Abstract
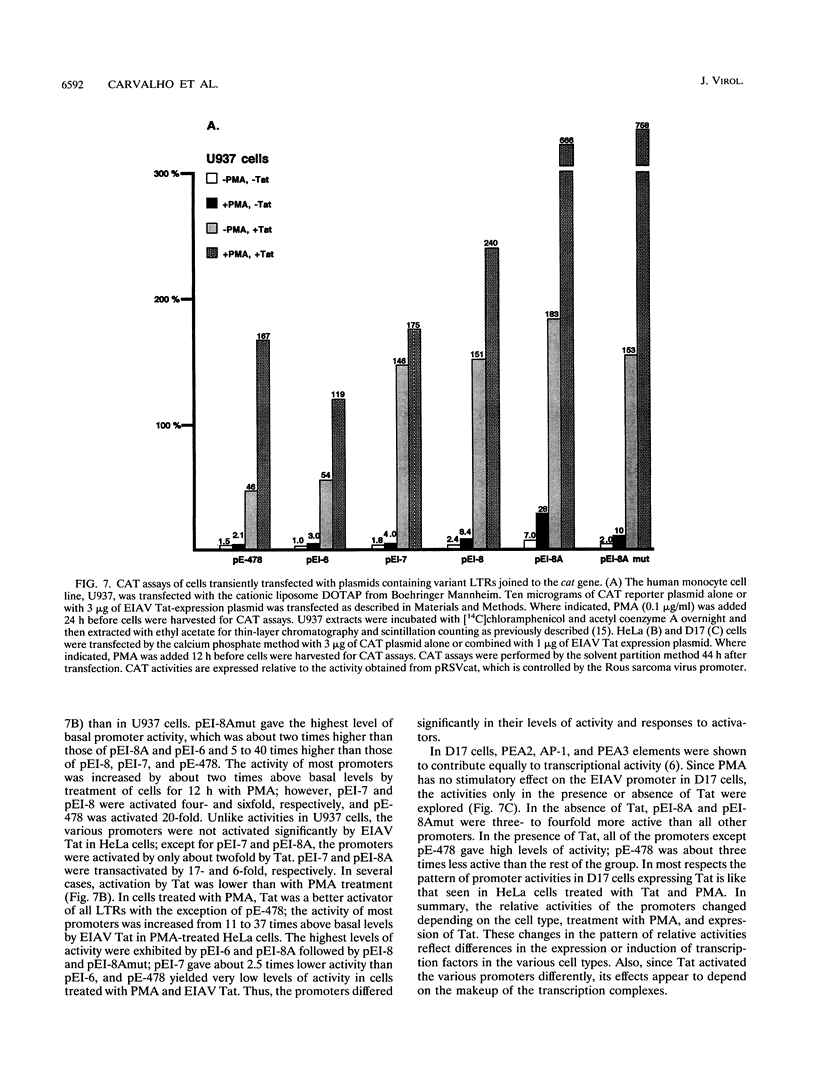
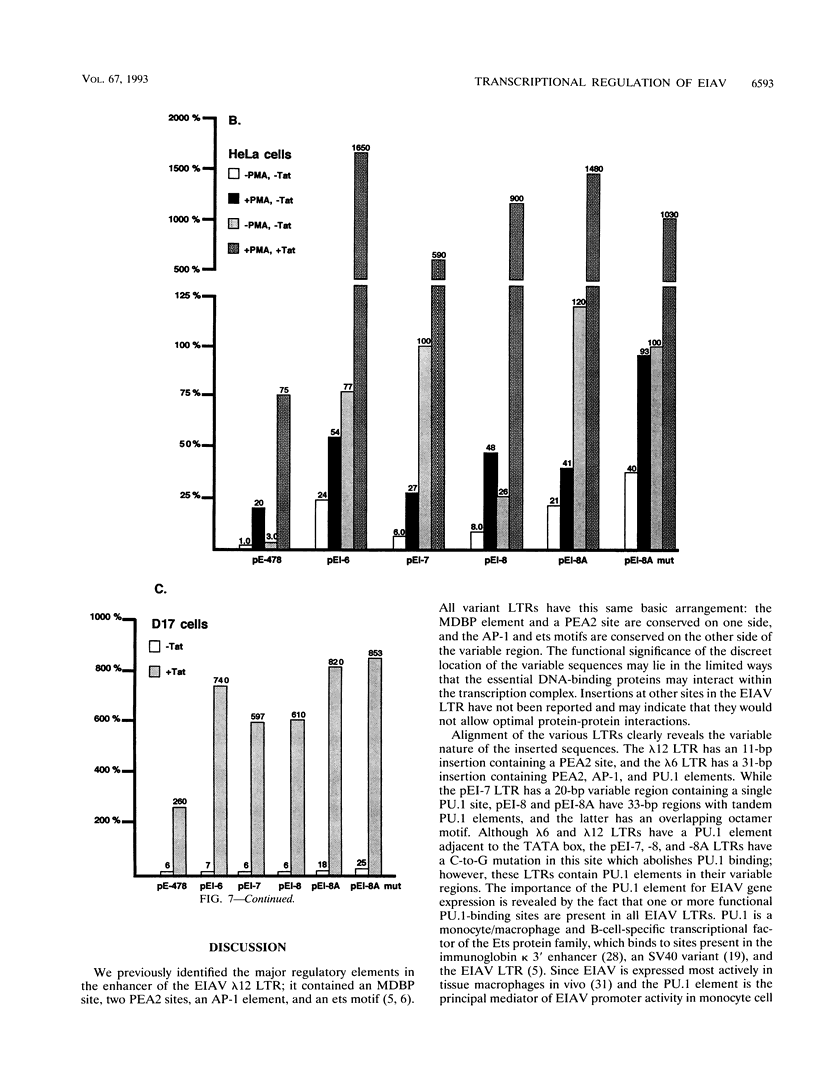
The long terminal repeats (LTRs) from various cloned equine infectious anemia virus (EIAV) proviruses differ significantly, but all contain cis-acting DNA elements identical to MDBP-, PEA2-, AP-1-, and PU.1 (ets)-binding sites. A prototype EIAV LTR would contain one of each of these conserved elements. The LTR variations originate from the insertion of novel sequences between the PEA2 and AP-1 elements in the transcriptional enhancer unit. Viewed in this way, the LTR from provirus clone lambda 12 has an 11-bp insertion containing a PEA2 site and the LTR of the lambda 6 provirus has a 31-bp insertion/duplication containing PEA2, AP-1, and PU.1 sites. Two other LTRs were cloned by amplification of cDNAs from the persistently infected cell line, EIAV-FEA. A third LTR was generated by site-directed mutagenesis of one of the LTRs from EIAV-FEA cells. The latter three had a single base change in the element next to the TATA box that abolished PU.1 binding; however, the variable regions of these LTRs were shown by gel mobility shift assays to contain one or two PU.1 sites. One variable region was shown to have an octamer site overlapping its tandem PU.1 elements. Basal, PMA-activated, and Tat trans-activated transcriptional activities of the LTRs were compared in several different cell lines by transient transfection. The various promoters displayed different relative levels of activity depending on the cell line used and the condition of activation. This natural set of variant promoters may help define how changes in the components of the transcription complex influence transactivation by Tat. The diverse LTRs could endow their respective proviruses with a unique pattern of expression and activation in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton C. V., Brown B. L., Harshman J. S., Gilden R. V. In vitro host range of equine infectious anemia virus. Intervirology. 1981;16(4):225–232. doi: 10.1159/000149271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S., Alexandersen S., Long M. J., Perryman S., Chesebro B. Identification of a hypervariable region in the long terminal repeat of equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1605–1610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1605-1610.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll R., Peterlin B. M., Derse D. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Tat activity by coexpression of heterologous trans activators. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2000–2007. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2000-2007.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho M., Derse D. Mutational analysis of the equine infectious anemia virus Tat-responsive element. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3468–3474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3468-3474.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho M., Derse D. Physical and functional characterization of transcriptional control elements in the equine infectious anemia virus promoter. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2064–2074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2064-2074.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho M., Derse D. The PU.1/Spi-1 proto-oncogene is a transcriptional regulator of a lentivirus promoter. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3885–3890. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3885-3890.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celander D., Haseltine W. A. Tissue-specific transcription preference as a determinant of cell tropism and leukaemogenic potential of murine retroviruses. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):159–162. doi: 10.1038/312159a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheevers W. P., McGuire T. C. Equine infectious anemia virus: immunopathogenesis and persistence. Rev Infect Dis. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):83–88. doi: 10.1093/clinids/7.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. The HIV-1 Tat protein: an RNA sequence-specific processivity factor? Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):655–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Dorn P. L., Levy L., Stephens R. M., Rice N. R., Casey J. W. Characterization of equine infectious anemia virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):743–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.743-747.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Embretson J. E., Anderson D. C., Mullins J. I., Fultz P. N. Sequence analysis and acute pathogenicity of molecularly cloned SIVSMM-PBj14. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):636–640. doi: 10.1038/345636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn P. L., Derse D. cis- and trans-acting regulation of gene expression of equine infectious anemia virus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3522–3526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3522-3526.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn P., DaSilva L., Martarano L., Derse D. Equine infectious anemia virus tat: insights into the structure, function, and evolution of lentivirus trans-activator proteins. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1616–1624. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1616-1624.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Thomas C. Y., Chattopadhyay S. K., Koehne C., O'Donnell P. V. Influence of enhancer sequences on thymotropism and leukemogenicity of mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1284–1292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1284-1292.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. Y., Calman A. F., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Anti-termination of transcription within the long terminal repeat of HIV-1 by tat gene product. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):489–493. doi: 10.1038/330489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato H., Sumimoto H., Pognonec P., Chen C. H., Rosen C. A., Roeder R. G. HIV-1 Tat acts as a processivity factor in vitro in conjunction with cellular elongation factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Apr;6(4):655–666. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Celada A., Van Beveren C., Maki R. A. The macrophage and B cell-specific transcription factor PU.1 is related to the ets oncogene. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koken S. E., van Wamel J. L., Goudsmit J., Berkhout B., Geelen J. L. Natural variants of the HIV-1 long terminal repeat: analysis of promoters with duplicated DNA regulatory motifs. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):968–972. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90274-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono Y., Kobayashi K., Fukunaga Y. Antigenic drift of equine infectious anemia virus in chronically infected horses. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;41(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01249923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marciniak R. A., Sharp P. A. HIV-1 Tat protein promotes formation of more-processive elongation complexes. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4189–4196. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04997.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Crawford T. B., Henson J. B. Immunofluorescent localization of equine infectious anemia virus in tissue. Am J Pathol. 1971 Feb;62(2):283–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelaro R. C., Parekh B., Orrego A., Issel C. J. Antigenic variation during persistent infection by equine infectious anemia virus, a retrovirus. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10539–10544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. L., Fang F. D., Liu C. P., Dhruva B. R., Rwambo P., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C. Antigenic variation and lentivirus persistence: variations in envelope gene sequences during EIAV infection resemble changes reported for sequential isolates of HIV. Virology. 1987 Dec;161(2):321–331. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90124-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. L., Rushlow K., Dhruva B. R., Issel C. J., Montelaro R. C. Localization of conserved and variable antigenic domains of equine infectious anemia virus envelope glycoproteins using recombinant env-encoded protein fragments produced in Escherichia coli. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):609–615. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90203-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pongubala J. M., Nagulapalli S., Klemsz M. J., McKercher S. R., Maki R. A., Atchison M. L. PU.1 recruits a second nuclear factor to a site important for immunoglobulin kappa 3' enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):368–378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray D., Culine S., Tavitain A., Moreau-Gachelin F. The human homologue of the putative proto-oncogene Spi-1: characterization and expression in tumors. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salinovich O., Payne S. L., Montelaro R. C., Hussain K. A., Issel C. J., Schnorr K. L. Rapid emergence of novel antigenic and genetic variants of equine infectious anemia virus during persistent infection. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.71-80.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellon D. C., Perry S. T., Coggins L., Fuller F. J. Wild-type equine infectious anemia virus replicates in vivo predominantly in tissue macrophages, not in peripheral blood monocytes. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5906–5913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5906-5913.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short M. K., Okenquist S. A., Lenz J. Correlation of leukemogenic potential of murine retroviruses with transcriptional tissue preference of the viral long terminal repeats. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1067-1072.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Golemis E., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Mutation of the core or adjacent LVb elements of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer alters disease specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):233–242. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. M., Derse D., Rice N. R. Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding equine infectious anemia virus tat and putative Rev proteins. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3716–3725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3716-3725.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]