Abstract
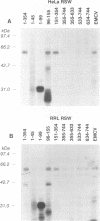
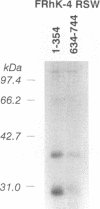
The 5' nontranslated region (5'NTR) of hepatitis A virus (HAV) RNA contains structural elements which facilitate 5' cap-independent initiation of virus translation and are likely to interact with cellular proteins functioning as translation initiation factors. To define these interactions, we characterized the binding of ribosome-associated proteins from several cell types to synthetic RNAs representing segments of the 5'NTR by using a UV cross-linking/label transfer assay. Four major proteins (p30, p39, p57, and p110) were identified. p30 and p39 were present in ribosomal salt washes prepared only from HAV-permissive BS-C-1 and FRhK-4 cells, while p57 was found only in HeLa cells and rabbit reticulocyte lysates. p110 was present in all cell types. Both p30 and p39 bound to multiple sites within the 5'NTR. Efficient transfer of label to p30 occurred with minimal RNA probes representing nucleotides (nt) 96 to 155, 151 to 354, and, to a much lesser extent, 634 to 744, while label transfer to p39 occurred with probes representing nt 96 to 155 and 634 to 744. All of these probes represent regions of the 5'NTR which are rich in pyrimidines. Competitive inhibition studies indicated that both p30 and p39 bound with greater affinity to sites in the 5' half of the NTR (a probe representing nt 1 to 354) than to the more 3' site (nt 634 to 744). Binding of p39 to the probe representing nt 96 to 155 was inhibited in the presence of an equal amount of proteins derived from HeLa cells, suggesting that p39 shares binding site specificity with one or more HeLa cell proteins. A 57-kDa protein in HeLa cell protein extracts reacted with antibody to polypyrimidine tract-binding protein in immunoblots, but no immunoreactive protein was identified in a similar BS-C-1 protein fraction. These results demonstrate that ribosome-associated proteins which bind to the 5'NTR of HAV vary substantially among different mammalian cell types, possibly accounting for differences in the extent to which individual cell types support growth of the virus. Mutations in the 5'NTR which enhance the growth of HAV in certain cell types may reflect specific adaptive responses to these or other proteins.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agol V. I. The 5'-untranslated region of picornaviral genomes. Adv Virus Res. 1991;40:103–180. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60278-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alsaadi S., Hassard S., Stanway G. Sequences in the 5' non-coding region of human rhinovirus 14 RNA that affect in vitro translation. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2799–2804. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andino R., Rieckhof G. E., Baltimore D. A functional ribonucleoprotein complex forms around the 5' end of poliovirus RNA. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):369–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90170-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borovjagin A. V., Ezrokhi M. V., Rostapshov V. M., Ugarova TYu, Bystrova T. F., Shatsky I. N. RNA--protein interactions within the internal translation initiation region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4999–5005. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bothwell A. L., Ballard D. W., Philbrick W. M., Lindwall G., Maher S. E., Bridgett M. M., Jamison S. F., Garcia-Blanco M. A. Murine polypyrimidine tract binding protein. Purification, cloning, and mapping of the RNA binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 25;266(36):24657–24663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Ehrenfeld E. Translation of poliovirus RNA in vitro: changes in cleavage pattern and initiation sites by ribosomal salt wash. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90350-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. A., Day S. P., Jansen R. W., Lemon S. M. The 5' nontranslated region of hepatitis A virus RNA: secondary structure and elements required for translation in vitro. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5828–5838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5828-5838.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Ticehurst J. R., Purcell R. H., Buckler-White A., Baroudy B. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of wild-type hepatitis A virus: comparison with different strains of hepatitis A virus and other picornaviruses. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):50–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.50-59.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulepis A. G., Tannock G. A., Locarnini S. A., Gust I. D. Evidence that the genome of hepatitis A virus consists of single-stranded RNA. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):473–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.473-477.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day S. P., Murphy P., Brown E. A., Lemon S. M. Mutations within the 5' nontranslated region of hepatitis A virus RNA which enhance replication in BS-C-1 cells. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6533–6540. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6533-6540.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Semler B. L., Jackson R. J., Hanecak R., Duprey E., Wimmer E. In vitro translation of poliovirus RNA: utilization of internal initiation sites in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):507–514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.507-514.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Blanco M. A., Jamison S. F., Sharp P. A. Identification and purification of a 62,000-dalton protein that binds specifically to the polypyrimidine tract of introns. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1874–1886. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebhard J. R., Ehrenfeld E. Specific interactions of HeLa cell proteins with proposed translation domains of the poliovirus 5' noncoding region. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3101–3109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3101-3109.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellen C. U., Witherell G. W., Schmid M., Shin S. H., Pestova T. V., Gil A., Wimmer E. A cytoplasmic 57-kDa protein that is required for translation of picornavirus RNA by internal ribosomal entry is identical to the nuclear pyrimidine tract-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7642–7646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Howell M. T., Kaminski A. The novel mechanism of initiation of picornavirus RNA translation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90302-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Davies M. V., Kaufman R. J., Wimmer E. Initiation of protein synthesis by internal entry of ribosomes into the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1651–1660. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1651-1660.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Duke G. M., Palmenberg A. C., Wimmer E. A segment of the 5' nontranslated region of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA directs internal entry of ribosomes during in vitro translation. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2636–2643. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2636-2643.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: structural elements of the internal ribosomal entry site and involvement of a cellular 57-kD RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1560–1572. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen R. W., Newbold J. E., Lemon S. M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a cell culture-adapted variant of hepatitis A virus: comparison with wild-type virus with restricted capacity for in vitro replication. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90270-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn R., Luz N., Beck E. Functional analysis of the internal translation initiation site of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4625–4631. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4625-4631.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Monica N., Racaniello V. R. Differences in replication of attenuated and neurovirulent polioviruses in human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2357–2360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2357-2360.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Menke J. G., Martin-Gallardo A., Hughes J. V., Young A., Mitra S. W. Molecular cloning and partial sequencing of hepatitis A viral cDNA. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):247–255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.247-255.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luz N., Beck E. Interaction of a cellular 57-kilodalton protein with the internal translation initiation site of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6486–6494. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6486-6494.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch K., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. A cellular protein that binds to the 5'-noncoding region of poliovirus RNA: implications for internal translation initiation. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1026–1034. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch K., Svitkin Y. V., Lee H. S., Lejbkowicz F., Kenan D. J., Chan E. K., Agol V. I., Keene J. D., Sonenberg N. La autoantigen enhances and corrects aberrant translation of poliovirus RNA in reticulocyte lysate. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3798–3807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3798-3807.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najarian R., Caput D., Gee W., Potter S. J., Renard A., Merryweather J., Van Nest G., Dina D. Primary structure and gene organization of human hepatitis A virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2627–2631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul A. V., Tada H., von der Helm K., Wissel T., Kiehn R., Wimmer E., Deinhardt F. The entire nucleotide sequence of the genome of human hepatitis A virus (isolate MBB). Virus Res. 1987 Aug;8(2):153–171. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Flynn M. E., Kaplan G., Racaniello V., Sonenberg N. Mutational analysis of upstream AUG codons of poliovirus RNA. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4486–4492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4486-4492.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Internal initiation of translation of eukaryotic mRNA directed by a sequence derived from poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):320–325. doi: 10.1038/334320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestova T. V., Hellen C. U., Wimmer E. Translation of poliovirus RNA: role of an essential cis-acting oligopyrimidine element within the 5' nontranslated region and involvement of a cellular 57-kilodalton protein. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6194–6204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6194-6204.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilipenko E. V., Gmyl A. P., Maslova S. V., Svitkin Y. V., Sinyakov A. N., Agol V. I. Prokaryotic-like cis elements in the cap-independent internal initiation of translation on picornavirus RNA. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90211-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscigno R. F., Weiner M., Garcia-Blanco M. A. A mutational analysis of the polypyrimidine tract of introns. Effects of sequence differences in pyrimidine tracts on splicing. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11222–11229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Lemon S. M. Recent advances in hepatitis A vaccine development. Virus Res. 1990 Oct;17(2):75–92. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90070-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodley C. L., Chen Y. C., Gupta N. K. Purification and properties of the peptide chain initiation factors from rabbit reticulocytes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:141–153. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30017-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Angel R. M., Papavassiliou A. G., Fernández-Tomás C., Silverstein S. J., Racaniello V. R. Cell proteins bind to multiple sites within the 5' untranslated region of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8299–8303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]