Abstract
We have tested whether breakdown of phosphatidylcholine (PC) initiated by exogenous addition of a PC-specific phospholipase C (PC-PLC) from Bacillus cereus or by endogenous overexpression of PC-PLC induces functional activation of NF-kappa B and increases human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) enhancer activity. PC-PLC-activated hydrolysis of PC was found to induce bona fide p50/p65 NF-kappa B binding activity in three different cell lines of human or murine origin. No significant changes in the turnover of other cellular phospholipids were detected in PC-PLC-treated cells. Induction of NF-kappa B by PC-PLC did not depend on de novo synthesis of proteins or autocrine secretion of either tumor necrosis factor or interleukin 1. In human monocytic and lymphoblastoid T-cell lines, induction of NF-kappa B by PC-PLC resulted in clear induction of luciferase expression vectors placed under the control of synthetic kappa B enhancers or wild type, but not kappa B-mutated, HIV long terminal repeat constructs. HIV replication was increased by PC-PLC in chronically infected monocytes and T lymphocytes. NF-kappa B activation promoted by addition of exogenous PC-PLC correlated with an intense production of diacylglycerol. However, addition of a phosphatidylinositol-specific PLC from B. cereus also induced diacylglycerol but did not activate kappa B enhancer-directed vectors. PC-PLC-induced NF-kappa B activation could not be blocked by a specific inhibitor of phorbol ester-inducible protein kinases C. These results indicate that a cellular transduction pathway, dependent on specific PC breakdown, is functional in T lymphocytes and monocytes and may be used by various transmembrane receptors to activate HIV transcription through NF-kappa B-dependent induction of the HIV enhancer.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
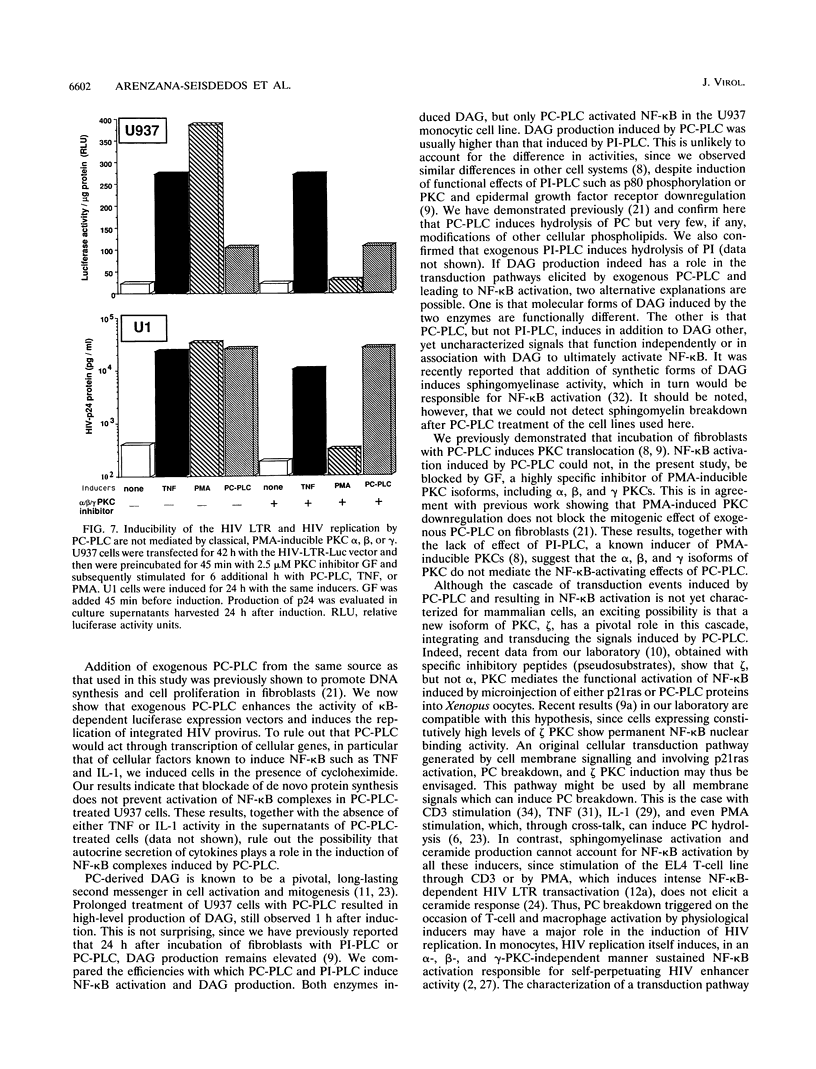
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Israël N., Bachelerie F., Hazan U., Alcami J., Dautry F., Virelizier J. L. c-Ha-ras transfection induces human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) transcription through the HIV-enhancer in human fibroblasts and astrocytes. Oncogene. 1989 Nov;4(11):1359–1362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelerie F., Alcami J., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L. HIV enhancer activity perpetuated by NF-kappa B induction on infection of monocytes. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):709–712. doi: 10.1038/350709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry N., Ase K., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. Activation of resting human T cells requires prolonged stimulation of protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry N., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C and T cell activation. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Apr 30;189(2):205–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besterman J. M., Duronio V., Cuatrecasas P. Rapid formation of diacylglycerol from phosphatidylcholine: a pathway for generation of a second messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Oliff A. I., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Lowy D. R. Genomes of murine leukemia viruses isolated from wild mice. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):777–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.777-791.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Laviada I., Larrodera P., Diaz-Meco M. T., Cornet M. E., Guddal P. H., Johansen T., Moscat J. Evidence for a role of phosphatidylcholine-hydrolysing phospholipase C in the regulation of protein kinase C by ras and src oncogenes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3907–3912. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07611.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Laviada I., Larrodera P., Nieto J. L., Cornet M. E., Diaz-Meco M. T., Sanchez M. J., Guddal P. H., Johansen T., Haro A., Moscat J. Mechanism of inhibition of adenylate cyclase by phospholipase C-catalyzed hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine. Involvement of a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein and protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1170–1176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz-Meco M. T., Berra E., Municio M. M., Sanz L., Lozano J., Dominguez I., Diaz-Golpe V., Lain de Lera M. T., Alcamí J., Payá C. V. A dominant negative protein kinase C zeta subspecies blocks NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4770–4775. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez I., Sanz L., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Diaz-Meco M. T., Virelizier J. L., Moscat J. Inhibition of protein kinase C zeta subspecies blocks the activation of an NF-kappa B-like activity in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):1290–1295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg M. B., Baltimore D., Frankel A. D. The role of Tat in the human immunodeficiency virus life cycle indicates a primary effect on transcriptional elongation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):4045–4049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.4045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazan U., Thomas D., Alcami J., Bachelerie F., Israel N., Yssel H., Virelizier J. L., Arenzana-Seisdedos F. Stimulation of a human T-cell clone with anti-CD3 or tumor necrosis factor induces NF-kappa B translocation but not human immunodeficiency virus 1 enhancer-dependent transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7861–7865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvat R. T., Wood C. HIV promoter activity in primary antigen-specific human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 15;143(8):2745–2751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël N., Hazan U., Alcami J., Munier A., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Bachelerie F., Israël A., Virelizier J. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates transcription of HIV-1 in human T lymphocytes, independently and synergistically with mitogens. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3956–3960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura A., Israël A., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. Detailed analysis of the mouse H-2Kb promoter: enhancer-like sequences and their role in the regulation of class I gene expression. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):261–272. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90760-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacal J. C., Moscat J., Aaronson S. A. Novel source of 1,2-diacylglycerol elevated in cells transformed by Ha-ras oncogene. Nature. 1987 Nov 19;330(6145):269–272. doi: 10.1038/330269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrodera P., Cornet M. E., Diaz-Meco M. T., Lopez-Barahona M., Diaz-Laviada I., Guddal P. H., Johansen T., Moscat J. Phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylcholine is an important step in PDGF-stimulated DNA synthesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1113–1120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90074-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Fujita T., Baltimore D. The NF-kappa B p50 precursor, p105, contains an internal I kappa B-like inhibitor that preferentially inhibits p50. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):3003–3009. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05370.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liscovitch M. Crosstalk among multiple signal-activated phospholipases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):393–399. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90007-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathias S., Younes A., Kan C. C., Orlow I., Joseph C., Kolesnick R. N. Activation of the sphingomyelin signaling pathway in intact EL4 cells and in a cell-free system by IL-1 beta. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):519–522. doi: 10.1126/science.8424175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C zeta subspecies from rat brain: its structure, expression, and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3099–3103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paya C. V., Ten R. M., Bessia C., Alcami J., Hay R. T., Virelizier J. L. NF-kappa B-dependent induction of the NF-kappa B p50 subunit gene promoter underlies self-perpetuation of human immunodeficiency virus transcription in monocytic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7826–7830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price B. D., Morris J. D., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Stimulation of phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis, diacylglycerol release, and arachidonic acid production by oncogenic ras is a consequence of protein kinase C activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16638–16643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosoff P. M., Savage N., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 stimulates diacylglycerol production in T lymphocytes by a novel mechanism. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):73–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S. M., Dillon P. J., Schreck R., Henkel T., Chen C. H., Maher M., Baeuerle P. A., Rosen C. A. Isolation of a rel-related human cDNA that potentially encodes the 65-kD subunit of NF-kappa B. Science. 1991 Mar 22;251(5000):1490–1493. doi: 10.1126/science.2006423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Berkovic D., Tomsing O., Unger C., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor induces rapid production of 1'2'diacylglycerol by a phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C. J Exp Med. 1991 Nov 1;174(5):975–988. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.5.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Josephs S. F., Dukovich M., Peffer N., Wong-Staal F., Greene W. C. Activation of the HIV-1 LTR by T cell mitogens and the trans-activator protein of HTLV-I. Science. 1987 Dec 11;238(4833):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2825351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. J., Cunningham G. R., Strupp J. A., House F. S., Kelley L. L., Henderson G. S., Exton J. H., Bocckino S. B. Activation of phospholipase D: a signaling system set in motion by perturbation of the T lymphocyte antigen receptor/CD3 complex. Cell Regul. 1991 Oct;2(10):841–850. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.10.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toullec D., Pianetti P., Coste H., Bellevergue P., Grand-Perret T., Ajakane M., Baudet V., Boissin P., Boursier E., Loriolle F. The bisindolylmaleimide GF 109203X is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15771–15781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virelizier J. L. Cellular activation and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989;2(3):409–413. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(89)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]