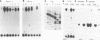Abstract
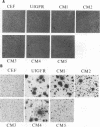
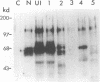
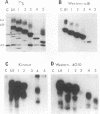
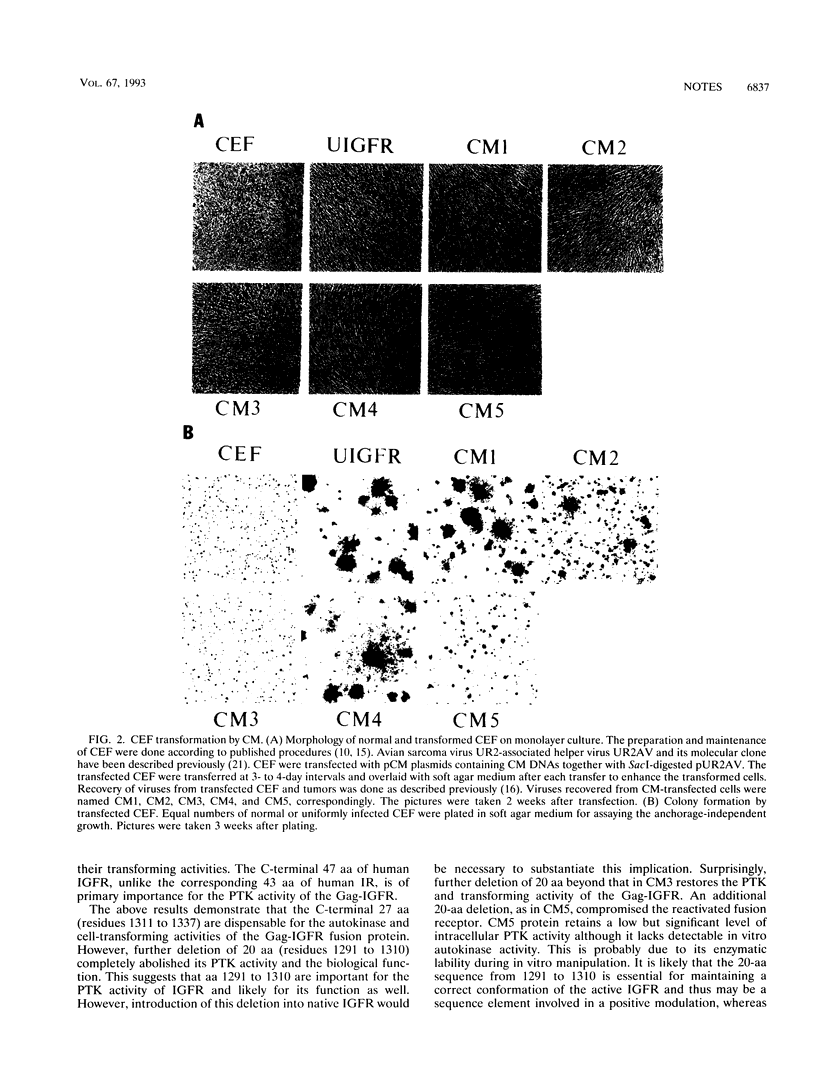
We have shown previously that the extracellular sequences of the human insulin receptor (IR) and the insulin-like growth factor I receptor (IGFR) have an inhibitory effect on protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) activity and on the biological functions of their respective Gag-receptor fusion proteins. To study the role of IGFR carboxyl sequence in modulation of the Gag-IGFR PTK and biological activities, five mutants, CM1, CM2, CM3, CM4, and CM5, containing carboxyl deletions of 17, 27, 47, 67, and 88 amino acids (aa), respectively, were constructed from the parental virus UIGFR encoding the Gag-IGFR. Deletion of up to 27 aa had little effect on the cell-transforming and PTK activities of UIGFR. Deletions of 47 aa in CM3 abolished PTK and transforming activities. Surprisingly, a further deletion of 20 aa in CM4 beyond that in CM3 reactivated the kinase and transforming activities. CM5, containing a deletion of 20 aa beyond that in CM4, had only marginal transforming and PTK activities. We conclude that deletion of the carboxyl region of the Gag-IGFR inactivates, instead of activating as in the case with Gag-IR, its transforming activity and the amino acid sequence 1250 to 1310 is essential for PTK and transforming activities. Analysis of the ability of the full-length IGFR and its mutant receptors described above to associate with phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase indicated that the association required PTK activity and tyrosine phosphorylation of the receptors and correlated well with their transforming activities. The carboxyl 88 aa are not essential for the association.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backer J. M., Schroeder G. G., Cahill D. A., Ullrich A., Siddle K., White M. F. Cytoplasmic juxtamembrane region of the insulin receptor: a critical role in ATP binding, endogenous substrate phosphorylation, and insulin-stimulated bioeffects in CHO cells. Biochemistry. 1991 Jul 2;30(26):6366–6372. doi: 10.1021/bi00240a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besmer P., Murphy J. E., George P. C., Qiu F. H., Bergold P. J., Lederman L., Snyder H. W., Jr, Brodeur D., Zuckerman E. E., Hardy W. D. A new acute transforming feline retrovirus and relationship of its oncogene v-kit with the protein kinase gene family. Nature. 1986 Apr 3;320(6061):415–421. doi: 10.1038/320415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Van Beveren C., Smith D., Chen E., Mitchell R. L., Isacke C. M., Verma I. M., Ullrich A. Structural alteration of viral homologue of receptor proto-oncogene fms at carboxyl terminus. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):277–280. doi: 10.1038/320277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endemann G., Yonezawa K., Roth R. A. Phosphatidylinositol kinase or an associated protein is a substrate for the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):396–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Escobedo J. A., Martin G. A., Turck C. W., del Rosario M., McCormick F., Williams L. T. Distinct phosphotyrosines on a growth factor receptor bind to specific molecules that mediate different signaling pathways. Cell. 1992 May 1;69(3):413–423. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90444-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H. Rapid transformation of cells by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):318–325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jong S. M., Zong C. S., Dorai T., Wang L. H. Transforming properties and substrate specificities of the protein tyrosine kinase oncogenes ros and src and their recombinants. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4909–4918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4909-4918.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapeller R., Chen K. S., Yoakim M., Schaffhausen B. S., Backer J., White M. F., Cantley L. C., Ruderman N. B. Mutations in the juxtamembrane region of the insulin receptor impair activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Jun;5(6):769–777. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-6-769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers R., Gray A., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Differential signalling potential of insulin- and IGF-1-receptor cytoplasmic domains. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1369–1375. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D., Rutter W. J., Wang L. H. Enhancement of transforming potential of human insulinlike growth factor 1 receptor by N-terminal truncation and fusion to avian sarcoma virus UR2 gag sequence. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):374–385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.374-385.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu D., Rutter W. J., Wang L. H. Modulating effects of the extracellular sequence of the human insulinlike growth factor I receptor on its transforming and tumorigenic potential. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):9–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.9-18.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maegawa H., McClain D. A., Freidenberg G., Olefsky J. M., Napier M., Lipari T., Dull T. J., Lee J., Ullrich A. Properties of a human insulin receptor with a COOH-terminal truncation. II. Truncated receptors have normal kinase activity but are defective in signaling metabolic effects. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8912–8917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain D. A., Maegawa H., Levy J., Huecksteadt T., Dull T. J., Lee J., Ullrich A., Olefsky J. M. Properties of a human insulin receptor with a COOH-terminal truncation. I. Insulin binding, autophosphorylation, and endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8904–8911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M. G., Backer J. M., Siddle K., White M. F. The insulin receptor functions normally in Chinese hamster ovary cells after truncation of the C terminus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10616–10623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckameyer W. S., Wang L. H. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus UR2 and comparison of its transforming sequence with those of other avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):914–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.914-921.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poon B., Dixon D., Ellis L., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J., Wang L. H. Molecular basis of the activation of the tumorigenic potential of Gag-insulin receptor chimeras. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):877–881. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Millauer B., Kostka G., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Differential effects of carboxy-terminal sequence deletions on platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling activities and interactions with cellular substrates. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4347–4356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segatto O., Lonardo F., Wexler D., Fazioli F., Pierce J. H., Bottaro D. P., White M. F., Di Fiore P. P. The juxtamembrane regions of the epidermal growth factor receptor and gp185erbB-2 determine the specificity of signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3191–3202. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shier P., Watt V. M. Primary structure of a putative receptor for a ligand of the insulin family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14605–14608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takata Y., Webster N. J., Olefsky J. M. Mutation of the two carboxyl-terminal tyrosines results in an insulin receptor with normal metabolic signaling but enhanced mitogenic signaling properties. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9135–9139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thies R. S., Ullrich A., McClain D. A. Augmented mitogenesis and impaired metabolic signaling mediated by a truncated insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):12820–12825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Lin B., Jong S. M., Dixon D., Ellis L., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Activation of transforming potential of the human insulin receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5725–5729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]