Abstract
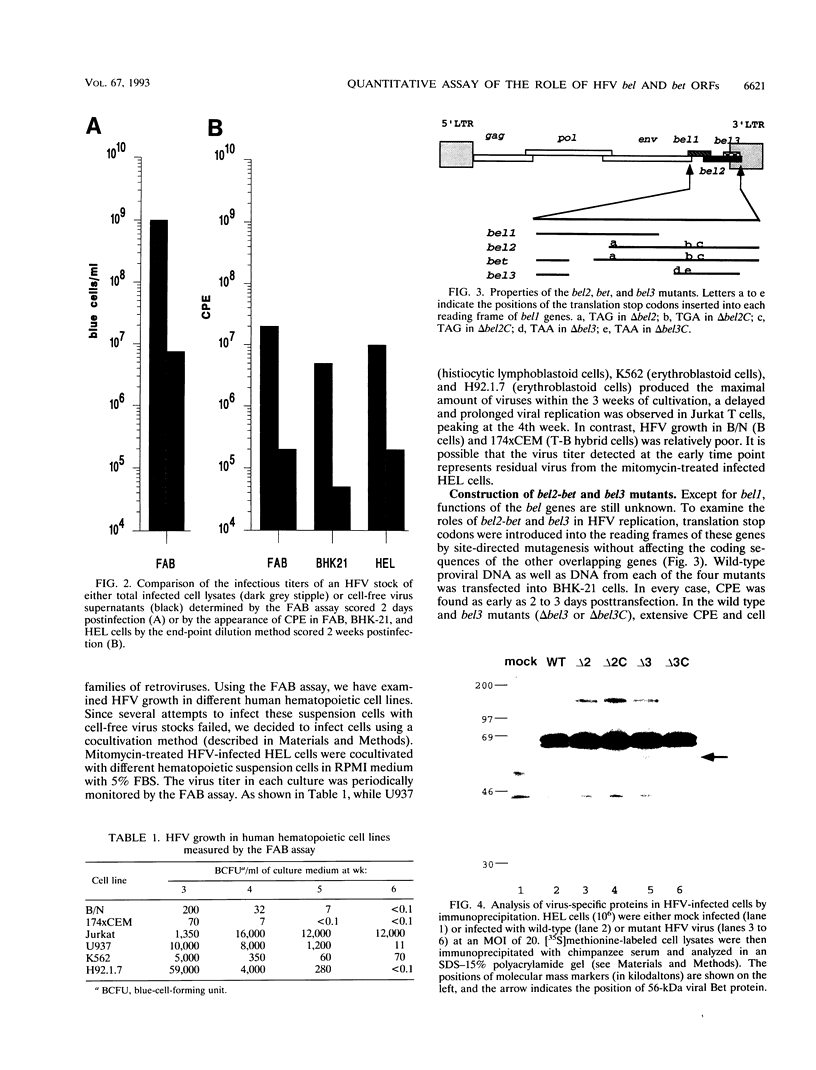
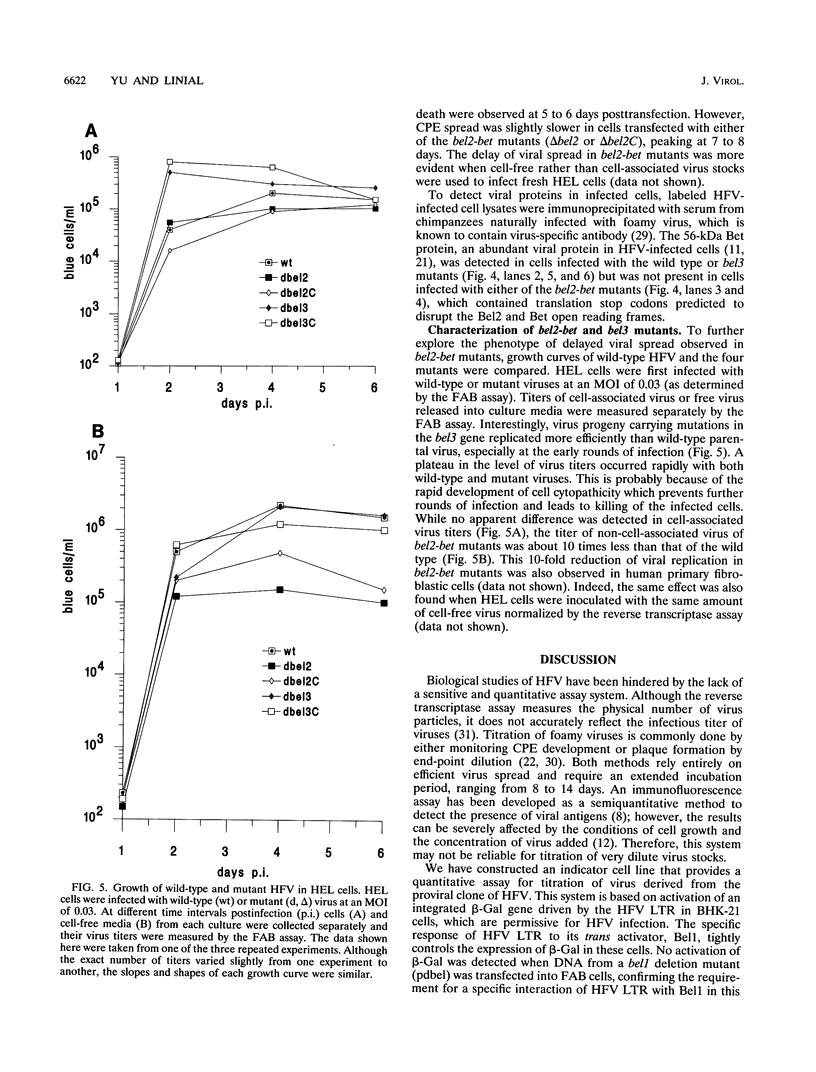
We have constructed a BHK-21-derived indicator cell line containing a single integrated copy of the beta-galactosidase (beta-Gal) gene under control of the human foamy virus (HFV) long terminal repeat promoter (from -533 to +20). These foamy virus-activated beta-Gal expression (FAB) cells can be used in a quantitative assay to measure the infectious titer of HFV. Our results show that the FAB assay is 50 times more sensitive than determination of the virus titer by the end-point dilution method. Using the FAB assay, we have found that HFV can productively replicate in several erythroblastoid cell lines as well as in the Jurkat T-cell line. We have also examined the roles of bel2, bet, and bel3 in viral replication by constructing proviral HFV clones in which the reading frame of Bel2, Bet, or Bel3 is disrupted by placement of translation stop codons. Analysis of these mutants reveals that while the bel3 gene is not required for viral replication in vitro, mutations in the bel2 or bet gene decrease cell-free viral transmission approximately 10-fold.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achong B. G., Mansell P. W., Epstein M. A., Clifford P. An unusual virus in cultures from a human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Feb;46(2):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguzzi A., Bothe K., Anhauser I., Horak I., Rethwilm A., Wagner E. F. Expression of human foamy virus is differentially regulated during development in transgenic mice. New Biol. 1992 Mar;4(3):225–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguzzi A., Wagner E. F., Netzer K. O., Bothe K., Anhauser I., Rethwilm A. Human foamy virus proteins accumulate in neurons and induce multinucleated giant cells in the brain of transgenic mice. Am J Pathol. 1993 Apr;142(4):1061–1071. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronoff R., Linial M. Specificity of retroviral RNA packaging. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):71–80. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.71-80.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothe K., Aguzzi A., Lassmann H., Rethwilm A., Horak I. Progressive encephalopathy and myopathy in transgenic mice expressing human foamy virus genes. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):555–557. doi: 10.1126/science.1650034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Ensoli B., Ivanoff L., Chamberlain M., Petteway S., Ratner L., Gallo R. C., Wong-Staal F. The sor gene of HIV-1 is required for efficient virus transmission in vitro. Science. 1987 Aug 21;237(4817):888–893. doi: 10.1126/science.3497453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming W. A., Clarke J. K. Fluorescence assay of foamy virus. J Gen Virol. 1970 Feb;6(2):277–284. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-6-2-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Rethwilm A., Maurer B., Darai G. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the env gene and its flanking regions of the human spumaretrovirus reveals two novel genes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2077–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M. Spumaviruses: a group of complex retroviruses. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(8):739–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giron M. L., Rozain F., Debons-Guillemin M. C., Canivet M., Peries J., Emanoil-Ravier R. Human foamy virus polypeptides: identification of env and bel gene products. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3596–3600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3596-3600.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould E. A., Hartley J. Factors affecting the growth and titration by immunofluorescence of simian foamy virus. Arch Virol. 1979;62(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF01314904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy B., Geist M., Dott K., Spehner D., Kieny M. P., Lecocq J. P. A specific inhibitor of cysteine proteases impairs a Vif-dependent modification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Env protein. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1325–1331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1325-1331.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooks J. J., Gibbs C. J., Jr The foamy viruses. Bacteriol Rev. 1975 Sep;39(3):169–185. doi: 10.1128/br.39.3.169-185.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A., Garrett E. D., Cullen B. R. The Bel-1 protein of human foamy virus activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gene expression via a novel DNA target site. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3946–3949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3946-3949.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller A., Partin K. M., Löchelt M., Bannert H., Flügel R. M., Cullen B. R. Characterization of the transcriptional trans activator of human foamy retrovirus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2589–2594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2589-2594.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimpton J., Emerman M. Detection of replication-competent and pseudotyped human immunodeficiency virus with a sensitive cell line on the basis of activation of an integrated beta-galactosidase gene. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2232–2239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2232-2239.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagaye S., Vexiau P., Morozov V., Guénebaut-Claudet V., Tobaly-Tapiero J., Canivet M., Cathelineau G., Périès J., Emanoil-Ravier R. Human spumaretrovirus-related sequences in the DNA of leukocytes from patients with Graves disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10070–10074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. H., Lee K. J., Kim S., Sung Y. C. Transactivation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat-directed gene expression by the human foamy virus bel1 protein requires a specific DNA sequence. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3236–3240. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3236-3240.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh P. C., Achong B. C., Epstein M. A. Further biological properties of the human syncytial virus. Intervirology. 1977;8(4):204–217. doi: 10.1159/000148896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh P. C., Ang K. S. Replication of human syncytium-forming virus in human cells: effect of certain biological factors and selective chemicals. J Med Virol. 1981;7(1):67–73. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890070108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh P. C., Matsuura F. M. Human spumavirus replication in human cells. J Med Virol. 1984;14(3):247–254. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890140308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löchelt M., Zentgraf H., Flügel R. M. Construction of an infectious DNA clone of the full-length human spumaretrovirus genome and mutagenesis of the bel 1 gene. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90820-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Bannert H., Darai G., Flügel R. M. Analysis of the primary structure of the long terminal repeat and the gag and pol genes of the human spumaretrovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1590-1597.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Flügel R. M. The 3'-orf protein of human immunodeficiency virus 2 shows sequence homology with the bel3 gene of the human spumaretrovirus. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):286–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Serfling E., ter Meulen V., Rethwilm A. Transcription factor AP-1 modulates the activity of the human foamy virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6353–6357. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6353-6357.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muranyi W., Flügel R. M. Analysis of splicing patterns of human spumaretrovirus by polymerase chain reaction reveals complex RNA structures. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):727–735. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.727-735.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Netzer K. O., Rethwilm A., Maurer B., ter Meulen V. Identification of the major immunogenic structural proteins of human foamy virus. J Gen Virol. 1990 May;71(Pt 5):1237–1241. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-5-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. P., Todaro G. J. Biological properties of syncytium-forming ("foamy") viruses. Virology. 1972 Mar;47(3):673–683. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90557-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. P., Todaro G. J., Scolnick E. M., Aaronson S. A. RNA dependent DNA polymerase in primate syncytium-forming (foamy) viruses. Nature. 1971 Jan 22;229(5282):258–260. doi: 10.1038/229258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Erlwein O., Baunach G., Maurer B., ter Meulen V. The transcriptional transactivator of human foamy virus maps to the bel 1 genomic region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):941–945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleiss M. R., Degnin C. R., Geballe A. P. Translational control of human cytomegalovirus gp48 expression. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6782–6789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6782-6789.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Daugherty D., Clouse K., Cohen D., Folks T., Martin M. A. The HIV 'A' (sor) gene product is essential for virus infectivity. Nature. 1987 Aug 20;328(6132):728–730. doi: 10.1038/328728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swack N. S., Hsiung G. D. Pathogenesis of simian foamy virus infection in natural and experimental hosts. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):470–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.470-474.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Theodorakis P. A., Chinnadurai G. Distinct cis-acting regions in U3 regulate trans-activation of the human spumaretrovirus long terminal repeat by the viral bel1 gene product. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3661–3666. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. A. Foamy retroviruses. A virus in search of a disease. Nature. 1988 Jun 9;333(6173):497–498. doi: 10.1038/333497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick G., Grubeck-Loebenstein B., Trieb K., Kalischnig G., Aguzzi A. Human foamy virus antigens in thyroid tissue of Graves' disease patients. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1992;99(1):153–156. doi: 10.1159/000236350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]