Abstract
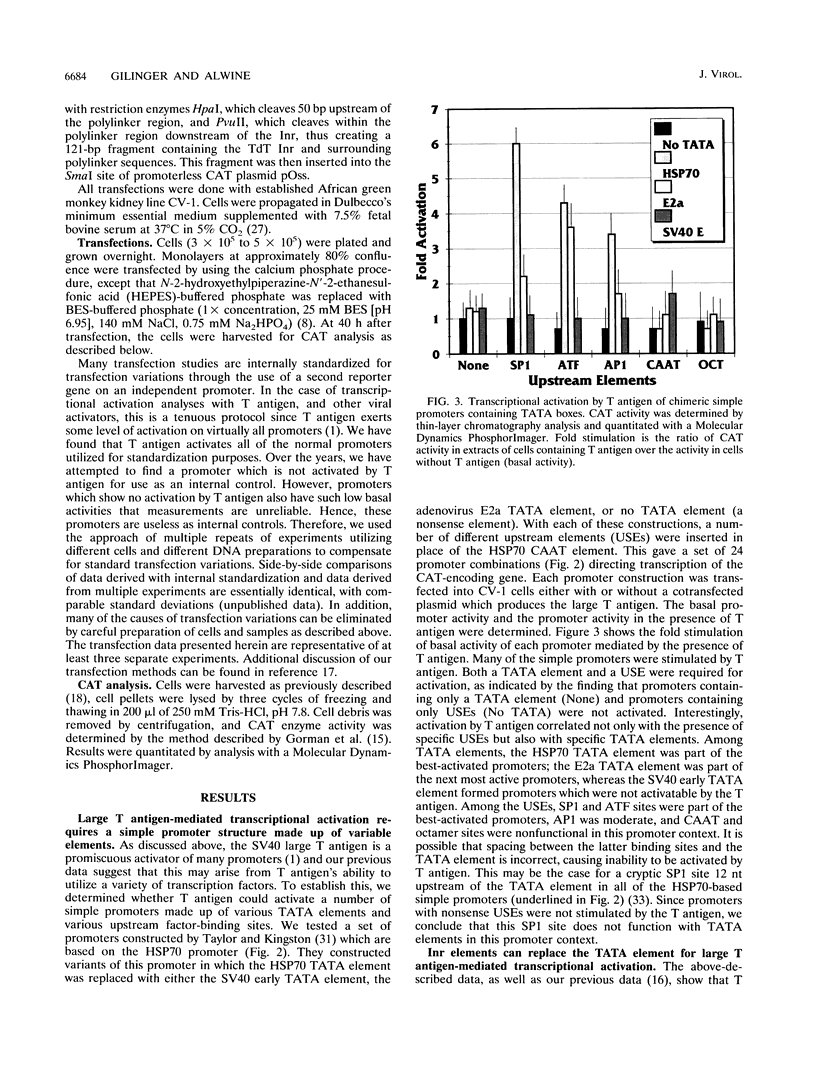
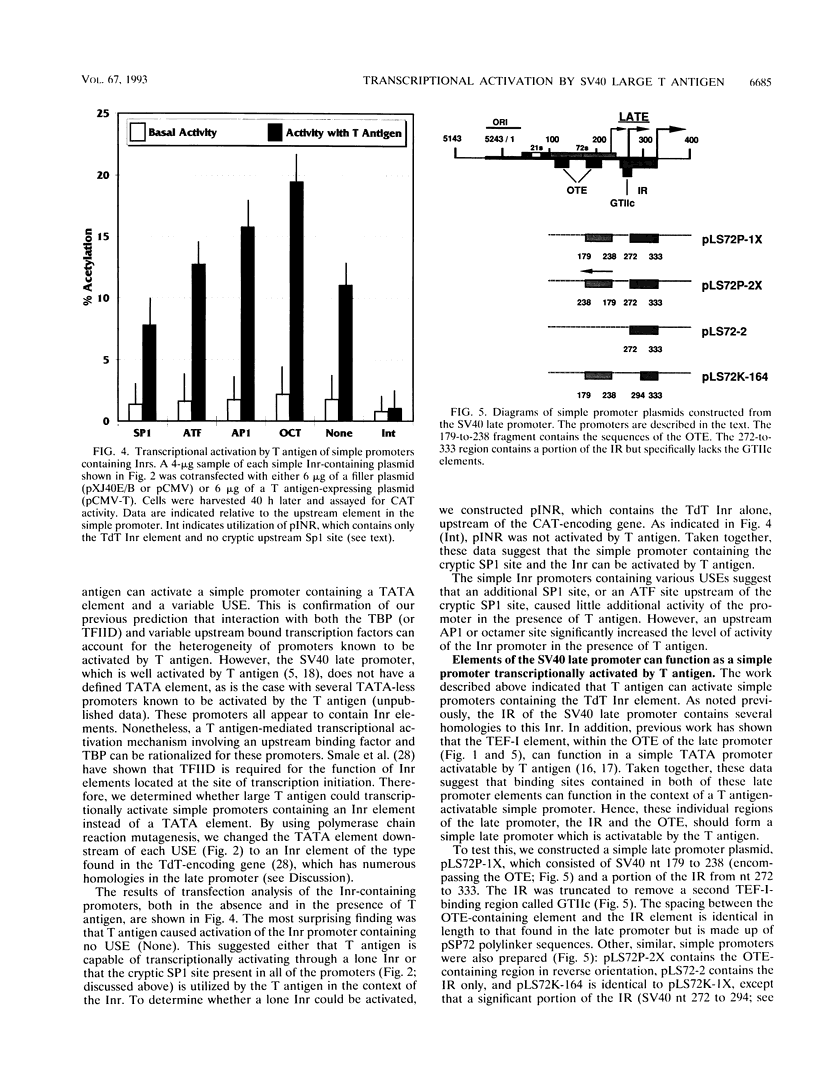
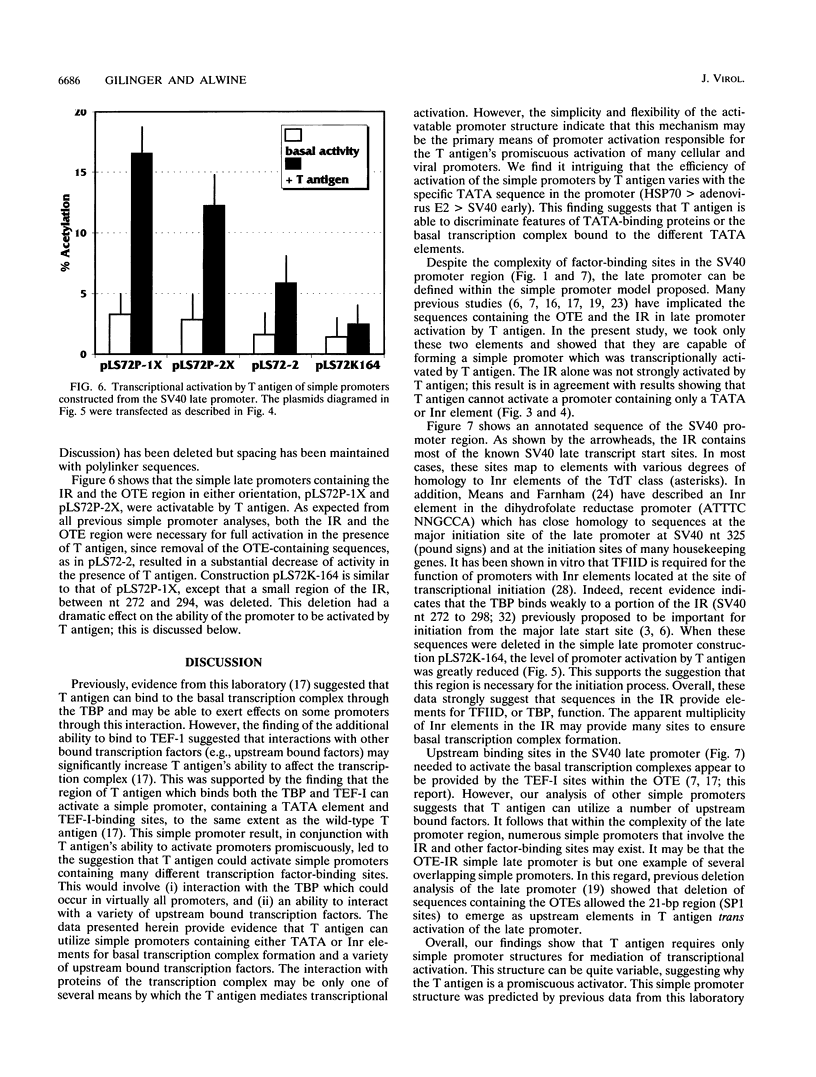
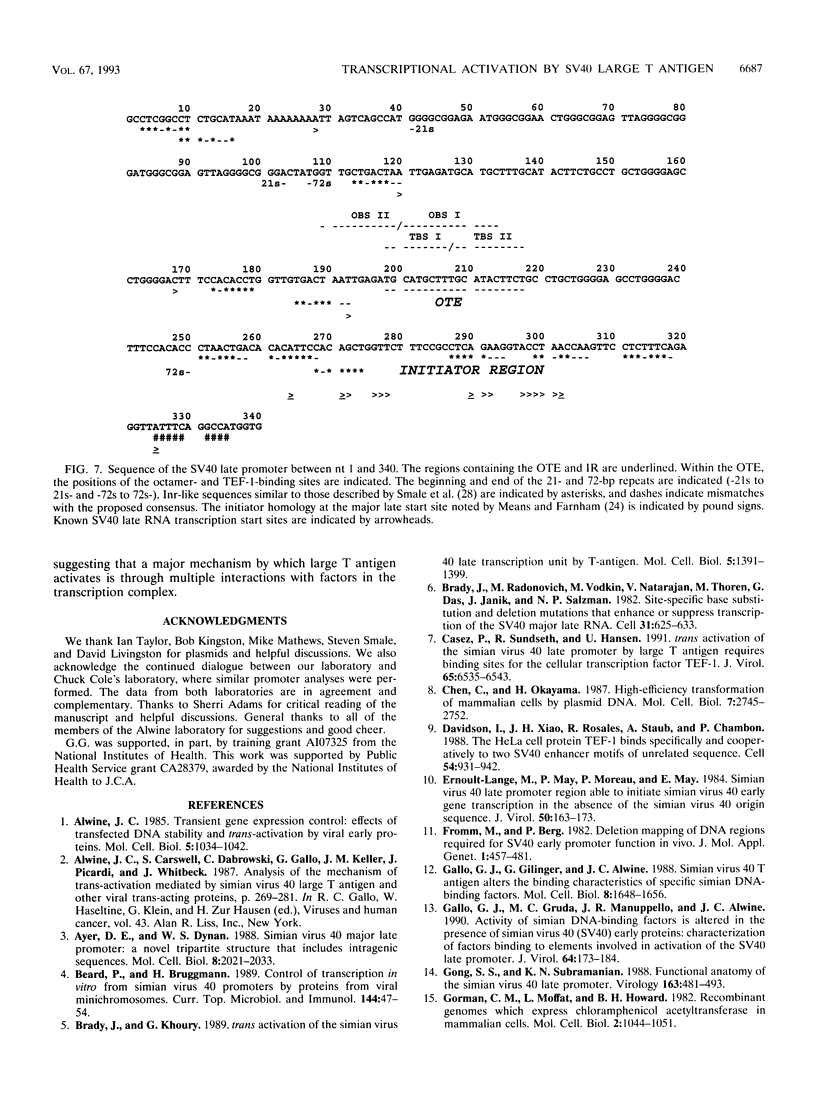
The simian virus 40 large T antigen is a promiscuous transcriptional activator of many viral and cellular promoters. We show that the promoter structure necessary for T antigen-mediated transcriptional activation is very simple. A TATA or initiator element is required, in addition to an upstream factor-binding site, which can be quite variable. We found that promoters containing an SP1-, ATF-, AP1-, or TEF-I-binding site, in conjunction with a TATA element, can all be activated in the presence of T antigen. In addition, preference for specific TATA elements was indicated. Promoters containing the HSP70 TATA element functioned better than those with the adenovirus E2 TATA element, while promoters containing the simian virus 40 (SV40) early TATA element failed to be activated. In addition, simple promoters containing the initiator element from the terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase gene could be activated by T antigen. The SV40 late promoter, a primary target for T antigen transcriptional activation, conforms to this simple promoter structure. The region from which most late transcripts initiate contains a cluster of initiator-like elements (SV40 nucleotides [nt] 250 to 335) forming an initiator region (IR). This lies downstream of the previously described octamer-TEF element (SV40 nt 199 to 218) which contains the TEF-I-binding sites shown to be necessary for T antigen-mediated transcriptional activation of the late promoter. We show that a simple late promoter made up of IR sequences and octamer-TEF element-containing sequences is transcriptionally activated by T antigen. These experiments also showed that specific sequences in the IR, SV40 nt 272 to 294, are particularly important for late promoter activation. Previous findings (M. C. Gruda, J. M. Zablotny, J. H. Xiao, I. Davidson, and J. C. Alwine, Mol. Cell. Biol. 13:961-969, 1993) suggested that T antigen could mediate transcriptional activation through interaction with the TATA-binding protein, as well as upstream bound transcription factors. Our present data are predicted by this model and suggest that at least one mechanism by which the T antigen manifests promiscuous transcriptional activation is its ability to interact with numerous transcription factors in a simple promoter context.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C. Transient gene expression control: effects of transfected DNA stability and trans-activation by viral early proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1034–1042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Dynan W. S. Simian virus 40 major late promoter: a novel tripartite structure that includes intragenic sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2021–2033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Bruggmann H. Control of transcription in vitro from simian virus 40 promoters by proteins from viral minichromosomes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;144:47–54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74578-2_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Khoury G. trans Activation of the simian virus 40 late transcription unit by T-antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1391–1399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Radonovich M., Vodkin M., Natarajan V., Thoren M., Das G., Janik J., Salzman N. P. Site-specific base substitution and deletion mutations that enhance or suppress transcription of the SV40 major late RNA. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):625–633. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90318-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casaz P., Sundseth R., Hansen U. trans activation of the simian virus 40 late promoter by large T antigen requires binding sites for the cellular transcription factor TEF-1. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6535–6543. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6535-6543.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I., Xiao J. H., Rosales R., Staub A., Chambon P. The HeLa cell protein TEF-1 binds specifically and cooperatively to two SV40 enhancer motifs of unrelated sequence. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):931–942. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernoult-Lange M., May P., Moreau P., May E. Simian virus 40 late promoter region able to initiate simian virus 40 early gene transcription in the absence of the simian virus 40 origin sequence. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):163–173. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.163-173.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. J., Gilinger G., Alwine J. C. Simian virus 40 T antigen alters the binding characteristics of specific simian DNA-binding factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1648–1656. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo G. J., Gruda M. C., Manuppello J. R., Alwine J. C. Activity of simian DNA-binding factors is altered in the presence of simian virus 40 (SV40) early proteins: characterization of factors binding to elements involved in activation of the SV40 late promoter. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):173–184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.173-184.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong S. S., Subramanian K. N. Functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 late promoter. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):481–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90289-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruda M. C., Alwine J. C. Simian virus 40 (SV40) T-antigen transcriptional activation mediated through the Oct/SPH region of the SV40 late promoter. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3553–3558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3553-3558.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruda M. C., Zabolotny J. M., Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Alwine J. C. Transcriptional activation by simian virus 40 large T antigen: interactions with multiple components of the transcription complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):961–969. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Analysis of an activatable promoter: sequences in the simian virus 40 late promoter required for T-antigen-mediated trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1859–1869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Heath C., Bertuch A., Hansen U. Specific stimulation of simian virus 40 late transcription in vitro by a cellular factor binding the simian virus 40 21-base-pair repeat promoter element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6025–6029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M., Bradley M. K. The simian virus 40 large T antigen. A lot packed into a little. Mol Biol Med. 1987 Apr;4(2):63–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May E., Omilli F., Ernoult-Lange M., Zenke M., Chambon P. The sequence motifs that are involved in SV40 enhancer function also control SV40 late promoter activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2445–2461. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Farnham P. J. Transcription initiation from the dihydrofolate reductase promoter is positioned by HIP1 binding at the initiation site. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):653–661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omilli F., Ernoult-Lange M., Borde J., May E. Sequences involved in initiation of simian virus 40 late transcription in the absence of T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1875–1885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatak M., Subramanian K. N., Roy P., Weissman S. M. Late messenger RNA production by viable simian virus 40 mutants with deletions in the leader region. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 15;153(3):589–618. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90409-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Schmidt M. C., Berk A. J., Baltimore D. Transcriptional activation by Sp1 as directed through TATA or initiator: specific requirement for mammalian transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somasekhar M. B., Mertz J. E. Sequences involved in determining the locations of the 5' ends of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):1002–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.1002-1013.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. E1a transactivation of human HSP70 gene promoter substitution mutants is independent of the composition of upstream and TATA elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):176–183. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley S. R., Kraus R. J., Mertz J. E. Functional binding of the "TATA" box binding component of transcription factor TFIID to the -30 region of TATA-less promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5814–5818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Berk A. Constraints on spacing between transcription factor binding sites in a simple adenovirus promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):403–411. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Liu J. K., DiPersio C. M. Site-directed mutagenesis reveals a liver transcription factor essential for the albumin transcriptional enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. Y., Rice P. W., Chamberlain M., Cole C. N. Mapping the transcriptional transactivation function of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2778–2790. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2778-2790.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


