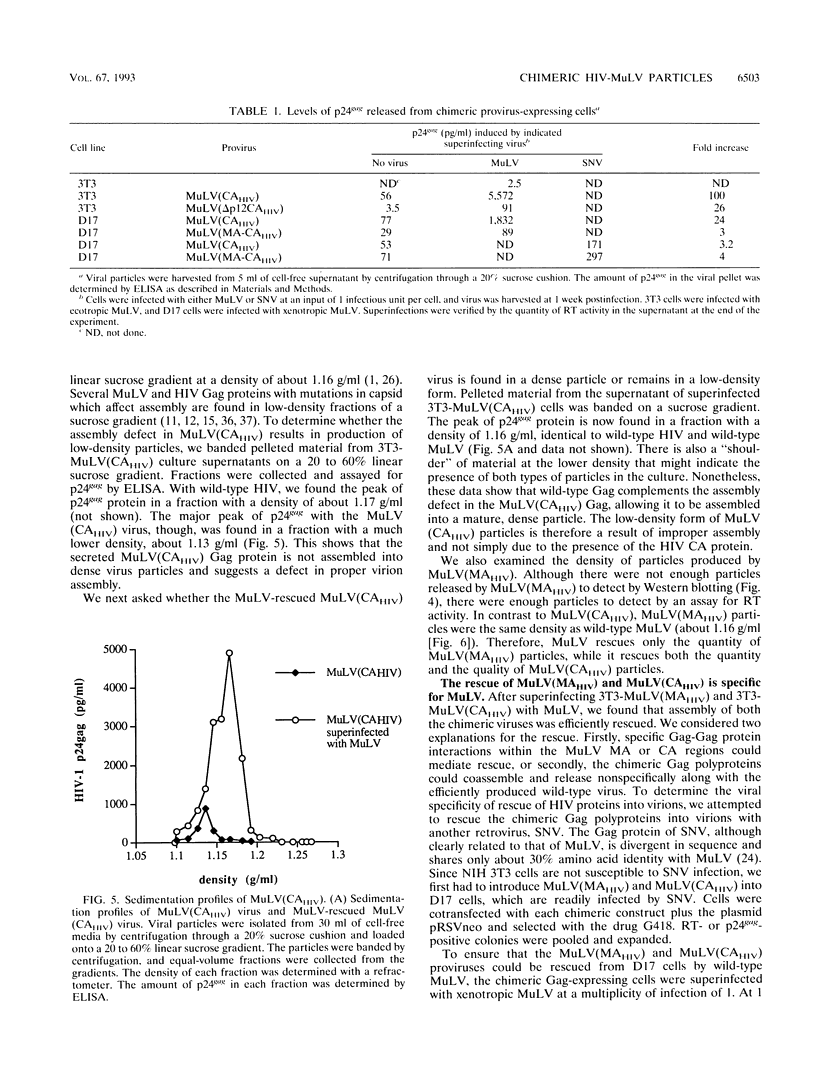
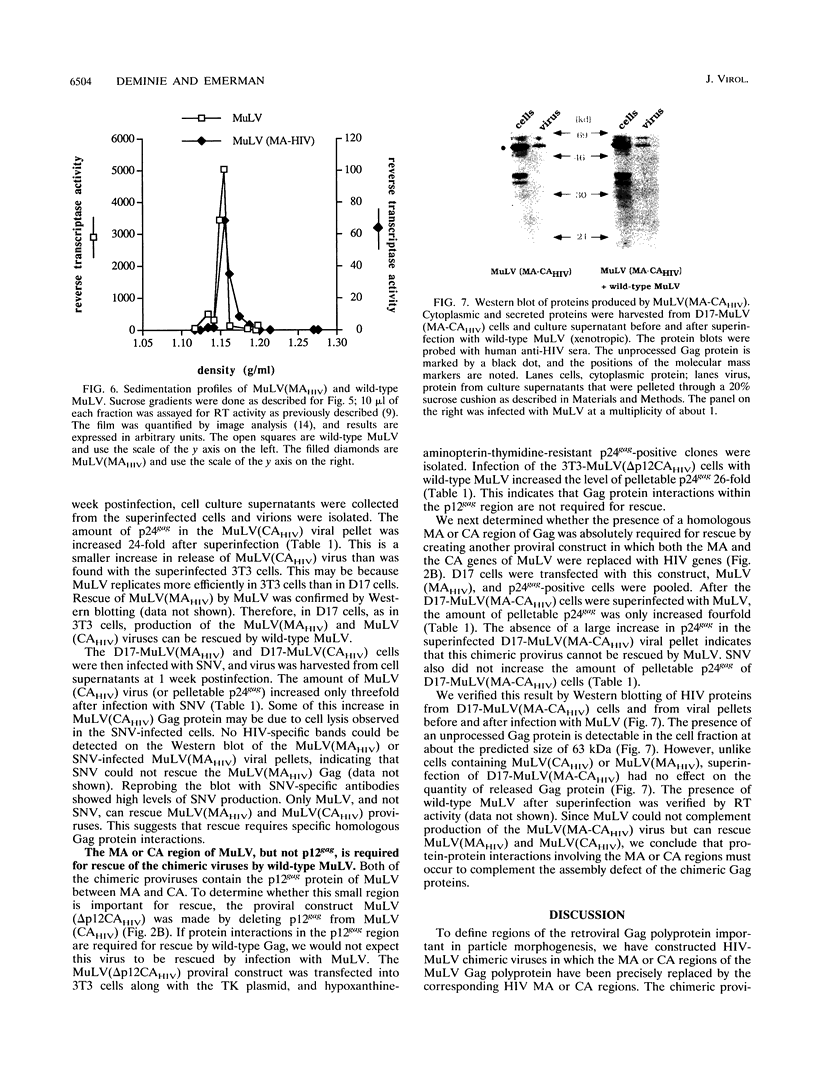
The retroviral Gag polyprotein is necessary and sufficient for assembly and budding of viral particles. However, the exact inter- and intramolecular interactions of the Gag polyproteins during this process are not known. To locate functional domains within Gag, we generated chimeric proviruses between human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and murine leukemia virus (MuLV). In these chimeric proviruses, the matrix or capsid proteins of MuLV were precisely replaced with the matrix or capsid proteins of HIV-1. Although the chimeric proviruses were unable to efficiently assemble into mature viral particles by themselves, coexpression of wild-type MuLV Gag rescued the HIV proteins into virions. The specificity of the rescue of HIV proteins into MuLV virions shows that specific interactions involving homologous matrix or capsid regions of Gag are necessary for retroviral particle formation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolognesi D. P., Luftig R., Shaper J. H. Localization of RNA tumor virus polypeptides. I. Isolation of further virus substructures. Virology. 1973 Dec;56(2):549–564. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowerman B., Brown P. O., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. A nucleoprotein complex mediates the integration of retroviral DNA. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):469–478. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M., Ratner L. Myristoylation-dependent replication and assembly of human immunodeficiency virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):523–527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. W., Jones K. S., Beidas S., Dillon P. J., Skalka A. M., Rosen C. A. Identification and characterization of intragenic sequences which repress human immunodeficiency virus structural gene expression. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5305–5313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5305-5313.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford S., Goff S. P. Mutations in gag proteins P12 and P15 of Moloney murine leukemia virus block early stages of infection. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):909–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.909-917.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelderblom H. R. Assembly and morphology of HIV: potential effect of structure on viral function. AIDS. 1991 Jun;5(6):617–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttlinger H. G., Dorfman T., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Effect of mutations affecting the p6 gag protein on human immunodeficiency virus particle release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3195–3199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M., Jelinek L., Whiting S., Barklis E. Transport and assembly of gag proteins into Moloney murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5306–5316. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5306-5316.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong S. S., Boulanger P. Assembly-defective point mutants of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Gag precursor phenotypically expressed in recombinant baculovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2787–2798. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2787-2798.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H. W., Schwartzberg P., Goff S. P. Point mutations in the P30 domain of the gag gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1985 Apr 15;142(1):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90435-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. F., Pickett S. C., Barker D. L. Autoradiography using storage phosphor technology. Electrophoresis. 1990 May;11(5):355–360. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150110503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Blaug G., Hansen M., Barklis E. Assembly of gag-beta-galactosidase proteins into retrovirus particles. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2265–2279. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2265-2279.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen E. C., Pedersen F. S., Jørgensen P. Matrix protein of Akv murine leukemia virus: genetic mapping of regions essential for particle formation. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4479–4487. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4479-4487.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Diehl R. E., Rands E., Davis L. J., Hanobik M. G., Wolanski B., Dixon R. A. Expression of active human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protease by noninfectious chimeric virus particles. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3007–3014. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3007-3014.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leis J., Baltimore D., Bishop J. M., Coffin J., Fleissner E., Goff S. P., Oroszlan S., Robinson H., Skalka A. M., Temin H. M. Standardized and simplified nomenclature for proteins common to all retroviruses. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1808–1809. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1808-1809.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis P., Hensel M., Emerman M. Human immunodeficiency virus infection of cells arrested in the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3053–3058. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldarelli F., Martin M. A., Strebel K. Identification of posttranscriptionally active inhibitory sequences in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA: novel level of gene regulation. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5732–5743. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5732-5743.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash M. A., Meyer M. K., Decker G. L., Arlinghaus R. B. A subset of Pr65gag is nucleus associated in murine leukemia virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1350–1356. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1350-1356.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K., Emerman M., Montagnier L. Changes in growth properties on passage in tissue culture of viruses derived from infectious molecular clones of HIV-1LAI, HIV-1MAL, and HIV-1ELI. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):661–672. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90537-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. Amino acid substitutions within the matrix protein of type D retroviruses affect assembly, transport and membrane association of a capsid. EMBO J. 1991 Mar;10(3):535–546. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. Structural role of the matrix protein of type D retroviruses in gag polyprotein stability and capsid assembly. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4383–4389. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4383-4389.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Rein A. Unmyristylated Moloney murine leukemia virus Pr65gag is excluded from virus assembly and maturation events. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2370–2373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2370-2373.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Pavlakis G. N. Distinct RNA sequences in the gag region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 decrease RNA stability and inhibit expression in the absence of Rev protein. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):150–159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.150-159.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartzberg P., Colicelli J., Gordon M. L., Goff S. P. Mutations in the gag gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus: effects on production of virions and reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):918–924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.918-924.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. J., Cho M. I., Hammarskjöld M. L., Rekosh D. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Pr55gag and Pr160gag-pol expressed from a simian virus 40 late replacement vector are efficiently processed and assembled into viruslike particles. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2743–2750. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2743-2750.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strambio-de-Castillia C., Hunter E. Mutational analysis of the major homology region of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus by use of saturation mutagenesis. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7021–7032. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7021-7032.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D., Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D. HIV-1 Gag mutants can dominantly interfere with the replication of the wild-type virus. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):113–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90874-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Craven R. C. Form, function, and use of retroviral gag proteins. AIDS. 1991 Jun;5(6):639–654. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199106000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Craven R. C., Weldon R. A., Jr, Nelle T. D., Erdie C. R. Suppression of retroviral MA deletions by the amino-terminal membrane-binding domain of p60src. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3804–3812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3804-3812.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X., Yuan X., Matsuda Z., Lee T. H., Essex M. The matrix protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is required for incorporation of viral envelope protein into mature virions. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4966–4971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4966-4971.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Poblotzki A., Wagner R., Niedrig M., Wanner G., Wolf H., Modrow S. Identification of a region in the Pr55gag-polyprotein essential for HIV-1 particle formation. Virology. 1993 Apr;193(2):981–985. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]