Abstract
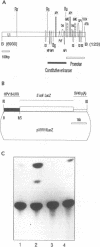
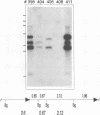
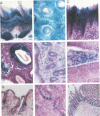
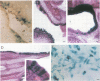
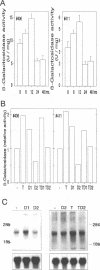
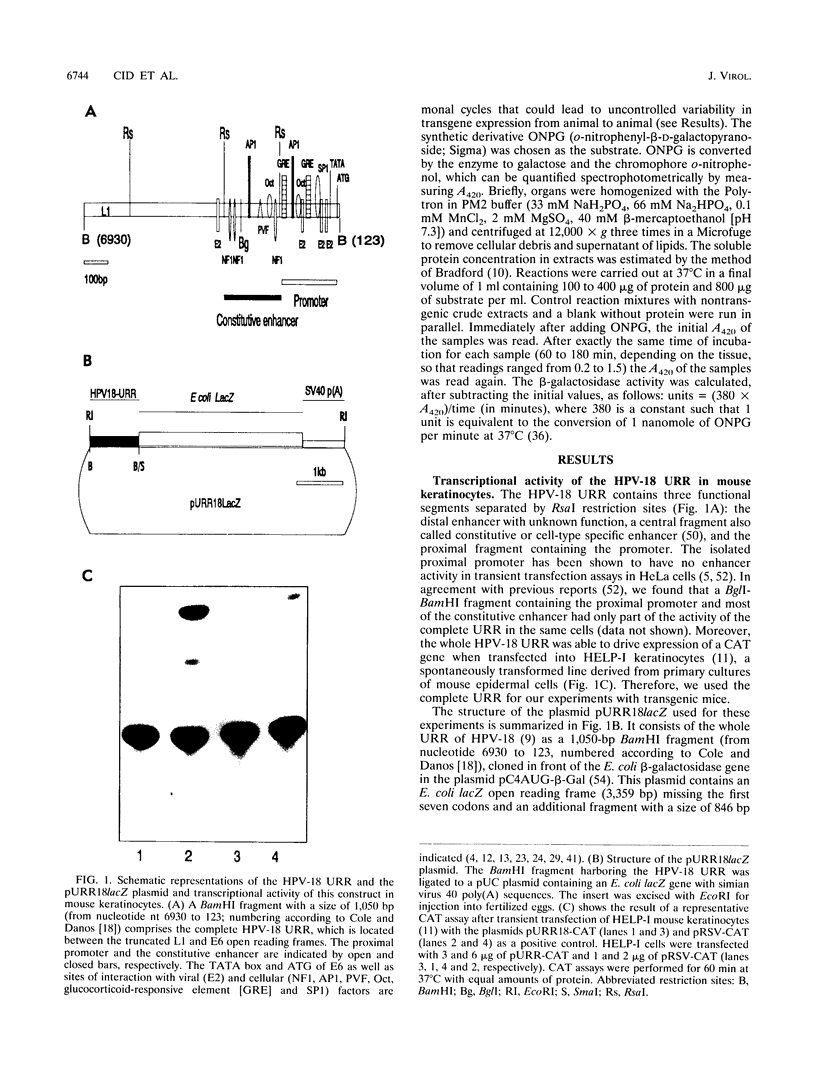
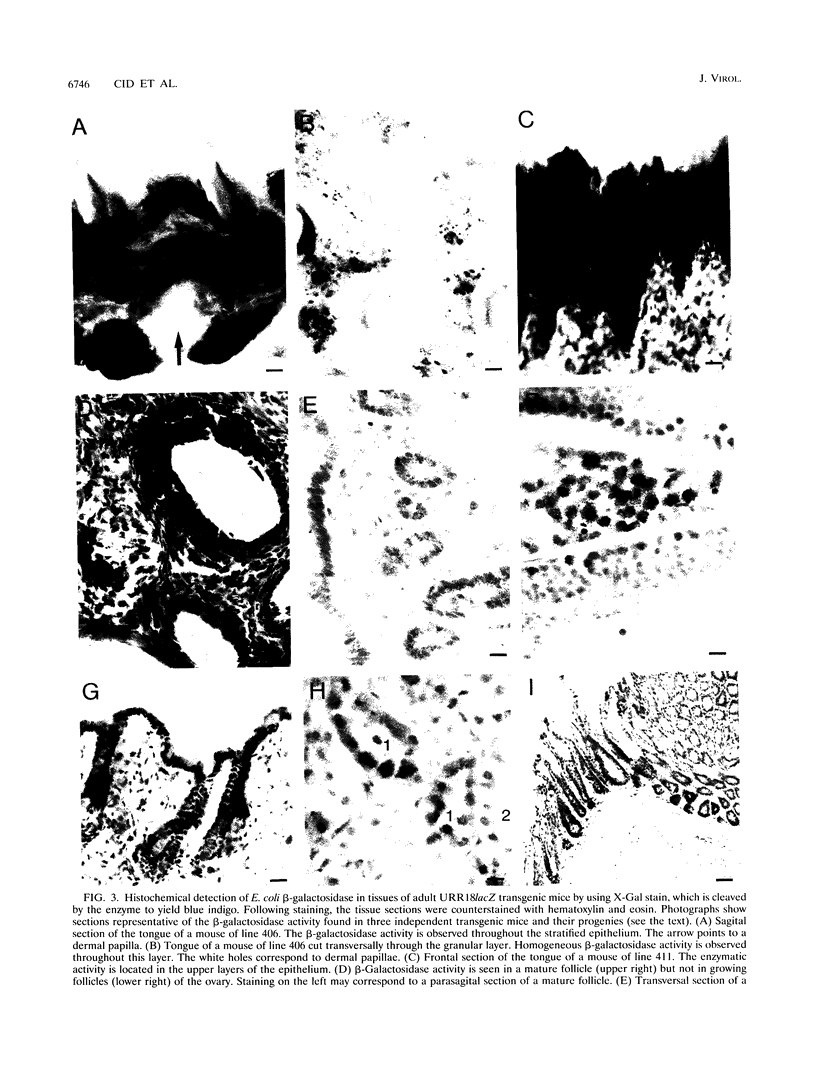
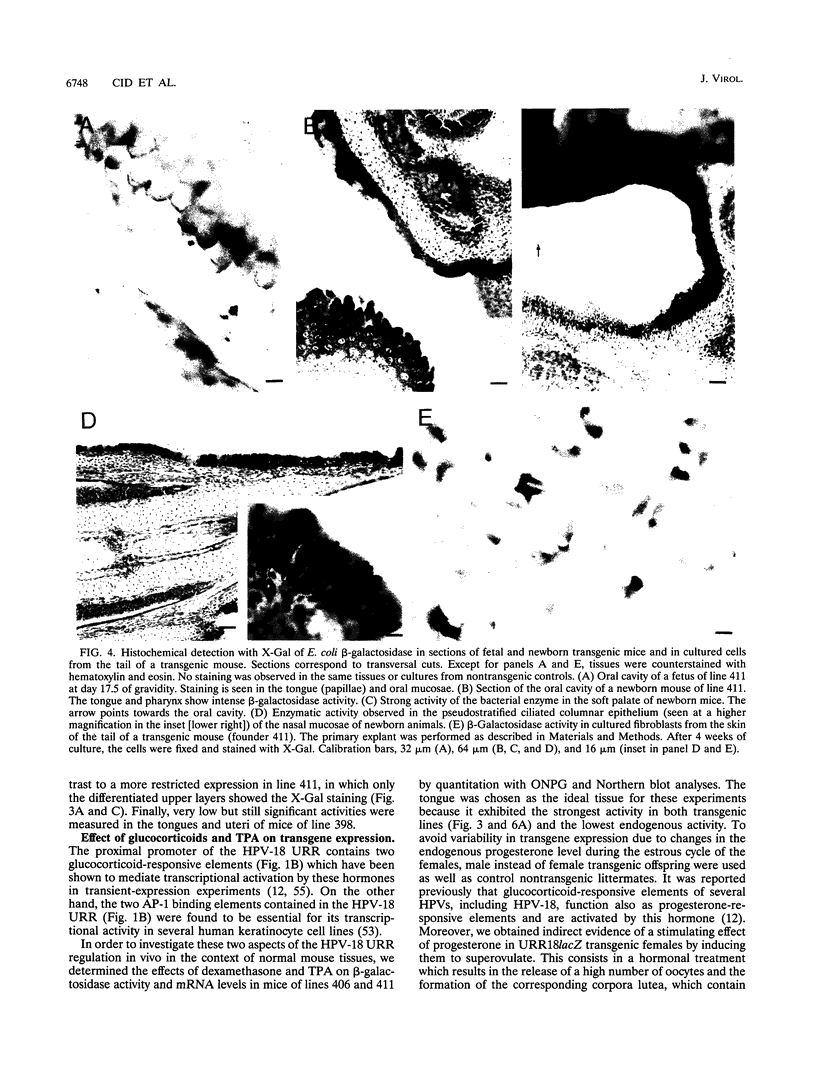
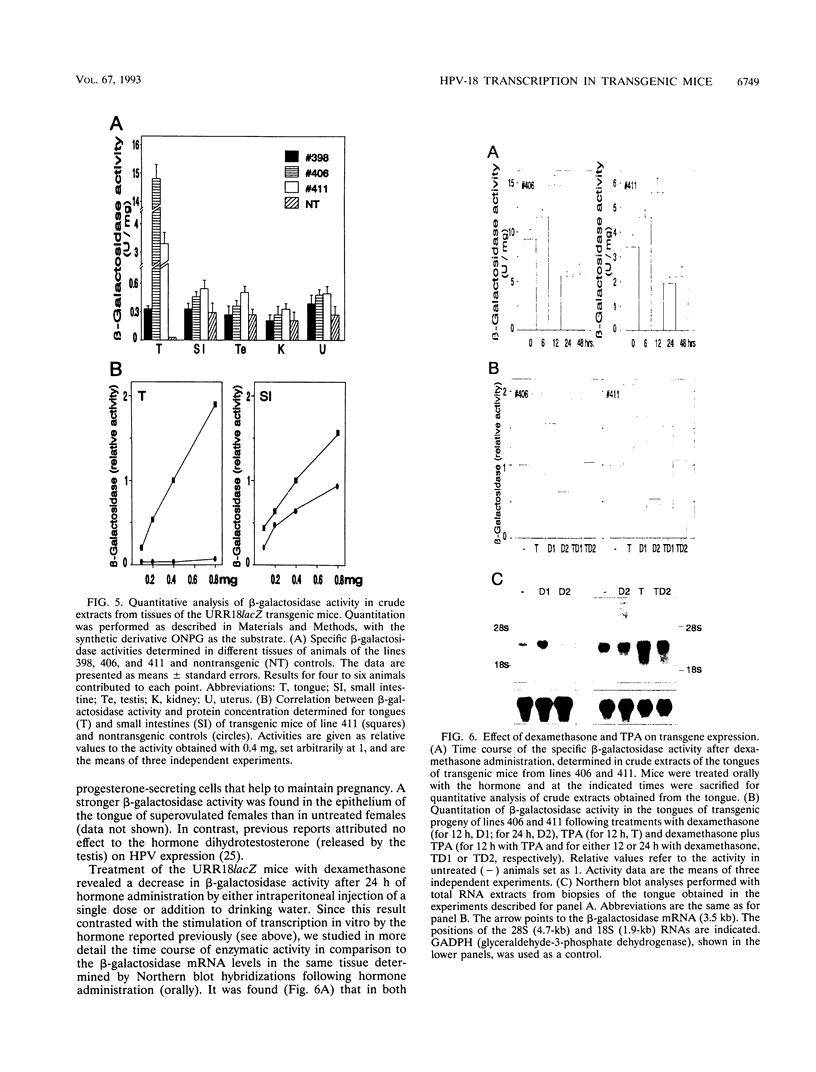
The upstream regulatory region (URR) of human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV-18) harbors transcriptional promoter and enhancer elements which are thought to determine the cell-type specificity of the virus. In order to study the regulation of HPV-18 expression in vivo, we constructed transgenic mice carrying the bacterial lacZ gene under the control of the HPV-18 URR. Analysis of beta-galactosidase activity by histochemical staining of tissue sections of four independent transgenic mice showed that the viral promoter was specifically active in epithelial cells within a variety of organs (e.g., tongue, ovary, uterus, testis, and small intestine). Very strong staining was observed in newborn transgenic mice in contrast to a weak activity found during fetal life. Determination of beta-galactosidase activity in crude extracts from tissues of three lines of transgenic mice proved to be a useful tool for a quantitative analysis of transgene expression. In mice from two different transgenic lines treated with dexamethasone such measurements revealed a biphasic effect of the hormone on the activity of the enzyme in the stratified epithelium of the tongue (transient increase followed by a decrease). Northern (RNA) blot analysis showed similar changes in beta-galactosidase mRNA in that tissue. Treatment with tetradecanoyl phorbol acetate (TPA) led to a twofold increase in both enzymatic activity and mRNA levels. Finally, combined treatments with dexamethasone and TPA showed that both factors interfered with each other in their respective effects on transgene expression, suggesting that a cross-talk mechanism between transcription factors could be involved in the regulation of the HPV-18 URR.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch D., Boye B., Baust C., zur Hausen H., Schwarz E. Retinoic acid-mediated repression of human papillomavirus 18 transcription and different ligand regulation of the retinoic acid receptor beta gene in non-tumorigenic and tumorigenic HeLa hybrid cells. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2283–2291. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauknecht T., Angel P., Royer H. D., zur Hausen H. Identification of a negative regulatory domain in the human papillomavirus type 18 promoter: interaction with the transcriptional repressor YY1. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4607–4617. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A. Identification of human papillomavirus type 18 transforming genes in immortalized and primary cells. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1247–1255. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1247-1255.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedell M. A., Jones K. H., Laimins L. A. The E6-E7 region of human papillomavirus type 18 is sufficient for transformation of NIH 3T3 and rat-1 cells. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3635–3640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3635-3640.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard B. A., Bailly C., Lenoir M. C., Darmon M., Thierry F., Yaniv M. The human papillomavirus type 18 (HPV18) E2 gene product is a repressor of the HPV18 regulatory region in human keratinocytes. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4317–4324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4317-4324.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshart M., Gissmann L., Ikenberg H., Kleinheinz A., Scheurlen W., zur Hausen H. A new type of papillomavirus DNA, its presence in genital cancer biopsies and in cell lines derived from cervical cancer. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1151–1157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01944.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitkreutz D., Hornung J., Pöhlmann J., Brown-Bierman L., Bohnert A., Bowden P. E., Fusenig N. E. Environmental induction of differentiation-specific keratins in malignant mouse keratinocyte lines. Eur J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;42(2):255–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. K., Klock G., Bernard H. U. Progesterone and glucocorticoid response elements occur in the long control regions of several human papillomaviruses involved in anogenital neoplasia. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3261–3269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3261-3269.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong T., Chan W. K., Bernard H. U. Transcriptional activation of human papillomavirus 16 by nuclear factor I, AP1, steroid receptors and a possibly novel transcription factor, PVF: a model for the composition of genital papillomavirus enhancers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):465–470. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. B., Chong K. Y., Liew L. N., Hsu H. C., Cheng W. T. Unregulated and basal transcriptional activities of the regulatory sequence of the type 18 human papillomavirus genome in transgenic mice. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):378–383. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90769-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Zullo J., Verma I. M., Stiles C. D. Expression of the c-fos gene and of an fos-related gene is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1080–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6093261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. fra-1: a serum-inducible, cellular immediate-early gene that encodes a fos-related antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2063–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook T., Storey A., Almond N., Osborn K., Crawford L. Human papillomavirus type 16 cooperates with activated ras and fos oncogenes in the hormone-dependent transformation of primary mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8820–8824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Carranca A., Thierry F., Yaniv M. Interplay of viral and cellular proteins along the long control region of human papillomavirus type 18. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4321–4330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4321-4330.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Bernard H. U., Seedorf K., Klock G. The upstream regulatory region of the human papilloma virus-16 contains an E2 protein-independent enhancer which is specific for cervical carcinoma cells and regulated by glucocorticoid hormones. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3735–3743. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Bernard H. U. The E6/E7 promoter of human papillomavirus type 16 is activated in the absence of E2 proteins by a sequence-aberrant Sp1 distal element. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5577–5584. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5577-5584.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe-Seyler F., Butz K., zur Hausen H. Repression of the human papillomavirus type 18 enhancer by the cellular transcription factor Oct-1. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5613–5618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5613-5618.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonat C., Rahmsdorf H. J., Park K. K., Cato A. C., Gebel S., Ponta H., Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey M., Alpert S., Hanahan D. Bovine papillomavirus genome elicits skin tumours in transgenic mice. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):609–612. doi: 10.1038/322609a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T., Simon J. A., Sutton C. A. New heat shock puffs and beta-galactosidase activity resulting from transformation of Drosophila with an hsp70-lacZ hybrid gene. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):403–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack D. H., Laimins L. A. A keratinocyte-specific transcription factor, KRF-1, interacts with AP-1 to activate expression of human papillomavirus type 18 in squamous epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9102–9106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton P. A., Coffin J. M. Bacterial beta-galactosidase as a marker of Rous sarcoma virus gene expression and replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):281–290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piette J., Hirai S., Yaniv M. Constitutive synthesis of activator protein 1 transcription factor after viral transformation of mouse fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3401–3405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Turner D., Cepko C. Lineage analysis in the vertebrate nervous system by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razin A., Cedar H. DNA methylation and gene expression. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):451–458. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.451-458.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer H. D., Freyaldenhoven M. P., Napierski I., Spitkovsky D. D., Bauknecht T., Dathan N. Delineation of human papillomavirus type 18 enhancer binding proteins: the intracellular distribution of a novel octamer binding protein p92 is cell cycle regulated. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2363–2371. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rösl F., Arab A., Klevenz B., zur Hausen H. The effect of DNA methylation on gene regulation of human papillomaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1993 May;74(Pt 5):791–801. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-5-791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanes J. R., Rubenstein J. L., Nicolas J. F. Use of a recombinant retrovirus to study post-implantation cell lineage in mouse embryos. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3133–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Gädicke A., Schwarz E. Different human cervical carcinoma cell lines show similar transcription patterns of human papillomavirus type 18 early genes. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2285–2292. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Evans R. M. Cross-coupling of signal transduction pathways: zinc finger meets leucine zipper. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90259-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Yang N., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Functional antagonism between oncoprotein c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1217–1226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90397-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler M. H., Rhodes C. R., Whitbeck A., Wolinsky S. M., Chow L. T., Broker T. R. Human papillomavirus type 16 and 18 gene expression in cervical neoplasias. Hum Pathol. 1992 Feb;23(2):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(92)90232-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift F. V., Bhat K., Younghusband H. B., Hamada H. Characterization of a cell type-specific enhancer found in the human papilloma virus type 18 genome. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1339–1344. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Bird A. Alternative chromatin structure at CpG islands. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90339-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thierry F., Spyrou G., Yaniv M., Howley P. Two AP1 sites binding JunB are essential for human papillomavirus type 18 transcription in keratinocytes. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3740–3748. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3740-3748.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang-Yen H. F., Chambard J. C., Sun Y. L., Smeal T., Schmidt T. J., Drouin J., Karin M. Transcriptional interference between c-Jun and the glucocorticoid receptor: mutual inhibition of DNA binding due to direct protein-protein interaction. Cell. 1990 Sep 21;62(6):1205–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90396-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers E. M. Heterogeneity of the human papillomavirus group. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4898–4903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4898-4903.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Knebel Doeberitz M., Bauknecht T., Bartsch D., zur Hausen H. Influence of chromosomal integration on glucocorticoid-regulated transcription of growth-stimulating papillomavirus genes E6 and E7 in cervical carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1411–1415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Intracellular surveillance of persisting viral infections. Human genital cancer results from deficient cellular control of papillomavirus gene expression. Lancet. 1986 Aug 30;2(8505):489–491. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen H. Viruses in human cancers. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1167–1173. doi: 10.1126/science.1659743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]